1. Data type
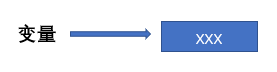
Variable = xxx only means to point the variable to the storage space where xxx data is located.
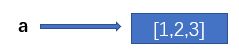
For example, a = [1,2,3] represents that the variable a points to the storage space where [1,2,3] is located.
python has two data types: variable data type and immutable data type. The difference is whether the value in memory can be modified.
ID (variable) you can view the memory address of the variable.
1.1 variable data type: list, Dictionary (key is immutable)
List:
# list # Modify the value in the list, and the direction of a variable does not change (variable data type) a = [1,2,3] print(id(a)) # 1949733739136 a.append(4) print(id(a)) # 1949733739136
Dictionaries:
# Dictionaries # Modify the value in the dictionary, and the direction of the a variable does not change (variable data type) a = dict(name="zs", age=27) print(id(a)) # 2955544943680 a["sex"] = "male" print(id(a)) # 2955544943680
1.2 immutable data types: number, string, tuple
Number:
# number # Modify the value of the number, and the direction of the a variable changes (immutable data type) a = 2 print(id(a)) # 140716966876864 a = 3 print(id(a)) # 140716966876896
character string:
# character string # Modify the value of the string, and the direction of the a variable changes (immutable data type) a = "python" print(id(a)) # 2546802488816 a = "javascript" print(id(a)) # 2546802807088
Tuple:
# tuple # Cannot modify the value of a tuple (immutable data type) a = (1,2,3) a[0] = 0 # An error will be reported and the tuple is immutable
2. Copy variable type data
2.1 copy.copy (light copy)
Shallow copy creates new memory space:
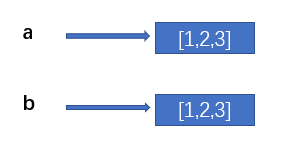
import copy a = [1,2,3] b = copy.copy(a) print(id(a)) # 1977249421888 print(id(b)) # 1977249419712
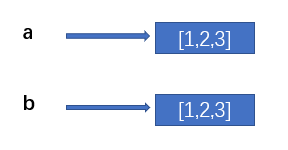
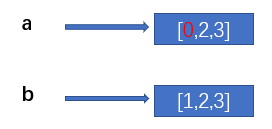
Because there are two different memory spaces, even if we change the data in a, the data in b will not change:
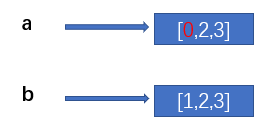
import copy a = [1,2,3] b = copy.copy(a) a[0] = 0 print(a) # [0, 2, 3] print(b) # [1, 2, 3]
2.2 copy.deep copy
Deep copy creates new memory space:
import copy a = [1,2,3] b = copy.deepcopy(a) print(id(a)) # 2077998963392 print(id(b)) # 2077998961280
Because there are two different memory spaces, even if we change the data in a, the data in b will not change:
import copy a = [1,2,3] b = copy.deepcopy(a) a[0] = 0 print(a) # [0, 2, 3] print(b) # [1, 2, 3]
2.3 summary
For variable type data, copy.copy and copy.deepcopy will recreate new memory space. The difference between the two is reflected in the case of sub objects.
- copy.copy does not create new memory space for child objects.
- copy.deepcopy creates new memory space for child objects.
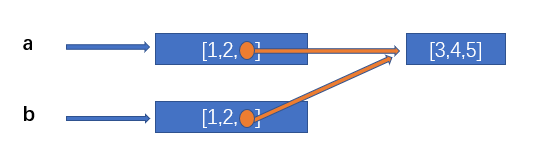
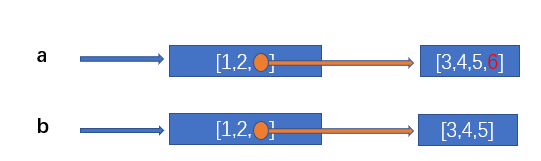
2.3.1 copy.copy the copied sub object will still point to the original sub object
import copy a = [1,2,[3,4,5]] b = copy.copy(a) print(id(a[2])) # 1690960124544 print(id(b[2])) # 1690960124544
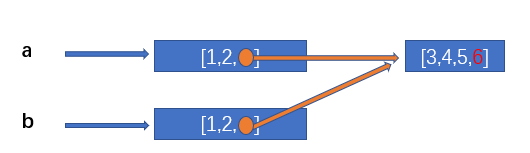
Therefore, when we modify the sub objects in a, the sub objects in b will also change
import copy a = [1,2,[3,4,5]] b = copy.copy(a) a[2].append(6) print(a[2]) # [3, 4, 5, 6] print(b[2]) # [3, 4, 5, 6]
2.3.2 copy.deepcopy the copied sub objects will also create new memory space
import copy a = [1,2,[3,4,5]] b = copy.deepcopy(a) print(id(a[2])) # 2268926565056 print(id(b[2])) # 2268926767808
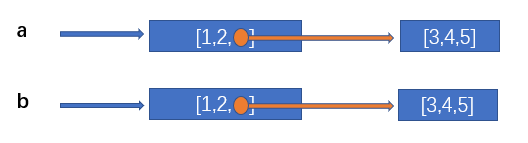
Therefore, when we modify the sub objects in a, the sub objects in b will not change
import copy a = [1,2,[3,4,5]] b = copy.deepcopy(a) a[2].append(6) print(a[2]) # [3, 4, 5, 6] print(b[2]) # [3, 4, 5]
3. Copy immutable type data
3.1 copy.copy (light copy)
Shallow copies point to the same memory space
import copy a = 1 b = copy.copy(a) print(id(a)) # 140716966876832 print(id(b)) # 140716966876832
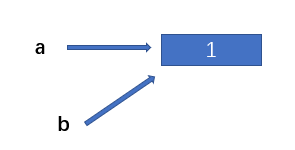
When we modify the value of a, the direction of a changes and the value of b remains unchanged
import copy a = 1 b = copy.copy(a) a = 5 print(a) # 5 print(b) # 1

3.2 copy.deep copy
The deep copy points to the same memory space
import copy a = 1 b = copy.deepcopy(a) print(id(a)) # 140716966876832 print(id(b)) # 140716966876832
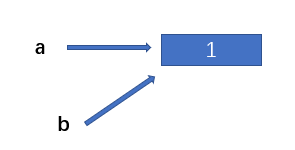
When we modify the value of a, the direction of a changes and the value of b remains unchanged
import copy a = 1 b = copy.copy(a) a = 5 print(a) # 5 print(b) # 1
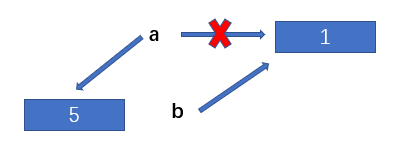
3.3 summary
For immutable type data, copy.copy and copy.deepcopy both point to the same memory space.