For project creation strategy, please refer to the introduction of previous documents.
The directory structure is as follows
Edit views.py
from django.shortcuts import render # Create your views here. from django.http import HttpResponse from django.shortcuts import render from common.DBHandle import DataBaseHandle import time def djangoHello(request): return HttpResponse('Hello Django!') def index(request): return render(request,'index.html') def login(request): print('login_func') usn = request.POST['username'] pwd = request.POST['password'] host = '127.0.0.1' username = 'username' password = 'password' database = 'dbname' port = 3306 # Instantiate database connection DbHandle = DataBaseHandle(host, username, password, database, port) localTime = time.localtime(time.time()) create_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", localTime) sql = "insert into user(username,password,create_time) values ('%s','%s','%s')" % (usn, pwd, create_time) DbHandle.insertDB(sql) DbHandle.closeDb() return render(request,'login.html')
Next edit urls.py
"""FirstWeb URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/topics/http/urls/ Examples: Function views 1. Add an import: from my_app import views 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', views.home, name='home') Class-based views 1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', Home.as_view(), name='home') Including another URLconf 1. Import the include() function: from django.urls import include, path 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('blog/', include('blog.urls')) """ from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from fistWeb import views urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('hello/',views.djangoHello), path('index/',views.index), path('login/',views.login), ]
Create templates folder under application
And create the HTML file index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>FirstWeb</title> </head> <body> <h1>Information registration</h1> <!-- action="/login/" This is the path to access after submission, so you need to urls Add path change --> <form action="/login/" method="post"> {% csrf_token %} User name:<input type="text" name="username" id="usn"><br> Password:<input type="password" name="password" id="pwd"><br> <input type="submit" value="register"> </form> </body> </html>
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>FirstWeb-Sign in</title> </head> <body> <h1>Hello, you have successfully registered!</h1> </body> </html>
Introduce the common file added
Add a database encapsulated class.
# FileName : DBHandle.py # Author : Adil # DateTime : 2018/11/29 2:03 PM # SoftWare : PyCharm import pymysql # username : adil # password : helloyyj class DataBaseHandle(object): ''' Define a MySQL Operation class''' def __init__(self,host,username,password,database,port): '''Initialize database information and create a database connection''' # The following assignments can be omitted. connect You can use parameters directly self.host = host self.username = username self.password = password self.database = database self.port = port self.db = pymysql.connect(self.host,self.username,self.password,self.database,self.port,charset='utf8') # The method of annotation connection here is to create a connection when the object is instantiated. Do not handle connections alone. # # def connDataBase(self): # ''' Database connection ''' # # self.db = pymysql.connect(self.host,self.username,self.password,self.port,self.database) # # # self.cursor = self.db.cursor() # # return self.db def insertDB(self,sql): ''' Insert database operation ''' self.cursor = self.db.cursor() try: # implement sql self.cursor.execute(sql) # tt = self.cursor.execute(sql) # Return the number of inserted data. The processing result can be determined according to the return value. # print(tt) self.db.commit() print('Successful implementation') except: # Rollback on error self.db.rollback() print('Execution failure') finally: self.cursor.close() def deleteDB(self,sql): ''' Operation database data deletion ''' self.cursor = self.db.cursor() try: # implement sql self.cursor.execute(sql) # tt = self.cursor.execute(sql) # Returning the number of deleted data can determine the processing result according to the returned value # print(tt) self.db.commit() except: # Rollback on error self.db.rollback() finally: self.cursor.close() def updateDb(self,sql): ''' Update database operation ''' self.cursor = self.db.cursor() try: # implement sql self.cursor.execute(sql) # tt = self.cursor.execute(sql) # To return the number of updated data, the processing result can be determined according to the return value. # print(tt) self.db.commit() except: # Rollback on error self.db.rollback() finally: self.cursor.close() def selectDb(self,sql): ''' Database query ''' self.cursor = self.db.cursor() try: self.cursor.execute(sql) # The number of returned query data can be used to determine the processing result according to the returned value. data = self.cursor.fetchall() # Return to all records list print(data) # Result traversal for row in data: sid = row[0] name = row[1] # Traverse print results print('sid = %s, name = %s'%(sid,name)) except: print('Error: unable to fecth data') finally: self.cursor.close() def closeDb(self): ''' Database connection closed ''' self.db.close() if __name__ == '__main__': DbHandle = DataBaseHandle('127.0.0.1','username','password','dbname',3306) sql = "insert into JdwSpider(image_name,image_url,Spider_time) values ('%s','%s','%s')" % ( '1', '2', '2018-12-04 15:25:21') DbHandle.insertDB(sql) # DbHandle.insertDB('insert into test(name) values ("%s")'%('FuHongXue')) # DbHandle.insertDB('insert into test(name) values ("%s")'%('FuHongXue')) # DbHandle.selectDb('select * from test') # DbHandle.updateDb('update test set name = "%s" where sid = "%d"' %('YeKai',22)) # DbHandle.selectDb('select * from test') # DbHandle.insertDB('insert into test(name) values ("%s")'%('LiXunHuan')) # DbHandle.deleteDB('delete from test where sid > "%d"' %(25)) # DbHandle.selectDb('select * from test') DbHandle.closeDb()
The above code implements a simple registration page and stores the registration information in the database table.
Launch project presentation
Open browser and input url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/index/
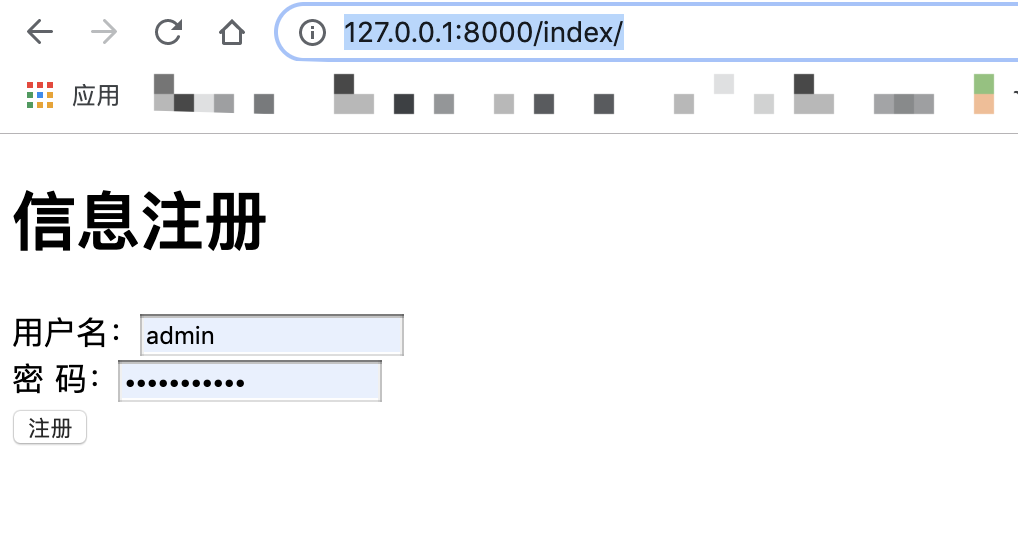
Click the registration submit button, and the page will jump to the following
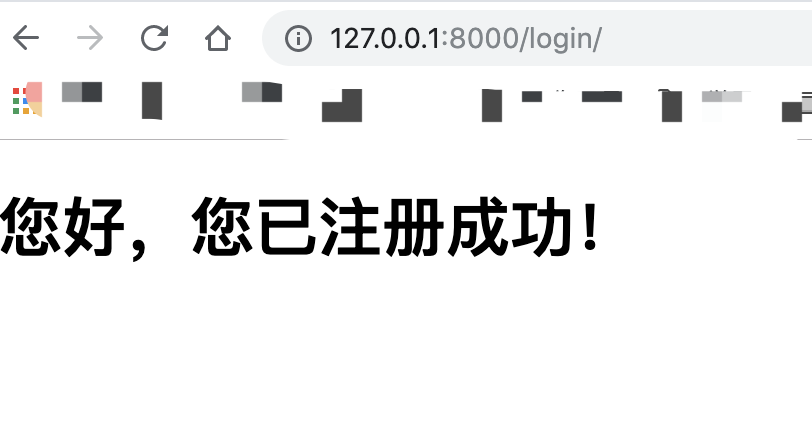
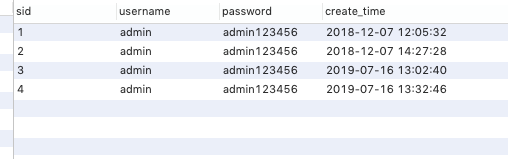
Viewing the database table, you can see the new user information.