Processing flow of request in RGW for source code interpretation
Request Processing Flowchart
Take civetweb as an example

-
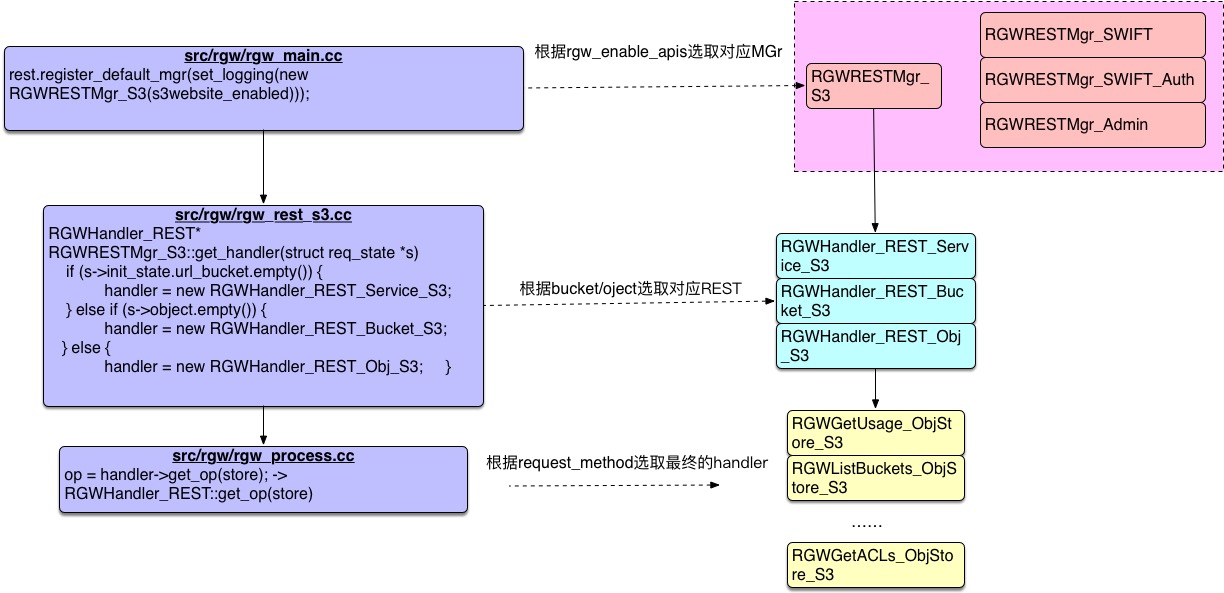
rgw_main.cc is the entry for the entire radosgw service. The main() function selects different front-end types based on the rgw frontends parameter settings in ceph.conf, and then executes the corresponding run() method to start the entire frontend service.Note that different handler s are generated for various types of interfaces, such as s3, swift, admin, depending on the rgw_enable_apis settings in ceph.conf, as follows
#src/rgw/rgw_main.cc get_str_list(g_conf->rgw_enable_apis, apis); #Get a list of interface types map<string, bool> apis_map; for (list<string>::iterator li = apis.begin(); li != apis.end(); ++li) { apis_map[*li] = true; } ... if (apis_map.count("s3") > 0 || s3website_enabled) { if (! swift_at_root) { rest.register_default_mgr(set_logging(new RGWRESTMgr_S3(s3website_enabled))); #Set S3 interface default handler to RGWRESTMgr_S3 ... if (apis_map.count("swift") > 0) { do_swift = true; swift_init(g_ceph_context); RGWRESTMgr_SWIFT* const swift_resource = new RGWRESTMgr_SWIFT;#Set swift interface default handler to RGWRESTMgr_SWIFT ... -
Then in the corresponding rgw_civetweb_fronted.cc, according to the civetweb start process described earlier, set the corresponding start parameters, and then use mg_start() to complete the start of civetweb.(Note that the callback setting in the parameter is civetweb_callback)
#src/rgw/rgw_civetweb_frontend.cc int RGWMongooseFrontend::run() { char thread_pool_buf[32]; snprintf(thread_pool_buf, sizeof(thread_pool_buf), "%d", (int)g_conf->rgw_thread_pool_size); string port_str; map<string, string> conf_map = conf->get_config_map(); conf->get_val("port", "80", &port_str); conf_map.erase("port"); std::replace(port_str.begin(), port_str.end(), '+', ','); conf_map["listening_ports"] = port_str; #civetweb default boot listening port set_conf_default(conf_map, "enable_keep_alive", "yes"); #keep_alive parameter settings set_conf_default(conf_map, "num_threads", thread_pool_buf); #Default threads settings set_conf_default(conf_map, "decode_url", "no"); ... struct mg_callbacks cb; memset((void *)&cb, 0, sizeof(cb)); cb.begin_request = civetweb_callback; #Callback function settings cb.log_message = rgw_civetweb_log_callback; cb.log_access = rgw_civetweb_log_access_callback; ctx = mg_start(&cb, &env, (const char **)&options); #Start Services if (!ctx) { return -EIO; } return 0; } /* RGWMongooseFrontend::run */ -
With the settings from the previous step, each request request in civetweb_callback needs to be processed by process_request(), noting that each request request will bind a set of RGWRados (responsible for data read and write of the underlying Librados)/RGWREST (processing corresponding requests and responses)/OpsLogSocket (logging messages)
#src/rgw/rgw_civetweb_frontend.cc static int civetweb_callback(struct mg_connection* conn) { struct mg_request_info* req_info = mg_get_request_info(conn); RGWMongooseEnv* pe = static_cast<RGWMongooseEnv *>(req_info->user_data); { // hold a read lock over access to pe->store for reconfiguration RWLock::RLocker lock(pe->mutex); RGWRados* store = pe->store; RGWREST* rest = pe->rest; OpsLogSocket* olog = pe->olog; RGWRequest req(store->get_new_req_id()); RGWMongoose client_io(conn); int ret = process_request(pe->store, rest, &req, &client_io, olog); #Each request request request binds a set of previous RGWRados, RGWREST, OpsLogSocket s ... -
The process_request() in rgw_process.cc is then called, where rest->get_handler obtains the corresponding handler type based on whether the requested URL contains bucket and object information, then calls handler->get_op(store) to get the final Handler Based on the corresponding request_method of the handler obtained earlier, and triggers the pre_exec(), execute(), complete() corresponding to the handler to complete the entire reqProcessing of UEST request, code as follows:
#src/rgw/rgw_process.cc int process_request(RGWRados* store, RGWREST* rest, RGWRequest* req,GWStreamIO* client_io, OpsLogSocket* olog) {int ret = 0; client_io->init(g_ceph_context); ... RGWHandler_REST *handler = rest->get_handler(store, s, client_io, &mgr,&init_error); #The corresponding handler type is further obtained here depending on whether the URL contains a bucket or an Object field if (init_error != 0) { abort_early(s, NULL, init_error, NULL); goto done; } dout(10) << "handler=" << typeid(*handler).name() << dendl; should_log = mgr->get_logging(); req->log_format(s, "getting op %d", s->op); op = handler->get_op(store); #Here you get the handler type that will ultimately process the request request request based on request_method ... req->log(s, "pre-executing"); op->pre_exec(); #Request Preprocessing req->log(s, "executing"); op->execute(); #Specific implementation of specific requests req->log(s, "completing"); op->complete(); #Complete Request Processing#src/rgw/rgw_process.cc RGWHandler_REST* RGWRESTMgr_S3::get_handler(struct req_state *s) { bool is_s3website = enable_s3website && (s->prot_flags & RGW_REST_WEBSITE); int ret = RGWHandler_REST_S3::init_from_header(s, is_s3website ? RGW_FORMAT_HTML : RGW_FORMAT_XML, true); if (ret < 0) return NULL; RGWHandler_REST* handler; // TODO: Make this more readable if (is_s3website) { if (s->init_state.url_bucket.empty()) { handler = new RGWHandler_REST_Service_S3Website; } else if (s->object.empty()) { handler = new RGWHandler_REST_Bucket_S3Website; } else { handler = new RGWHandler_REST_Obj_S3Website; } } else { if (s->init_state.url_bucket.empty()) { handler = new RGWHandler_REST_Service_S3; #Switch to RGWHandler_REST_Service_S3 if the bucket is empty } else if (s->object.empty()) { handler = new RGWHandler_REST_Bucket_S3; #Switch RGWHandler_REST_Bucket_S3 if obj is empty } else { handler = new RGWHandler_REST_Obj_S3; #bucket and Object are not empty, switch to RGWHandler_REST_Obj_S3 } } ldout(s->cct, 20) << __func__ << " handler=" << typeid(*handler).name() << dendl; return handler; }#src/rgw/rgw_rest.cc RGWOp* RGWHandler_REST::get_op(RGWRados* store) { RGWOp *op; switch (s->op) #Here s corresponds to the structure of a req_state { rest->op case OP_GET: op = op_get(); break; case OP_PUT: op = op_put(); break; case OP_DELETE: op = op_delete(); break; case OP_HEAD: op = op_head(); break; case OP_POST: op = op_post(); break; case OP_COPY: op = op_copy(); break; case OP_OPTIONS: op = op_options(); break; default: return NULL; } if (op) { op->init(store, s, this); } return op; } /* get_op */Structural Definition struct req_state { CephContext *cct; RGWClientIO *cio; RGWRequest *req; /// XXX: re-remove?? http_op op; #Corresponds to an enumeration type, as follows RGWOpType op_type; ... enum http_op { OP_GET, OP_PUT, OP_DELETE, OP_HEAD, OP_POST, OP_COPY, OP_OPTIONS, OP_UNKNOWN, };
URL->handler procedure
Understand the entire URL conversion handler process, feel request information quickly locate specific op operations, debug, the entire process is summarized in the following figure.