Process:
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 import multiprocessing,threading,time 5 6 def run(name): 7 t=threading.Thread(target=run2)#Create new threads 8 t.start() 9 print('process[%s],In printing...'%name) 10 time.sleep(1) 11 12 def run2(): 13 print(threading.get_ident())#Print thread ID 14 time.sleep(2) 15 16 17 if __name__ == '__main__': 18 for i in range(10): 19 p=multiprocessing.Process(target=run,args=('The first[%s]A process'%i,))#Create a new process 20 p.start()
Process number:
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 5 import multiprocessing,threading,time,os 6 from multiprocessing import Process#from multprocessing open Process 7 def info_l(file): 8 print('Current module name:',__name__) 9 print('Parent process ID:',os.getppid()) 10 print('process ID:',os.getpid()) 11 print('\n\n') 12 13 def f(name): 14 print('See:',name) 15 info_l('Related list') 16 17 18 if __name__ == '__main__': 19 info_l('Home Process Related List') 20 p=Process(target=f,args=('Current process',)) 21 p.start() 22 p.join()
Process lock:
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 5 from multiprocessing import Process,Lock # Lock Process Lock Communication Middleware 6 7 def f(lock,i): 8 lock.acquire()#Process lock 9 print('The first[%s]A process'%i) 10 lock.release()#Unlock 11 if __name__ =='__main__': 12 lock=Lock()#Process Lock Object 13 for i in range(10): 14 p=Process(target=f,args=(lock,i)).start()
Interprocess communication:
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 5 import multiprocessing,queue,threading 6 from multiprocessing import Process,Queue # Queue Process Communication Middleware 7 8 9 ''' Sharing queues between threads 10 def f(): 11 q.put([1,None,'Add data'])#queue 12 if __name__ =='__main__': 13 q=queue.Queue()#Thread queue 14 #q=Queue()#Process queue 15 p=threading.Thread(target=f,)#Create thread 16 p.start() 17 print(q.get())#Output 18 p.join() 19 ''' 20 def f(q):#Deposit in q object 21 q.put([1,None,'Add data'])#queue 22 if __name__ =='__main__': 23 q=Queue()#Process queue 24 p=Process(target=f,args=(q,))#Create process 25 p.start() 26 print(q.get())#output,Removed 27 p.join()
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 import os 5 from multiprocessing import Process,Pipe,Manager # Pipe Pipeline process communication middleware 6 7 8 def f(d,l): 9 d[os.getpid()]=os.getpid()#Modify dictionary 10 l.append(os.getpid())#Add List Content 11 print(d) 12 print(l) 13 14 15 if __name__ =='__main__': 16 with Manager() as manager: 17 d=manager.dict()#Create a modifiable dictionary between processes 18 l=manager.list(range(5))#Create a modifiable list between processes 19 p_list=[]#join Use 20 for i in range(10): 21 p=Process(target=f,args=(d,l))#Create process incoming data, 22 p.start() 23 p_list.append(p) 24 for r in p_list:#Waiting for the process to complete 25 r.join() 26 print(d) 27 print(l)
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 5 from multiprocessing import Process,Pipe # Pipe Pipeline process communication middleware 6 7 def f(conn):#Deposit in conn object 8 conn.send(['Subprocesses send information','....']) 9 print('Receiving information from the parent process:',conn.recv()) 10 conn.close() 11 if __name__ =='__main__': 12 parent_conn,child_conn=Pipe()#Generate a pipe,Returns two values,Manage double ends 13 p=Process(target=f,args=(child_conn,))#Create process 14 p.start() 15 print('Receiving information from subprocesses:',parent_conn.recv()) 16 parent_conn.send(['Parent process sends information']) 17 p.join()
Process pool:
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 #__author__=2017/6/23 5 import time,os 6 from multiprocessing import Process,Lock,Pool # Pool Process Pool Communication Middleware 7 8 def Foo(i): 9 print('The first[%s]A process,ID:'%i,os.getpid()) 10 time.sleep(3) 11 return i+100 12 def Bar(arg): 13 print('Callback>>>>:',arg,os.getpid()) 14 if __name__ =='__main__': 15 #pool=Pool(processes=5)#Defining a process pool means allowing a process pool to be placed in five processes at the same time 16 pool=Pool(5)#Defining a process pool means allowing a process pool to be placed in five processes at the same time 17 for i in range(10): 18 #pool.apply(func=Foo,args=(i,))#Creating process serial using process pool 19 #pool.apply_async(func=Foo,args=(i,))#Using process pool to create process parallelism 20 pool.apply_async(func=Foo,args=(i,),callback=Bar)#Callback 21 22 print('End') 23 #pool.join() 24 pool.close()#Must close the process pool first 25 pool.join()#Carry out afterwards join
Association:
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 #python 5 #2017/6/24 10:10 6 #__author__='Administrator' 7 8 import time 9 import queue 10 def consumer(name):#Consumer function 11 print('[%s]Consumer Products.......'%name) 12 while True: 13 new_b=yield #Jump point 14 print('[%s] consumption [%s]'%(name,new_b)) 15 def producer():#Producer Function 16 r=con.__next__() 17 r2=con2.__next__() 18 n=0 19 while n<10: 20 n+=1 21 con.send(n)#Send to Consumers 22 con2.send(n) 23 print('\033[32;1m[Producer]\033[0m yield a product[%s]'%n) 24 25 if __name__=='__main__': 26 con=consumer('Consumer A') 27 con2=consumer('Consumer B') 28 p=producer()
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 #python 5 #2017/6/24 10:31 6 #__author__='Administrator' 7 #import greenlet 8 from greenlet import greenlet 9 10 def test1(): 11 print('Function 1: 12') 12 ger2.switch()#Conduct coprocess switching 13 print('Function 1: 34') 14 ger2.switch() 15 16 def test2(): 17 print('Function two: 56') 18 ger1.switch() 19 print('Function two: 78') 20 ger1.switch() 21 22 ger1=greenlet(test1)#Create Association 23 ger2=greenlet(test2) 24 ger1.switch()
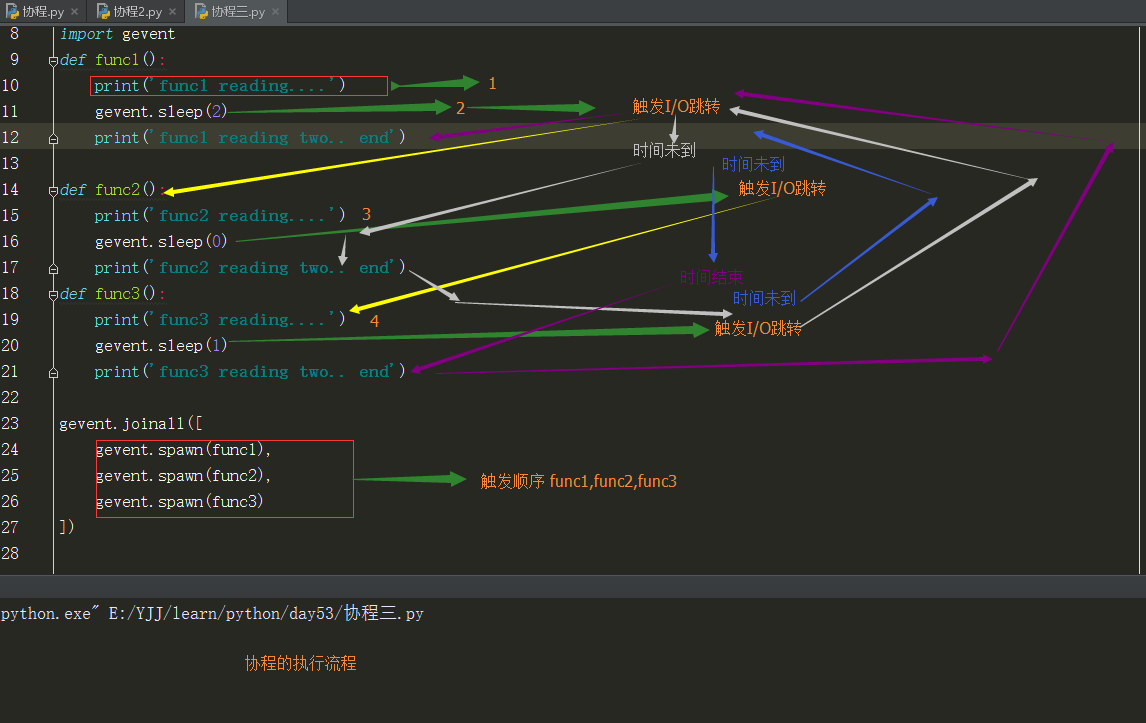
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 #python 5 #2017/6/24 10:47 6 #__author__='Administrator' 7 8 import gevent 9 def func1(): 10 print('func1 reading....') 11 gevent.sleep(2) 12 print('func1 reading two.. end') 13 14 def func2(): 15 print('func2 reading....') 16 gevent.sleep(0) 17 print('func2 reading two.. end') 18 def func3(): 19 print('func3 reading....') 20 gevent.sleep(1) 21 print('func3 reading two.. end') 22 23 gevent.joinall([ 24 gevent.spawn(func1), 25 gevent.spawn(func2), 26 gevent.spawn(func3) 27 ])
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 #python 5 #2017/6/24 14:03 6 #__author__='Administrator' 7 from urllib import request 8 import gevent,time 9 from gevent import monkey 10 monkey.patch_all()#For all I/O Operation Marking 11 12 def f(url):#Crawl web page 13 print('Website: ',url) 14 resp=request.urlopen(url)#Open web page 15 data=resp.read()#Read webpage 16 print('Website:[%s]Web data size:[%s]'%(url,len(data))) 17 18 urls=['https://www.python.org/', 19 'https://hao.360.cn/', 20 'https://www.yahoo.com/'] 21 22 time_start=time.time()#Synchronized serial start time 23 for url in urls: 24 f(url) 25 print('Synchronization duration:',time.time()-time_start) 26 27 time_start_asy=time.time()#Asynchronous parallel start time 28 gevent.joinall([ 29 gevent.spawn(f,'https://www.python.org/'), 30 gevent.spawn(f,'https://hao.360.cn/'), 31 gevent.spawn(f,'https://www.yahoo.com/') 32 ]) 33 print('Asynchronous duration:',time.time()-time_start_asy)
Cooperative socket_server implements concurrency
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 #python 5 #2017/6/24 14:42 6 #__author__='Administrator' 7 8 import sys 9 import socket 10 import time 11 import gevent 12 13 from gevent import socket,monkey 14 monkey.patch_all() 15 16 17 def server(port): 18 s = socket.socket()#socket object 19 s.bind(('0.0.0.0', port))#Server side,bind IP port 20 s.listen(500) 21 print('Monitoring....') 22 while True: 23 cli, addr = s.accept() 24 gevent.spawn(handle_request, cli)#Create a new collaboration 25 26 27 28 def handle_request(conn): 29 try: 30 while True: 31 data = conn.recv(1024) 32 print("recv:", data) 33 conn.send(data) 34 if not data: 35 conn.shutdown(socket.SHUT_WR) 36 37 except Exception as ex: 38 print(ex) 39 finally: 40 conn.close() 41 if __name__ == '__main__': 42 server(8001)
select :
socket_server
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 #python 5 #2017/6/24 19:34 6 #__author__='Administrator' 7 8 import select,socket,sys ,queue 9 10 s=socket.socket()#Instantiate a connection object 11 s.setblocking(0)#Set to non-blocking 12 server_addr=('localhost',9500)#Setting Binding IP port 13 s.bind(server_addr)#Connection Object Binding IP port 14 s.listen(100)#Queue Connectable Number 15 inputs=[s,]#The first thing to do is to monitor itself. 16 17 outputs=[]#Send list 18 19 meg_queues={} #Queue Set Dictionary for Sending Connected Objects 20 21 while True: 22 print('Monitoring......') 23 readable,writeable,exeptional=select.select(inputs,outputs,inputs)#generate select object,Returns three list connections,Hair pass,error 24 25 for i in readable: #i For one socket 26 if i is s:#If i yes s Represents a new connection coming in 27 conn,client_addr=i.accept()#Create a new connection 28 print('Access a new connection...',client_addr) 29 conn.setblocking(0)#Also set to non-blocking 30 inputs.append(conn)#join select,Connection List,Avoid blocking 31 meg_queues[conn]=queue.Queue()#Create a queue to add to the dictionary 32 else: 33 try: 34 data=i.recv(1024)#Receive data if it is not a new connection 35 except Exception as e: 36 print(e) 37 if data: #If the data is not empty 38 print('[%s] Data sent [%s]'%(i.getpeername,data)) 39 meg_queues[i].put(data)#Currently connected message queues join data 40 if i not in outputs:#If the current connection is not in the send list,Join the Send List 41 outputs.append(i) 42 else: 43 print('The client has been disconnected....')#Start cleaning up 44 if i in outputs:#In the Send List 45 outputs.remove(i)#Delete in the Send List 46 inputs.remove(i)#Delete in connection list 47 del meg_queues[i]#Delete in Queue Dictionary 48 49 for w in writeable:#Circular Send List 50 try: 51 msg=meg_queues[w].get_nowait()#Remove the data from the queue,judge 52 except queue.Empty:#If the data is empty 53 outputs.remove(w)##Delete from the Send List 54 else: 55 w.send(msg)#Send out 56 57 for e in exeptional:#Loop error list 58 print('Connect[%s]error!'%e.getpeername) 59 inputs.remove(e)##Delete from the Send List 60 if e in outputs:#In the Send List 61 outputs.remove(e)#Delete in the Send List 62 e.close() 63 del meg_queues[e]#Delete in Queue Dictionary
socket_client
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 #python 5 #2017/6/24 19:23 6 #__author__='Administrator' 7 8 import socket 9 10 server_addr=('localhost',9500)#Setting Binding IP port 11 s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) 12 s.connect(server_addr) 13 while True: 14 msg = bytes(input(">>:"),encoding="utf8")#Define a data message 15 if msg: 16 s.sendall(msg)#send data 17 else: 18 print('Can not be empty') 19 continue 20 data = s.recv(1024)#Data collection(Read data) 21 #print(data) 22 23 print('Received', repr(data.decode())) 24 s.close()
selectors :
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 #python 5 #2017/6/24 21:58 6 #__author__='Administrator' 7 import selectors 8 import socket 9 10 sel = selectors.DefaultSelector()#Generate a create selectors object 11 12 def accept(sock, mask): 13 conn, addr = sock.accept() # Create new connections 14 print('accepted', conn, 'from', addr) 15 conn.setblocking(False)#Set it as non-blocking 16 sel.register(conn, selectors.EVENT_READ, read)#Registered Connection,callback read 17 18 def read(conn, mask): 19 data = conn.recv(1024) # receive data 20 if data:#Not empty 21 print('echoing', repr(data), 'to', conn) 22 conn.send(data) # send data 23 else:#If it is empty 24 print('closing', conn) 25 sel.unregister(conn)#Cancellation of registration 26 conn.close()#Close connection 27 28 server_addr=('localhost',9501)#Setting Binding IP port 29 sock = socket.socket()#Create a sock object 30 sock.bind(server_addr)#binding IP port 31 sock.listen(100) 32 print('Monitoring...') 33 sock.setblocking(False)#Non blocking 34 sel.register(sock, selectors.EVENT_READ, accept)#The registered connection callback function is accept 35 36 while True: 37 events = sel.select()#Default blocking mode 38 for key, mask in events:#If there is a connection,Access 39 callback = key.data#New connection handle 40 callback(key.fileobj, mask)
Event Driven and Asynchronous IO
There are several models when the server processes the program of the model:
(1) Every time a request is received, a new process is created to process the request.
(2) Every time a request is received, a new thread is created to process the request.
(3) For each request received, a list of events is placed so that the main process can process the request in a non-blocking I/O manner.
The method in (1) will result in poor performance of the server, but its implementation is relatively simple because of the high cost of creating new processes.
The second way, because it involves thread synchronization, may face deadlock And so on.
In the third way, when writing application code, the logic is more complex than the first two.
Considering all factors, it is generally accepted that the third way is the majority. Network Server Approaches adopted
Event-driven programming is a programming paradigm where the execution flow of a program is determined by external events. It is characterized by an event cycle, in which callback mechanism is used to trigger corresponding processing when external events occur. Two other common programming paradigms are synchronization (single thread) and multithreaded programming.