yml loads configuration information through the way of @ ConfigurationProperties and @ value
1. There are two ways to bind values:
- @ConfigurationProperties
- @Value
- Priority: if you mix @ ConfigurationProperties, the priority is higher than @ value, but they can complement each other;
- @The data of ConfigurationProperties comes from application.properties and application.yml files;
The @ Value data is write dead, which is not related to the configuration file;
@ configurationproperties supports batch loading / injection, @ Value single injection;
4. Loose syntax: (user name > user name (in the form of hump)
@ ConfigurationProperties is supported; @ Value is not supported;
5. SpEL:
@ ConfigurationProperties is not supported, @ value is supported;
6. JSR303 data verification:
@ ConfigurationProperties is supported; @ Value is not supported;
7. Inject complex type
@ ConfigurationProperties supports, @ Value does not;
II @ PropertySource:
- By default, the data in the application.yml and applicationton.properties files will be loaded. If the data is not in these two files, you need to specify it through this annotation: @ PropertySource("classpath:user.properties");
- @The PropertySource annotation can only load properties files, but not yml files;
- Load the specified properties file (*. properties) into the Spring container. You can use @ PropertySource with @ Value and @ ConfigurationProperties;
- The combination of @ PropertySource and @ Value can inject the Value of the property variable in the custom property file into the member variable of the current class annotated with @ Value.
- The combination of @ PropertySource and @ ConfigurationProperties can bind the property file to a Java class and inject the variable values in the property file into the member variables of the Java class.
Source code
package org.springframework.context.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertySourceFactory; @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Repeatable(PropertySources.class) public @interface PropertySource { String name() default ""; String[] value(); boolean ignoreResourceNotFound() default false; String encoding() default ""; Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factory() default PropertySourceFactory.class; }
Using examples
Create user.properties under project and path
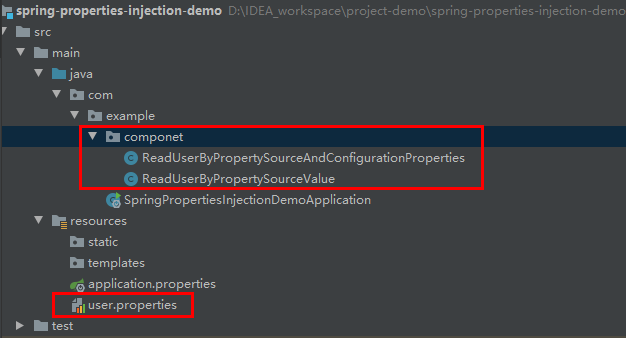
Properties file user.properties
user.name=jacklin user.age=22 user.job=IT user.email=793066408@qq.com
Demo 1: @ PropertySource and @ Value
/** * @Author Lin Bi Zhao * @Date 2019/11/28 16:28 * @descr */ @Component @PropertySource(value = "classpath:user.properties") public class ReadUserByPropertySourceValue { @Value("${user.name}") private String name; @Value("${user.age}") private Integer age; @Value("${user.job}") private String job; @Value("${user.email}") private String email; @Override public String toString() { return "ReadUserByPropertySourceValue{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", job='" + job + '\'' + ", email='" + email + '\'' + '}'; } }
Example 2: @ PropertySource and @ ConfigurationProperties
@Component @PropertySource(value = {"classpath:user.properties"}) @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user") public class ReadUserByPropertySourceAndConfigurationProperties { private String name; private Integer age; private String job; private String email; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public String getJob() { return job; } public void setJob(String job) { this.job = job; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email;} @Override public String toString() { return "ReadUserByPropertySourceAndConfigurationProperties{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", job='" + job + '\'' + ", email='" + email + '\'' + '}'; } }
Test example
@Slf4j @SpringBootApplication public class SpringPropertiesInjectionDemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner { @Autowired private ReadUserByPropertySourceValue readUserByPropertySourceValue; @Autowired private ReadUserByPropertySourceAndConfigurationProperties readUserByPropertySourceAndConfigurationProperties; public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringPropertiesInjectionDemoApplication.class, args); } @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { log.info(readUserByPropertySourceValue.toString()); log.info(readUserByPropertySourceAndConfigurationProperties.toString()); } }
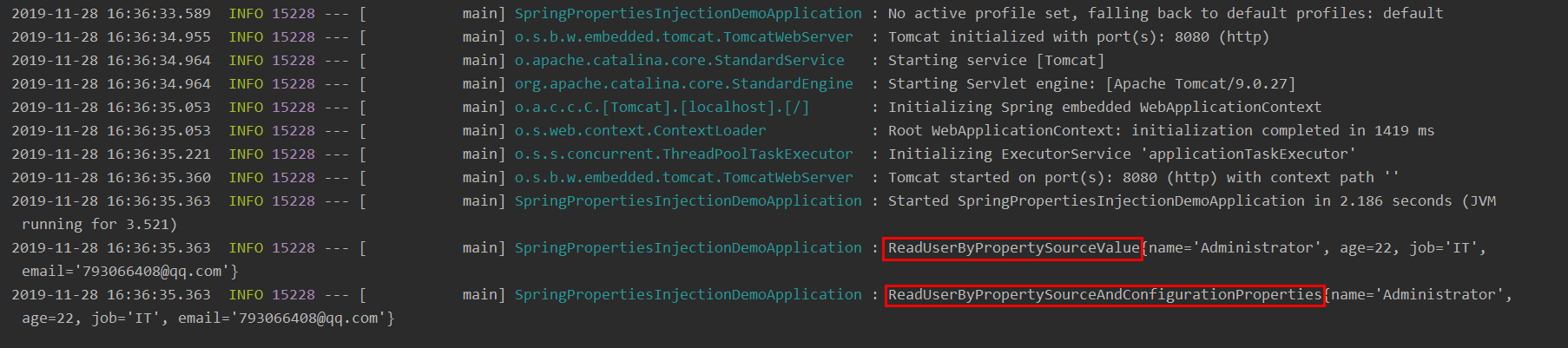
Start project observation console log printout: