Note: the notes are from the video Shang Silicon Valley Web front end Promise tutorial from introduction to mastery
Note: if you are a beginner, you only need to learn the basic use of Promise. Don't fall into the process of realizing handwritten Promise yourself.
Understanding and use of Promise
What is Promise
- Promise is a new technology, ES6 technical specification.
- Promise is a new solution for asynchronous programming with JavaScript. The old scheme simply used callback functions.
- Syntactically, Promise is a constructor.
- Functionally, promise object is used to encapsulate an asynchronous operation and obtain the result values of its success and failure.
Common asynchronous programming scenarios in JavaScript include:
- FS module file operation: require ('fs'). Readfile ('. / test. TXT', (err, data) = > {});
- Database operation
- Ajax: $.get('/server', (data)=>{});
- Timer: setTimeout (() = > {}, 2000);
Promise solves the problem of callback Hell:
// The so-called callback hell is to continuously nest callback functions in callback functions
asyncFunc1(opt, function (args1) {
asyncFunc2(opt, function (args2) {
asyncFunc3(opt, function (args3) {
asyncFunc4(opt, function (args4) {
// ...
})
})
})
});
The syntax format of Promise is as follows:
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// Both resolve and reject are parameters of function type
// The resolve() function is called when successful
// The reject() function is called when it fails
if (/*Asynchronous operation succeeded*/){
resolve([List of successful parameters]);
} else {
reject([Failed parameter list]);
}
});
promise.then(function ([List of successful parameters]) {
// The method called when the execution is successful, that is, resolve
}, function ([Failed parameter list]) {
// The method called when the execution fails, that is, reject
});
case
Gets a random number to print a string
It is realized by asynchronous programming, as follows:
setTimeout(function () {
var random = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 10);
// If the random number is greater than 5, the value of the random number is directly output; If the random number is less than or equal to 5, print "hello world" circularly
if (random > 5) {
console.log("random = " + random);
} else {
for (var i = 0; i < random; i++) {
console.log("hello world");
}
}
}, 3000);
Another setTimeout() function is nested in one setTimeout() function, which are asynchronous operations. If Promise is used instead, the code is as follows:
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
// Get a one bit random number
var random = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 10);
if (random > 5) {
// When the random number is greater than 5, we set the asynchronous operation to succeed
// The resolve() function is called and a parameter is passed in
resolve(random);
} else {
// When the random number is less than or equal to 5, we set the asynchronous operation to fail
// The reject() function is called and an object parameter is passed in
reject({random: random, text: "hello world"});
}
}, 100)
});
promise.then(function (random) {
// The function executed when the asynchronous operation is successful, i.e. resolve()
console.log("random = " + random);
}, function (obj) {
// The function executed when an asynchronous operation fails, i.e. reject()
for (var i = 0; i < obj.random; i++) {
console.log(obj.text);
}
});
File reading
Use the readFile() method of fs module to read the file content, and implement it as follows by callback function:
var fs = require('fs');
// File read operation the readFile() function is an asynchronous operation
fs.readFile('./text.txt', function (err, data) {
if (err) {
// If a file reading error occurs, the error object is printed
console.log(err);
} else {
// If the file is read successfully, the contents of the file are printed
console.log(data.toString())
}
});
Rewrite with Promise, and the code is as follows:
var fs = require('fs');
// File read operation the readFile() function is an asynchronous operation
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
fs.readFile('./text.txt', function (err, data) {
if (err) {
// If the file reading fails, the reject function is called
reject(err);
} else {
// If the file is read successfully, the resolve function is called
resolve(data.toString());
}
});
});
promise.then(function (content) {
// When the asynchronous operation succeeds, the function called is resolve
console.log(content.toUpperCase());
}, function (err) {
// The function called when the asynchronous operation fails, that is, reject
console.log(err)
});
Native Ajax
Use native Ajax to send a GET request. The code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 1. Create object
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2. Initialization
xhr.open('GET', 'http://poetry.apiopen.top/sentences ');
// 3. Send
xhr.send();
// 4. Process response results
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
// Judgment response status code 2xx
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
// Console output response body
console.log(xhr.response)
} else {
console.log(xhr.status)
}
}
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
After rewriting with Promise, the code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// 1. Create object
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2. Initialization
xhr.open('GET', 'http://poetry.apiopen.top/sentences ');
// 3. Send
xhr.send();
// 4. Process response results
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
// Judgment response status code 2xx
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
// When the response is successful, the resolve function is called
resolve(xhr.response);
} else {
// When the response fails, the reject function is called
reject(xhr.status)
}
}
};
});
promise.then(function (response) {
// The method that is called after the asynchronous operation is successful, that is, resolve
console.log(response);
}, function (reason) {
// The method that is called after the asynchronous operation fails, that is, reject
console.log(reason);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Promise encapsulates fs module read operations
Use Promise to package the fs module to read the file. The code is as follows:
/**
* Encapsulates a function to read the contents of a file
* @param path File content
* @returns {Promise<any>} Promise object
*/
function readFile(path) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
var fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile(path, function (err, data) {
if (!err) {
resolve(data.toString());
} else {
reject(err);
}
});
});
}
// Call function
readFile('./text.txt')
.then(function (data) {
console.log(data);
}, function (err) {
console.log(err);
});
Promise encapsulates Ajax operations
Use Promise to encapsulate the Ajax GET request. The code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
/**
* Encapsulate an Ajax operation
* @param method Request mode: GET or POST
* @param url Request path
* @returns {Promise<any>} Promise object
*/
function ajax(method, url) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// 1. Create object
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2. Initialization
xhr.open(method, url);
// 3. Send
xhr.send();
// 4. Process response results
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
// Judgment response status code 2xx
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
// When the response is successful, the resolve function is called
resolve(xhr.response);
} else {
// When the response fails, the reject function is called
reject(xhr.status)
}
}
};
})
}
// Send Ajax request
ajax('GET', 'http://poetry.apiopen.top/sentences')
.then(function (response) {
// The method that is called after the asynchronous operation is successful, that is, resolve
console.log(response);
}, function (reason) {
// The method that is called after the asynchronous operation fails, that is, reject
console.log(reason);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
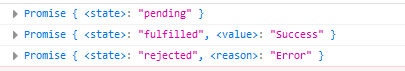
Promise status
Promise will only change in two ways:
- The pending state changes to the resolved state
- The pending state changes to the rejected state
There are only these two, and a Promise object can only be changed once. Whether it becomes success or failure, there will be a result data. The successful result data is generally called value, and the failed result data is generally called reason. Note: value and reason are only the names of formal parameters and can be customized.
A state attribute in the promise instance object indicates the state of promise. It has three values:
- pending: indicates whether success or failure is not determined.
- resolved (or fully filled): indicates the status of success.
- rejected: indicates the failed status.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// pending status
var promise1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// If neither resolve nor reject is called, the status is pending
});
console.log(promise1);
// resolved (fully filled) status
var promise2 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// Call resolve to change to the resolved state
resolve('Success');
});
console.log(promise2);
// rejected status
var promise3 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// Call reject to change to the rejected state
reject('Error');
});
console.log(promise3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Promise basic process
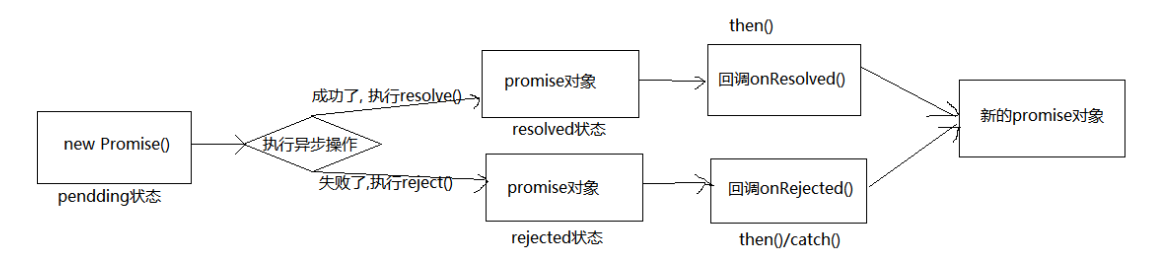
How to use Promise?
Promise API
1. Promise constructor: Promise(excutor) {}
- Executor is a function that represents an executor. That is, function(resolve, reject) {}.
- resolve is a callback function that is called when it succeeds in Promise.
- reject is also a callback function, which is called when it fails in Promise.
Note: the executor will immediately call synchronously within Promise, and the asynchronous operation will be executed in the executor.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
/*
new Promise(excutor); Constructor that returns a Promise object
*/
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// The resolve function is called when successful
// The reject function is called when it fails
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2. Promise.prototype.then method: promise.then(onResolved, onRejected)
- onResolved function, that is, the callback function when successful. function(value) {}.
- onRejected function, that is, the callback function in case of failure. function(reason) {}.
Note: specify the success callback used to get the success value and the failure callback used to get the failure reason, and return a new Promise object.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// The resolve function is called when successful
// The reject function is called when it fails
});
// Returns a new Promise object
var newPromise = promise.then(function (value) {
// The successful callback function is resolve
}, function (reason) {
// The failed callback function, namely reject
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. Promise.prototype.catch method: promise.catch(onRejected)
- onRejected function: failed callback function, namely function(reason) {}.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var promise1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// Modify the state of promise object
reject('Error');
});
promise1.catch(function (reason) {
// catch is called only in the failed state
console.log(reason);
});
var promise2 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// Modify the state of the promise object. When the status is modified to successful, the callback function of catch will not be called
resolve('Success');
});
promise2.catch(function (reason) {
// Because the Promise object is in the success state, the callback function in the catch will not be called
console.log(reason);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. Promise.resolve method
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
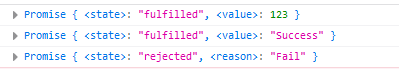
<script type="text/javascript">
// If the passed in parameter is an object of non Promise type, the result returned is a successful Promise object
var promise1 = Promise.resolve(123);
console.log(promise1);
// If the passed in parameter is a Promise object, the result of the parameter determines the result of resolve
var promise2 = Promise.resolve(new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('Success');// Successful results
}));
console.log(promise2);
var promise3 = Promise.resolve(new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
reject('Fail');// Result of failure
}));
console.log(promise3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
5. Promise.reject method
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
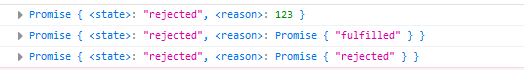
<script type="text/javascript">
// If the passed in parameter is an object of non Promise type, the result returned is the failed Promise object
var promise1 = Promise.reject(123);
console.log(promise1);
// If the passed in parameter is a Promise object, a failed Promise object will always be returned regardless of whether the result of the parameter is success or failure
var promise2 = Promise.reject(new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('Success');// Successful results
}));
console.log(promise2);
var promise3 = Promise.reject(new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
reject('Fail');// Result of failure
}));
console.log(promise3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
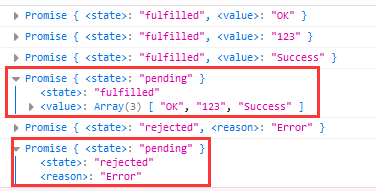
6. Promise.all method
- The parameter passed in by this method is an array containing n Promise objects; This method returns a new Promise object. Only if all promises are successful, it means success. As long as one fails, it will fail directly.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var p1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('OK');
});
console.log(p1);
var p2 = Promise.resolve('123');
console.log(p2);
var p3 = Promise.resolve(new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('Success');
}));
console.log(p3);
// Success occurs only when p1, p2, and p3 all return successful results
var result1 = Promise.all([p1, p2, p3]);
console.log(result1);
var p4 = Promise.reject('Error');
console.log(p4);
var result2 = Promise.all([p1, p3, p4]);
console.log(result2);
</script>
</body>
</html>
7. Promise.race method
- The parameter passed in by this method is an array containing n promise objects; The return value of this method is a new promise object, and the result state of the first completed promise is the final result state. But it is not the first result state in the array. If there is a delay operation in the first promise, the last one is the final result state.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var p1 = Promise.resolve('OK');
var p2 = Promise.reject('ERROR');
var p3 = Promise.resolve('SUCCESS');
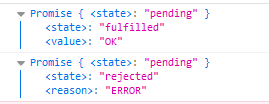
var promise1 = Promise.race([p1, p2, p3]);
console.log(promise1);
var promise2 = Promise.race([p2, p3]);
console.log(promise2);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Promise key issues
How to change the state of poise
There are three ways to change the state of promise:
- resolve(value): if the current status is pending, it will become resolved.
- reject(reason): if the current status is pending, it will become rejected.
- Throw exception: use the throws keyword to throw an exception. If the current status is pending, it will become rejected.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
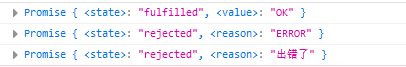
var p1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// 1. Use the resolve function
resolve('OK');
});
console.log(p1);
var p2 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// 2. Use reject function
reject('ERROR');
});
console.log(p2);
var p3 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// 3. Throw an exception
throw 'Error ';
});
console.log(p3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Does a promise specify that multiple success / failure callback functions will be called
Called when promise changes to the corresponding state.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('OK');
});
promise.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
});
promise.then(function (value) {
alert(value);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Change the promise state and specify who comes first and who comes later in the callback function
It is possible to specify the callback first and then change the state, but you can also change the state and then specify the callback.
- How to change the state first and then specify the callback: directly call resolve() or reject() in the executor; Or use setTimeout() to delay calling then() for a longer time.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// For synchronization tasks, the state will be changed first and then the callback will be executed
var promise1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('OK');
});
promise1.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}, function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
});
// For asynchronous tasks, the callback will be executed first and then the state will be changed
var promise2 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('OK');
}, 1000);
});
promise2.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}, function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Note: if the callback is specified first, when the state changes, the callback function will be called and the data will be obtained; If you change the state first, when you specify a callback, the callback function will call and get the data.
What determines the result status of the new promise returned by promise.then()
The result of the callback function specified by then() determines the result status of the new promise returned.
- If an exception is thrown, the new promise becomes rejected, and reason is the exception thrown.
- If any value of a non promise object is returned, the new promise becomes resolved, and value is the returned value.
- If a new promise object is returned, the promise result will become the result of the new promise.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('OK');
});
var result = promise.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
// 1. Throw an exception
// throw 'something went wrong!';
// 2. The returned result is an arbitrary value of a non promise object
// return '123';
// 3. The returned result is promise object
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// resolve('ok');
reject('error');
})
}, function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
});
console.log(result);
</script>
</body>
</html>
How promise concatenates multiple operation tasks
Promise's then() returns a new promise object that can be connected into a chain call to then(). Connect multiple synchronous or asynchronous tasks in series through the chain call of then.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('OK');
}, 1000);
});
promise.then(function (value) {
console.log(value);// OK
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('success');
});
}).then(function (value) {
console.log(value);// success
}).then(function (value) {
console.log(value);// undefined
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Exception penetration of promise
When you use promise's then chain call, you can specify the failed callback at the end. Any exception in any previous operation will be transferred to the last failed callback for processing, and you don't need a callback to handle the exception once.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
reject('ERROR');
}, 1000);
});
promise.then(function (value) {
console.log(111);
}).then(function (value) {
console.log(222);
throw 'Failed!';
}).then(function (value) {
console.log(333);
}).catch(function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Interrupt promise chained call
The so-called interrupt chain call, that is, when using promise's then chain call, interrupt in the middle and no longer call the subsequent callback function. If you want to interrupt the chain call, you only need to return a promise object in pending status in the callback function, that is, return new promise (() = > {});
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('OK');
}, 1000);
});
promise.then(function (value) {
console.log(111);
}).then(function (value) {
console.log(222);
// Interrupt chain call, with and only this method
return new Promise(() => {});
}).then(function (value) {
console.log(333);
}).catch(function (reason) {
console.log(reason);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Handwritten Promise
Note: handwritten Promise is an advanced application of JavaScript, which can not be mastered at this stage, so the following only provides the code of each step without notes. If you only learn the use of Promise preliminarily, you don't have to care too much about how to realize it by handwriting. For the implementation of each step of the code, you can watch the video and explain it clearly. Promise custom encapsulation
Initial structure construction
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 1 - Initial structure construction</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('OK');
});
p.then(value => {
console.log(value);
}, reason=>{
console.warn(reason);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
function Promise(executor){
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
}
Structure construction of resolve and reject
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 2 - resolve And reject </title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('OK');
});
p.then(value => {
console.log(value);
}, reason=>{
console.warn(reason);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
}
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
}
Implementation of resolve and reject functions
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 2 - resolve And reject </title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve('OK');
reject("error");
});
console.log(p);
// p.then(value => {
// console.log(value);
// }, reason=>{
// console.warn(reason);
// })
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
}
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
}
throw throws an error to change the state
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 4 - throw Throw an exception to change the state </title>
<!-- <script src="./promise.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body>
<script>
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve('OK');
// reject("error");
//Throw exception
throw "error";
});
console.log(p);
// p.then(value => {
// console.log(value);
// }, reason=>{
// console.warn(reason);
// })
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
}
The status can only be modified once
If you execute resolve or reject again in Promise, changing the state will not succeed, so that its state can only be changed once.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 5 - The status can only be modified once </title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject("error");
resolve('OK');
//Throw exception
// throw "error";
});
console.log(p);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
}
The then method performs a callback
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 6 - then Method to execute a callback </title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Instantiate object
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve('OK');
// reject("Error");
throw "ERROR";
});a
p.then(value => {
console.log(value);
}, reason=>{
console.warn(reason);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
onResolved(this.PromiseResult);
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
onRejected(this.PromiseResult);
}
}
The asynchronous task then method performs a callback
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 7 - Asynchronous task then Method implementation </title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Instantiate object
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// resolve('OK');
reject("error");
}, 1000);
});
p.then(value => {
console.log(value);
}, reason=>{
console.warn(reason);
});
console.log(p);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callback = {};
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
if(self.callback.onResolved){
self.callback.onResolved(data);
}
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Execute callback
if(self.callback.onResolved){
self.callback.onResolved(data);
}
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
onResolved(this.PromiseResult);
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
onRejected(this.PromiseResult);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callback = {
onResolved: onResolved,
onRejected: onRejected
}
}
}
Specify multiple callbacks
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 8 - Specify multiple callbacks </title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Instantiate object
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// resolve('OK');
reject('No');
}, 1000);
});
p.then(value => {
console.log(value);
}, reason=>{
console.warn(reason);
});
p.then(value => {
alert(value);
}, reason=>{
alert(reason);
});
console.log(p);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
onResolved(this.PromiseResult);
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
onRejected(this.PromiseResult);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: onResolved,
onRejected: onRejected
});
}
}
Synchronously modify the status. The then method returns the result
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 9 - Synchronization task then Return results</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Instantiate object
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('OK');
});
//Execute then method
const res = p.then(value => {
//Throw exception
throw "FAIL";
}, reason=>{
console.warn(reason);
});
console.log(res);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = onResolved(this.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
onRejected(this.PromiseResult);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: onResolved,
onRejected: onRejected
});
}
})
}
Asynchronously modify the state, and the then method returns the result
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 10 - Asynchronous task then Return results</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Instantiate object
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// resolve('OK');
reject("Error");
}, 1000)
});
//Execute then method
const res = p.then(value => {
// return 'oh Yeah';
throw 'error';
}, reason=>{
// console.warn(reason);
throw 'error';
});
console.log(res);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
const self = this;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = onResolved(this.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
onRejected(this.PromiseResult);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
try{
//Execute callback function successfully
let result = onResolved(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
},
onRejected: function(){
try{
//Execute callback function successfully
let result = onRejected(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
});
}
})
}
then method code optimization
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 10 - Asynchronous task then Return results</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Instantiate object
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('ok');
// reject('Error');
}, 100);
});
//Execute then method
const res = p.then(value => {
console.log(value);
}, reason=>{
console.warn(reason);
});
console.log(res);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
const self = this;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Encapsulation function
function callback(type){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
callback(onResolved);
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
callback(onRejected);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
callback(onResolved);
},
onRejected: function(){
callback(onRejected);
}
});
}
})
}
catch method and exception penetration
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 11 - catch Method and exception penetration</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Instantiate object
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// reject('OK');
resolve('OK');
}, 1000);
});
//pass by value
p.then()
.then(value=>{
console.log(222);
}).then(value => {
console.log(333);
}).catch(reason => {
console.warn(reason);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
const self = this;
//Determine callback function parameters
if(typeof onRejected !== 'function'){
onRejected = reason => {
throw reason;
}
}
if(typeof onResolved !== 'function'){
onResolved = value => value;
//value => { return value};
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Encapsulation function
function callback(type){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
callback(onResolved);
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
callback(onRejected);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
callback(onResolved);
},
onRejected: function(){
callback(onRejected);
}
});
}
})
}
//Add catch method
Promise.prototype.catch = function(onRejected){
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
Implement Promise.resolve method
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 12 - Promise.resolve encapsulation</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const p = Promise.resolve('OK');
const p2 = Promise.resolve(new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve('Success');
reject("error");
}));
const p3 = Promise.resolve(Promise.resolve('Oh Yeah'));
console.log(p3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
const self = this;
//Determine callback function parameters
if(typeof onRejected !== 'function'){
onRejected = reason => {
throw reason;
}
}
if(typeof onResolved !== 'function'){
onResolved = value => value;
//value => { return value};
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Encapsulation function
function callback(type){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
callback(onResolved);
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
callback(onRejected);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
callback(onResolved);
},
onRejected: function(){
callback(onRejected);
}
});
}
})
}
//Add catch method
Promise.prototype.catch = function(onRejected){
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
//Add resolve method
Promise.resolve = function(value){
//Return promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(value instanceof Promise){
value.then(v=>{
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The status is set to success
resolve(value);
}
});
}
Implement the Promise.reject method
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 13 - Promise.reject encapsulation</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Promise.reject
const p = Promise.reject('Error');
const p2 = Promise.reject(new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('OK');
}));
console.log(p);
console.log(p2);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
const self = this;
//Determine callback function parameters
if(typeof onRejected !== 'function'){
onRejected = reason => {
throw reason;
}
}
if(typeof onResolved !== 'function'){
onResolved = value => value;
//value => { return value};
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Encapsulation function
function callback(type){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
callback(onResolved);
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
callback(onRejected);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
callback(onResolved);
},
onRejected: function(){
callback(onRejected);
}
});
}
})
}
//Add catch method
Promise.prototype.catch = function(onRejected){
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
//Add resolve method
Promise.resolve = function(value){
//Return promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(value instanceof Promise){
value.then(v=>{
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The status is set to success
resolve(value);
}
});
}
//Add reject method
Promise.reject = function(reason){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
reject(reason);
});
}
Implement Promise.all method
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 14 - Promise.all encapsulation</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('OK');
}, 1000)
})
let p2 = Promise.reject('Success');
let p3 = Promise.resolve('Oh Yeah');
//Call the all method
let result = Promise.all([p1, p2, p3]);
console.log(result);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
const self = this;
//Determine callback function parameters
if(typeof onRejected !== 'function'){
onRejected = reason => {
throw reason;
}
}
if(typeof onResolved !== 'function'){
onResolved = value => value;
//value => { return value};
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Encapsulation function
function callback(type){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
callback(onResolved);
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
callback(onRejected);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
callback(onResolved);
},
onRejected: function(){
callback(onRejected);
}
});
}
})
}
//Add catch method
Promise.prototype.catch = function(onRejected){
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
//Add resolve method
Promise.resolve = function(value){
//Return promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(value instanceof Promise){
value.then(v=>{
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The status is set to success
resolve(value);
}
});
}
//Add reject method
Promise.reject = function(reason){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
reject(reason);
});
}
//Add all method
Promise.all = function(promises){
//The returned result is promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Declare variable
let count = 0;
let arr = [];
//ergodic
for(let i=0;i<promises.length;i++){
//
promises[i].then(v => {
//Know that the status of the object is successful
//Each promise object succeeded
count++;
//Store the successful result of the current promise object into the array
arr[i] = v;
//judge
if(count === promises.length){
//modify state
resolve(arr);
}
}, r => {
reject(r);
});
}
});
}
Implement Promise.race method
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 15 - Promise.race encapsulation</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('OK');
});
});
let p2 = Promise.reject('Success');
let p3 = Promise.resolve('Oh Yeah');
//Call the race method
let result = Promise.race([p1, p2, p3]);
console.log(result);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
const self = this;
//Determine callback function parameters
if(typeof onRejected !== 'function'){
onRejected = reason => {
throw reason;
}
}
if(typeof onResolved !== 'function'){
onResolved = value => value;
//value => { return value};
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Encapsulation function
function callback(type){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
callback(onResolved);
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
callback(onRejected);
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
callback(onResolved);
},
onRejected: function(){
callback(onRejected);
}
});
}
})
}
//Add catch method
Promise.prototype.catch = function(onRejected){
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
//Add resolve method
Promise.resolve = function(value){
//Return promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(value instanceof Promise){
value.then(v=>{
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The status is set to success
resolve(value);
}
});
}
//Add reject method
Promise.reject = function(reason){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
reject(reason);
});
}
//Add all method
Promise.all = function(promises){
//The returned result is promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Declare variable
let count = 0;
let arr = [];
//ergodic
for(let i=0;i<promises.length;i++){
//
promises[i].then(v => {
//Know that the status of the object is successful
//Each promise object succeeded
count++;
//Store the successful result of the current promise object into the array
arr[i] = v;
//judge
if(count === promises.length){
//modify state
resolve(arr);
}
}, r => {
reject(r);
});
}
});
}
//Add race method
Promise.race = function(promises){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
for(let i=0;i<promises.length;i++){
promises[i].then(v => {
//Modify the status of the returned object to success
resolve(v);
},r=>{
//Modify the status of the returned object to "failed"
reject(r);
})
}
});
}
Implementation of asynchronous execution of then callback function
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 16 - Callback function『Asynchronous execution』</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject('OK');
console.log(111);
});
p1.then(value => {
console.log(222);
}, reason => {
console.log(444);
});
console.log(333);
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
//Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
setTimeout(() => {
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
setTimeout(() => {
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//Add then method
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){
const self = this;
//Determine callback function parameters
if(typeof onRejected !== 'function'){
onRejected = reason => {
throw reason;
}
}
if(typeof onResolved !== 'function'){
onResolved = value => value;
//value => { return value};
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Encapsulation function
function callback(type){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
setTimeout(() => {
callback(onResolved);
});
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
setTimeout(() => {
callback(onRejected);
});
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
callback(onResolved);
},
onRejected: function(){
callback(onRejected);
}
});
}
})
}
//Add catch method
Promise.prototype.catch = function(onRejected){
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
//Add resolve method
Promise.resolve = function(value){
//Return promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(value instanceof Promise){
value.then(v=>{
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The status is set to success
resolve(value);
}
});
}
//Add reject method
Promise.reject = function(reason){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
reject(reason);
});
}
//Add all method
Promise.all = function(promises){
//The returned result is promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Declare variable
let count = 0;
let arr = [];
//ergodic
for(let i=0;i<promises.length;i++){
//
promises[i].then(v => {
//Know that the status of the object is successful
//Each promise object succeeded
count++;
//Store the successful result of the current promise object into the array
arr[i] = v;
//judge
if(count === promises.length){
//modify state
resolve(arr);
}
}, r => {
reject(r);
});
}
});
}
//Add race method
Promise.race = function(promises){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
for(let i=0;i<promises.length;i++){
promises[i].then(v => {
//Modify the status of the returned object to success
resolve(v);
},r=>{
//Modify the status of the returned object to "failed"
reject(r);
})
}
});
}
class version encapsulation
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise-encapsulation | 17 - class Version encapsulation</title>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// setTimeout(() => {
// // resolve("OK");
// reject("Eror");
// })
// });
// p1.then(value => {
// console.log(value);
// }, reason => {
// console.warn(reason);
// });
console.log(Promise.resolve('OK'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
promise.js
class Promise{
//Construction method
constructor(executor){
//Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
//Declare properties
this.callbacks = [];
//Save the value of this of the instance object
const self = this;// self _this that
//resolve function
function resolve(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';// resolved
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Call successful callback function
setTimeout(() => {
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data);
});
});
}
//reject function
function reject(data){
//Judgment state
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
//1. Modify the object's state (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';//
//2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data;
//Failed callback execution
setTimeout(() => {
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected(data);
});
});
}
try{
//Synchronously call "actuator function"
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
//Modify the promise object status to fail
reject(e);
}
}
//then method encapsulation
then(onResolved,onRejected){
const self = this;
//Determine callback function parameters
if(typeof onRejected !== 'function'){
onRejected = reason => {
throw reason;
}
}
if(typeof onResolved !== 'function'){
onResolved = value => value;
//value => { return value};
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Encapsulation function
function callback(type){
try{
//Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult);
//judge
if(result instanceof Promise){
//If it is an object of Promise type
result.then(v => {
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The object status of the result is success
resolve(result);
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
//Call the callback function PromiseState
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
setTimeout(() => {
callback(onResolved);
});
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
setTimeout(() => {
callback(onRejected);
});
}
//Determine pending status
if(this.PromiseState === 'pending'){
//Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
callback(onResolved);
},
onRejected: function(){
callback(onRejected);
}
});
}
})
}
//catch method
catch(onRejected){
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
//Add resolve method
static resolve(value){
//Return promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(value instanceof Promise){
value.then(v=>{
resolve(v);
}, r=>{
reject(r);
})
}else{
//The status is set to success
resolve(value);
}
});
}
//Add reject method
static reject(reason){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
reject(reason);
});
}
//Add all method
static all(promises){
//The returned result is promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//Declare variable
let count = 0;
let arr = [];
//ergodic
for(let i=0;i<promises.length;i++){
//
promises[i].then(v => {
//Know that the status of the object is successful
//Each promise object succeeded
count++;
//Store the successful result of the current promise object into the array
arr[i] = v;
//judge
if(count === promises.length){
//modify state
resolve(arr);
}
}, r => {
reject(r);
});
}
});
}
//Add race method
static race (promises){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
for(let i=0;i<promises.length;i++){
promises[i].then(v => {
//Modify the status of the returned object to success
resolve(v);
},r=>{
//Modify the status of the returned object to "failed"
reject(r);
})
}
});
}
}
async and await
aysnc function
Async is a keyword used in front of a function. It is usually like this: async function() {}. After using async keyword, the effect is as follows:
- The return value of the function will become a Promise object.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// Ordinary function
function hello() {
}
var h = hello();
console.log(h);
// async modified function
async function world() {
}
var w = world();
console.log(w);
</script>
</body>
</html>
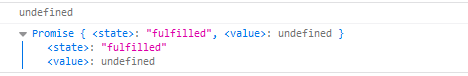
- The result of Promise object is determined by the return value of async modified function. If the returned value is a non Promise type data, the returned Promise is a successful object; If the return value is a Promise object, the result of the return value is determined by the result of the Promise object; If an exception is thrown, the return value is a failed Promise object.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// If the return value is a data of non Promise type
async function hello1() {
return "hello world";
}
var h1 = hello1();
console.log(h1);
// If the return value is a Promise object
async function hello2() {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('OK');// successful
})
}
var h2=hello2();
console.log(h2);
async function hello3() {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
reject('NO');// aborted
})
}
var h3=hello3();
console.log(h3);
// If an exception is thrown
async function hello4() {
throw 'ERROR';
}
var h4=hello4();
console.log(h4);
</script>
</body>
</html>
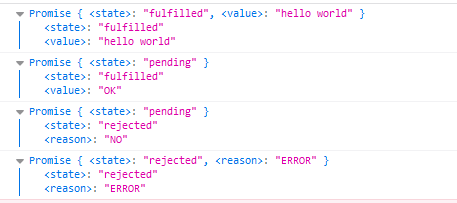
Summary: the function of async keyword is to turn the return value of a function into a Promise object.
await expression
await is also a keyword, which is usually used in front of a Promise object. It is mainly used to obtain the results of the success status of the Promise object. Its instructions are as follows:
- The expression to the right of await is generally Promise object, but it can also be other values.
- If the expression on the right is a promise object, use await to return the value of promise success.
- If the expression on the right is another value, this value is directly used as the return value of await.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// If the expression on the right of await is Promise object (successful state)
async function main1() {
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve('OK');
});
var result = await promise;
console.log(result);// OK
}
main1();
// If the expression to the right of await is a non Promise object
async function main2() {
var result = await '123';
console.log(result);// 123
}
main2();
// If the expression on the right of await is Promise object (failed state)
async function main3() {
var promise=new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
reject('NO');
});
try{
var result=await promise;
}catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
}
main3();
</script>
</body>
</html>
be careful:
- Await must be written in the async function, but there can be no await in the async function.
- If the promise of await fails, an exception will be thrown, which must be captured and processed through try...catch.
Case: async and await combine to read files
Use fs to read the contents of hello1.txt, hello2.txt, hello3.txt and hello4.txt, and then print them together.
- How to use callback functions
var fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('./hello1.txt', function (err, data1) {
if (err) throw err;
fs.readFile('./hello2.txt', function (err, data2) {
if (err) throw err;
fs.readFile('./hello3.txt', function (err, data3) {
if (err) throw err;
fs.readFile('./hello4.txt', function (err, data4) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(data1 + '\t' + data2 + '\t' + data3 + '\t' + data4);
});
});
});
});
- How to use async and await
var fs = require('fs');
function readFile(path) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
fs.readFile(path, function (err, data) {
if (err) {
reject(err);
}
resolve(data);
})
})
}
async function main() {
try {
var data1 = await readFile('./hello1.txt');
var data2 = await readFile('./hello2.txt');
var data3 = await readFile('./hello3.txt');
var data4 = await readFile('./hello4.txt');
console.log(data1 + '\t' + data2 + '\t' + data3 + '\t' + data4);
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
}
main();
Case: async and await combine to send Ajax requests
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>async And await Combined transmission AJAX</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">Click to get the segment</button>
<script>
//axios
function sendAJAX(url){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.responseType = 'json';
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.send();
//Processing results
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
//Judge success
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){
//Successful results
resolve(xhr.response);
}else{
reject(xhr.status);
}
}
}
});
}
//Segment sub interface address https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke
let btn = document.querySelector('#btn');
btn.addEventListener('click',async function(){
//Get segment information
let duanzi = await sendAJAX('https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke');
console.log(duanzi);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Summary: encapsulate the asynchronous operation into a function, set the result of the asynchronous operation into the Promise object, and finally return the Promise object in this function. Then use async to modify a function, and use the await keyword inside the function to read the successful result of the Promise object returned by the asynchronous operation.