linked list
Linked list (Linked list) is the basic data structure and linear table, but unlike sequential table, it stores data continuously. Linked list is the location information (address) of each node (data storage unit).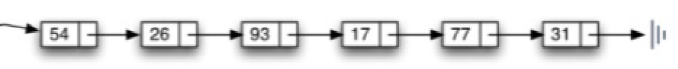
Two way linked list
The more complex types of linked lists are "bi-directional linked list" or "double linked list". Each node has two links: one points to the front node, and when the node is the first node, it points to the null value; the other points to the next node, when the node is the last node, it points to the null value.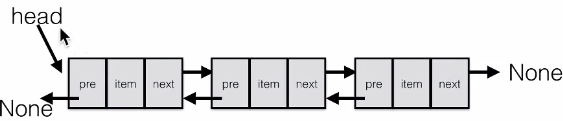
Grammar realization:
class Node(object):
"""Node Class"""
def __init__(self, item):
self.item = item
self.next = None
self.pre = None
class DoubleLinkList():
"""Two way linked list"""
def __init__(self, node=None):
self.__head = node
def is_empty(self):
"""Is the list empty?
:return If the list is empty, return true
"""
return self.__head is None
def length(self):
"""Length of linked list"""
cur = self.__head
count = 0
while cur is not None:
count += 1
cur = cur.next
return count
def travel(self):
"""Traversing the entire list"""
cur = self.__head
while cur is not None:
print(cur.item, end=" ")
cur = cur.next
print("")
def search(self, item):
"""Find out if the node exists"""
cur = self.__head
while cur is not None:
if cur.item == item:
return True
cur = cur.next
return False
def add(self, item):
"""Adding Elements to the Header of the List
:param item: Specific data to be saved
"""
node = Node(item)
# A linked list is an empty list.
node.next = self.__head
self.__head = node
# The list has at least one node
if node.next: # If node.next exists
node.next.pre = node
def append(self, item):
"""Adding elements at the end of the list"""
node = Node(item)
# If the list is empty, add nodes directly
if self.is_empty():
self.__head = node
else:
cur = self.__head
while cur.next is not None:
cur = cur.next
# When you exit the loop, cur points to the endpoint
node.pre = cur
cur.next = node
def insert(self, pos, item):
"""Adding elements at specified locations"""
# Add elements to the header
if pos <= 0:
self.add(item)
# Add elements at the tail
elif pos >= self.length():
self.append(item)
else:
cur = self.__head
count = 0
while count < pos:
count += 1
cur = cur.next
# When you exit the loop, cur points to the current location of pos
# node is inserted before pos position
node = Node(item)
node.next = cur
node.pre = cur.pre
cur.pre.next = node
cur.pre = node
def remove(self, item):
"""Delete Vertex"""
# Current cursor
cur = self.__head
while cur is not None:
# Find the element to delete
if cur.item == item:
# Elements found in the head
if cur == self.__head:
#A list has only one node
self.__head = cur.next
#The list has multiple nodes
# if self.__head:
if cur.next: #If cur.next exists
self.__head.pre = None
else:
# Find the element in the middle
cur.pre.next = cur.next
# If it's not the end
if cur.next:
cur.next.pre = cur.pre
# Not the element to be looked for, move the cursor
cur = cur.next
if __name__ == '__main__':
ll = DoubleLinkList()
print(ll.length())
ll.travel()
ll.append(1)
print(ll.length()) # 1
ll.travel() # 1
ll.add(2)
print(ll.length()) # 2
ll.travel() # 2 1
ll.insert(1, 3)
ll.travel() # 2 3 1
ll.remove(1)
ll.travel() # 2 3