Summary
Official website: http://www.graphviz.org/
Graphviz (Graph Visualization Software) is an Open Source Toolkit launched by at & T lab. DOT is a graphic description language, very simple,
Graphviz is a tool for dealing with this language. Just a brief understanding of the DOT language, you can use graphviz drawing, it is particularly useful for programmers.
So in short, if you are a programmer, it is born for you.
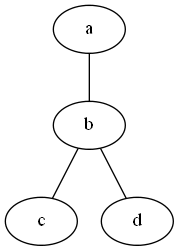
Undirected graph
graph graphname { a -- b -- c; b -- d; }
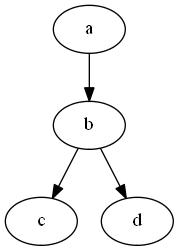
Digraph
digraph graphname { a -> b -> c; b -> d; }
attribute
//In the DOT language, you can add different attributes to nodes and edges. digraph graphname { //Attribute of node, name of node a [lable = "Foo"]; //Attribute of node, shape of node b [shape = box]; //Edge properties, edge color a -> b -> c [color = blue]; //Edge attribute, edge line b -> d [style = dotted]; }
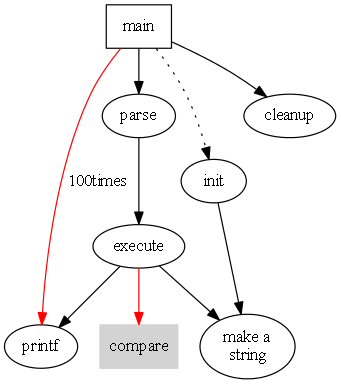
elementary school figure
digraph G { //Set the size of the picture to 4inch * 4inch size = "4,4"; main [shape = box]; //Edge importance, default is 1 main->parse [weight = 8]; parse->execute; //dotted main->init[style = dotted]; main->cleanup; //Two lines connected execute->{make_string;printf} init->make_string; //Set the default color of the edge to red edge [color = red]; main->printf [sytle=bold, label = "100times"]; //Name of the node make_string [label = "make a\nstring"]; //Set default properties for nodes node [shape=box,style =filled,color=lightgrey]; execute->compare; }
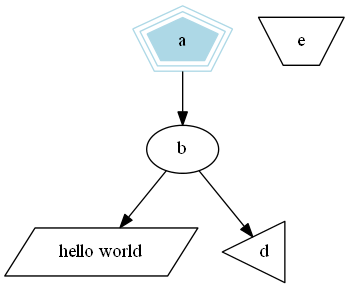
polygon
digraph G{ a -> b -> c; b -> d; /* The shape is polygon, the number of sides is 5, the outer frame is 3, the color is light blue, and the style is fill */ a [shape = polygon, sides = 5, peripheries = 3, color = lightblue, style = filled]; /* The shape is polygon, the number of sides is 4, the inclination of angle is 0.4, and the content is hello world*/ c [shape = polygon, sides = 4, skew = 0.4, label = "hello world"]; /* The shape is inverted triangle, and the overall rotation is 30 degrees */ d [shape = invtriangle,orientation = 30]; /* Polygon shape, 4 sides, 0.7 twist */ e [shape = polygon, sides = 4, distortion = 0.7]; }
data structure
Complex Tags
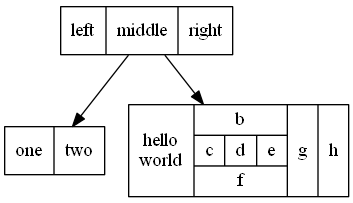
digraph structs { /* Set the default shape of the node as rectangular record, and the default shape is rounded rectangle Mrecord */ node [shape = record]; struct1 [label = "left|middle|right"]; struct2 [label = "one|two"]; struct3 [label = "hello\nworld|{b|{c|d|e}|f}|g|h"]; struct1 -> struct2; struct1 -> struct3; }
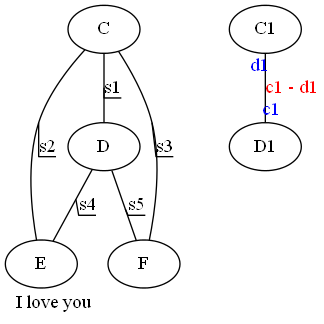
graph picture { //The name of this picture label = "I love you"; //The name of the graph is in bottom, or t labelloc = b; //The location of the figure name is left, or r labeljust = l; edge[decorate = true]; C -- D [label = "s1"]; C -- E [label = "s2"]; C -- F [label = "s3"]; D -- E [label = "s4"]; D -- F [label = "s5"]; edge[decorate = false, labelfontcolor = blue, fontcolor = red]; C1 -- D1 [headlabel = "c1",taillabel = "d1",label = "c1 - d1"]; }
line up icon
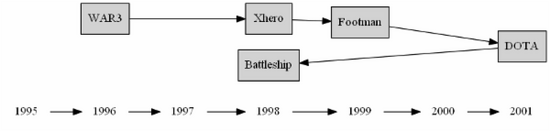
digraph html { rankdir = LR; { node[shape = plaintext]; 1995 -> 1996 -> 1997 -> 1998 -> 1999 -> 2000 -> 2001; } { node[shape = box, style = filled]; WAR3 -> Xhero -> Footman -> DOTA: WAR3 -> Battleship; } {rank = same; 1996; WAR3;} {rank = same; 1998; Xhero; Battleship;} {rank = same; 1999; Footman;} {rank = same; 2001; DOTA;} }
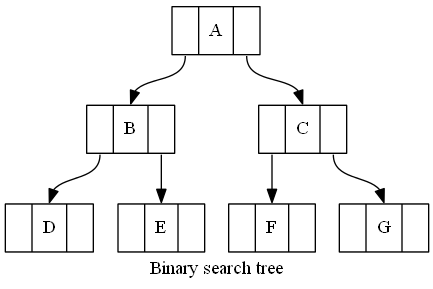
Binary tree
digraph G { label = "Binary search tree"; node [shape = record]; A [label = "<f0>|<f1>A|<f2>"]; B [label = "<f0>|<f1>B|<f2>"]; C [label = "<f0>|<f1>C|<f2>"]; D [label = "<f0>|<f1>D|<f2>"]; E [label = "<f0>|<f1>E|<f2>"]; F [label = "<f0>|<f1>F|<f2>"]; G [label = "<f0>|<f1>G|<f2>"]; A:f0 -> B:f1; A:f2 -> C:f1; B:f0 -> D:f1; B:f2 -> E:f1; C:f0 -> F:f1; C:f2 -> G:f1; }
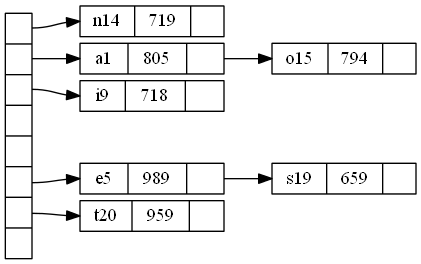
Hashtable
digraph G{ nodesep = .05; rankdir = LR; node [shape = record,width = .1,height = .1]; node0 [label = "<f0>|<f1>|<f2>|<f3>|<f4>|<f5>|<f6>|",height = 2.5]; node [width = 1.5]; node1 [label = "{<n>n14|719|<p>}"]; node2 [label = "{<n>a1|805|<p>}"]; node3 [label = "{<n>i9|718|<p>}"]; node4 [label = "{<n>e5|989|<p>}"]; node5 [label = "{<n>t20|959|<p>}"]; node6 [label = "{<n>o15|794|<p>}"]; node7 [label = "{<n>s19|659|<p>}"]; node0:f0 -> node1:n; node0:f1 -> node2:n; node0:f2 -> node3:n; node0:f5 -> node4:n; node0:f6 -> node5:n; node2:p -> node6:n; node4:p -> node7:n; }
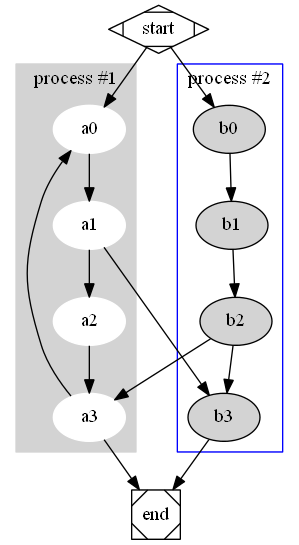
flow chart
digraph G{ subgraph cluster0 { node [style = filled,color = white]; style = filled; color = lightgrey; a0 -> a1 -> a2 -> a3; label = "process #1"; } subgraph cluster1 { node [style = filled]; b0 -> b1 -> b2 -> b3; label = "process #2"; color = blue; } start -> a0; start -> b0; a1 -> b3; b2 -> a3; a3 -> a0; a3 -> end; b3 -> end; start [shape = Mdiamond]; end [shape = Msquare]; }
Reference
[1] http://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-cn/DOT Brief introduction of language, DOT language.
[2] http://zh.wikipedia.org/zh/Graphviz , simple background knowledge.
From: http://blog.csdn.net/zhangskd/article/details/8250470?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral
above.
