Experimental purpose: Using software to achieve network batch automatic installation
Experimental environment: one linux desktop, more than one new virtual machine, in the same local area network
Experimental steps:
1. Install software dependency packages on desktop systems
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install dhcp tftp tftp-server vsftpd syslinux system-config-kickstart
2. Modify the tftp configuration file and change the tftp root directory to / tftpboot
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/xinetd.d/tftp
1 service tftp 2 { 3 socket_type = dgram 4 protocol = udp 5 wait = yes 6 user = root 7 server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd 8 server_args = -s /tftpboot #Change to/tftpboot 9 disable = no #yes to no 10 per_source = 11 11 cps = 100 2 12 flags = IPv4 13 }
3. Create tftp root and subdirectories
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
4. Mount the installation disc to the anonymous login directory of vsftp
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /var/ftp/pub/cd [root@localhost ~]# mount /dev/sr0/ /var/ftp/pub/cd #Note the installation location of the discCopy the kernel and boot file totftp Catalog
5. Copy the kernel and boot files to the tftp directory
[root@localhost ~]# cp /var/ftp/pub/cd/isolinux/isolinux.cfg /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default [root@localhost ~]# chmod 644 /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default #Give file write permission
Copy the installation boot file to the root directory of tftp:
[root@localhost ~]# cp -a /var/ftp/pub/cd/isolinux/vmlinuz /tftpboot/ [root@localhost ~]# cp -a /var/ftp/pub/cd/isolinux/initrd.img /tftpboot/ [root@localhost ~]# cp -a /usr/share/syslinux/pxelinux.0 /tftpboot/
6. Generate DHCP profile and edit
[root@localhost ~]# cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp-4.*/dhcpd.conf.sample /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
subnet 192.168.135.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { #Network Address and Subnet Mask range 192.168.135.100 192.168.135.200; #Declare dhcp allocation IP range option domain-name-servers ns1.internal.example.org; #dhcp Assigned Domain Namedefault-lease-time 600; max-lease-time 7200; filename "pxelinux.0"; #Declare dhcp to assign this file next-server 192.168.135.50; Tell me the location of the file dhcp,I.e. local machine ip }
Start related services
[root@localhost ~]# service dhcpd start [root@localhost ~]# service vsftpd start [root@localhost ~]# service xinetd start
7. Edit default file and modify boot parameters
vim /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default 1 #default vesamenu.c32 #Comment first line 2 #prompt 1 3 timeout 600 4 display boot.msg 5 default linux #Add this line
8. Start network batch installation configuration software
[root@localhost ~]# system-config-kickstart #Configuration as GUI requires mouse clicks
Basic Configuration: Set the current time zone and password for the root user
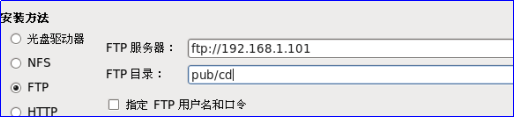
Installation method: Select FTP, server address is ftp://native IP, directory is the previously created mount point
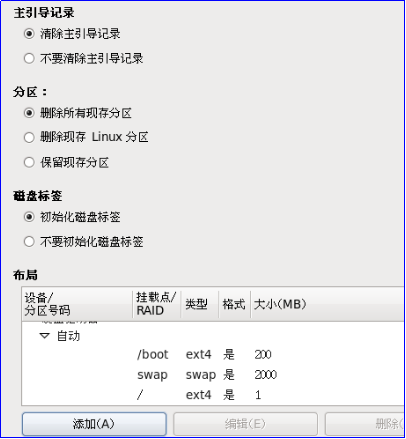
Partition information: Select Clear master boot record, Delete all partitions, Initialize disk labels and manually create new partitions. Click Add in the red box to create partitions
Network Configuration: Add the device name eth0 to the network device information and the network type is DHCP
Firewall Configuration: Firewall can be disabled
Package Selection: Select as needed
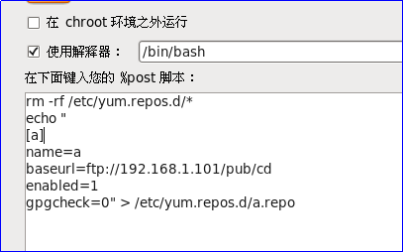
Post-installation script: Write script to modify local yum source
rm -rf /etc/yum.repos.d/* echo " [a] name=a baseurl=ftp://192.168.1.101/pub/cd enabled=1 gpgcheck=0" > /etc/yum.repos.d/a.repo
Save the configuration file to the / var/ftp/pub directory (pop-up save with mouse click in the upper left corner)
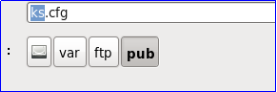
9. Modify ks.cfg to add a line reboot at the end of the file
[root@localhost ~]# vim /var/ftp/pub/ks.cfg #Add a line reboot at the end
10. Edit the boot file to inform clients where to automatically install the configuration
[root@localhost ~]# vim /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
label linux #Find this label menu label ^Install or upgrade an existing system menu default kernel vmlinuz append initrd=initrd.img ks=ftp://192.168.135.50/pub/ks.cfg #Add ftpks.cfg file path to this line
11. Open the new virtual machine test