Generally, the drawing function is realized through three classes: QPainter, QPen and QBrush. QPixmap is used to load and render this
Map image, its image presentation is essentially realized by drawing.
QPainter
QPainter class performs drawing operations on QWidget (control), provides highly optimized functions for most graphical interfaces, and can draw from simple lines to complex pie charts.
The drawing operation is completed in QWidget.paintEvent(). The drawing method must be placed between begin() and end() of the QtGui.QPainter object. The QPainter class performs lower-level drawing functions on controls or other drawing devices.
Common methods are as follows
| begin() | Start drawing on target device |
| drawArc() | Draw an arc between the starting angle and the final angle |
| drawEllipse() | Draw an ellipse inside a rectangle |
| drawLine(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2) | Draw a line with endpoint coordinates specified. Draw a straight well from (x1,y1) to (x2,y2) and set the current brush position to (x2,y2) |
| drawPixmap() | Extract Pixmap from the image file and display it in the specified location |
| drawPolygon() | Drawing polygons using an array of coordinates |
| drawRect(int x,int y, int w,int h) | Draw a rectangle from the upper left coordinates (x,y) with a given width w and height h |
| drawText() | Displays the text at the given coordinates |
| fillRect() | Fill the rectangle with the QColor parameter |
| setBrush() | Set brush style |
| setPen() | Sets the color, size, and style of the pen used for drawing |
You can also set the pen style, which is an enumeration class that can be drawn by the QPainter class.
| Qt.NoPen | No line. For example, QPainter.drawRect() fills, but does not draw any boundary lines |
| Qt.SolidLine | A simple line |
| Qt.DashLine | A short line separated by some pixels |
| Qt.DotLine | Points separated by pixels |
| Qt.DashDotLine | Alternating dots and short lines |
| Qt.DashDotDotLine | One short line, two points |
| Qt.MPenStyle | Brush style mask |
Code example 1
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPainter, QColor, QFont
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class Drawing(QWidget):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super(Drawing, self).__init__(parent)
self.setWindowTitle("Draw text examples in the form")
self.resize(300, 200)
self.text = 'Welcome to study PyQt5'
def paintEvent(self, event):
painter = QPainter(self)
painter.begin(self)
# Custom painting method
self.drawText(event, painter)
painter.end()
def drawText(self, event, qp):
# Sets the color of the pen
qp.setPen(QColor(168, 34, 3))
# Set font
qp.setFont(QFont('SimSun', 20))
# Draw the text
qp.drawText(event.rect(), Qt.AlignCenter, self.text)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
demo = Drawing()
demo.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())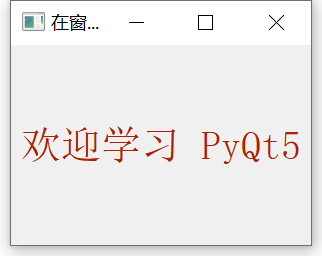
Code example 2
import sys, math
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class Drawing(QWidget):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super(Drawing, self).__init__(parent)
self.resize(300, 200)
self.setWindowTitle("Draw a point in the form")
def paintEvent(self, event):
qp = QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
# Custom point drawing method
self.drawPoints(qp)
qp.end()
def drawPoints(self, qp):
qp.setPen(Qt.red)
# Keep centered
size = self.size()
for i in range(1000):
# [- 100, 100] sinusoidal function image of two cycles
x = 100 * (-1 + 2.0 * i / 1000) + size.width() / 2.0
y = -50 * math.sin((x - size.width() / 2.0) * math.pi / 50) + size.height() / 2.0
qp.drawPoint(int(x), int(y))
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
demo = Drawing()
demo.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())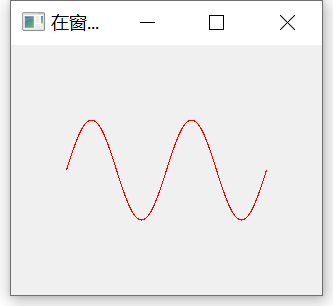
QPen
Qpen (pen) is a basic graphic object, which is used to draw lines, curves or draw rectangles, ellipses, polygons and other shapes for the outline.
Code example
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class Drawing(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 270)
self.setWindowTitle('Pen style example')
def paintEvent(self, e):
qp = QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawLines(qp)
qp.end()
def drawLines(self, qp):
pen = QPen(Qt.black, 2, Qt.SolidLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 40, 250, 40)
pen.setStyle(Qt.DashLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 80, 250, 80)
pen.setStyle(Qt.DashDotLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 120, 250, 120)
pen.setStyle(Qt.DotLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 160, 250, 160)
pen.setStyle(Qt.DashDotDotLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 200, 250, 200)
pen.setStyle(Qt.CustomDashLine)
pen.setDashPattern([1, 4, 5, 4])
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 240, 250, 240)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
demo = Drawing()
demo.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())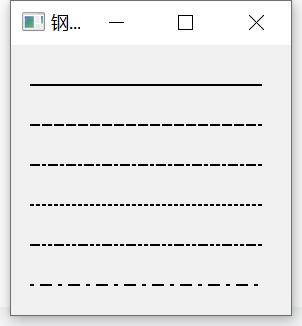
QBrush
QBrush is a basic graphic object used to fill shapes such as rectangles, ellipses, or polygons. There are three types of QBrush: predefined, transition, and texture patterns.
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class Drawing(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 365, 280)
self.setWindowTitle('Brush example')
self.show()
def paintEvent(self, e):
qp = QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawLines(qp)
qp.end()
def drawLines(self, qp):
brush = QBrush(Qt.SolidPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(10, 15, 90, 60)
brush = QBrush(Qt.Dense1Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(130, 15, 90, 60)
brush = QBrush(Qt.Dense2Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(250, 15, 90, 60)
brush = QBrush(Qt.Dense3Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(10, 105, 90, 60)
brush = QBrush(Qt.DiagCrossPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(10, 105, 90, 60)
brush = QBrush(Qt.Dense5Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(130, 105, 90, 60)
brush = QBrush(Qt.Dense6Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(250, 105, 90, 60)
brush = QBrush(Qt.HorPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(10, 195, 90, 60)
brush = QBrush(Qt.VerPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(130, 195, 90, 60)
brush = QBrush(Qt.BDiagPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(250, 195, 90, 60)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
demo = Drawing()
demo.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())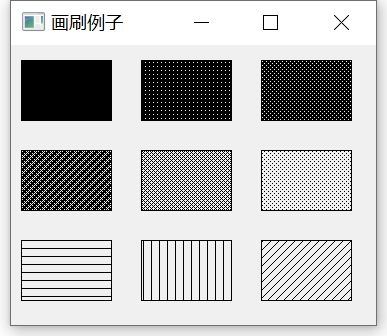
QPixmap
QPixmap class is used for image display of drawing equipment. It can be used as a QPaintDevice object or loaded into a control, usually a label or button, to display images on labels or buttons.
The image file types that QPixmap can read include BMP, GIF, JPG, JPEG, PNG, PBM, PGM, PPM, XBM, XPM, etc.
common method
| copy() | Copy from QRect object to QPixmap object |
| fromImage() | Convert QImage object to QPixmap object |
| grabWidget() | Creates a pixel graph from a given widget |
| grabWindow() | Create a pixel map of the data in the window |
| load() | Load image file as QPixmap object |
| save() | Save QPixmap objects as files |
| tolmage() | Convert QPixmap object to QImage object |
import sys
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
win = QWidget()
lab1 = QLabel()
lab1.setPixmap(QPixmap("./images/python.jpg"))
vbox = QVBoxLayout()
vbox.addWidget(lab1)
win.setLayout(vbox)
win.setWindowTitle("QPixmap example")
win.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())