Problems encountered in development
Processing scheme of enumeration type
Scheme 1: synchronize the set value by using the key value method
1. Define a new field to store the field description corresponding to the enumeration value
Here, quarter is the enumeration value of the corresponding database field
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Quarter, enumeration value: 1, 2, 3, 4 four values represent the quarter of a year Q1,Q2,Q3,Q4 Four quarters can be defined as enumeration in the code") private Integer quarter;
quarterName is a self-defined property used to display the description information corresponding to the enumeration value (this field does not exist in the database)
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Quarter, city_info Table fields")
@Excel(name = "quarter")
public String quarterName;
2. Define a method in the enumeration that can obtain the corresponding description through the enumeration value
//@ApiModelProperty(value = "quarter, enumeration values: 1, 2, 3 and 4 represent Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 of a year, which can be defined as enumeration in the code")
public enum quarters {
/**
* KPI(1L, "Q1")
*/
Q1(1, "Q1"),
/**
* PRAISE(2L, "Q2")
*/
Q2(2, "Q2"),
/**
* COMPLAINT(3L, "Q3")
*/
Q3(3, "Q3"),
/**
* INCENTIVE(4L, "Q4")
*/
Q4(4, "Q4");
/**
* Quarter enumeration value, corresponding to QM_ accessories_ type field of info table
*/
public final Integer value;
/**
* Quarter corresponding enumeration description
*/
public final String desc;
quarters (Integer value, String desc) {
this.value = value;
this.desc = desc;
}
public Integer getValue() {
return value;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
//Get the value according to the key
public static String getValueByKey(Integer value){
for (QmMassIntegralStatVo.quarters q : QmMassIntegralStatVo.quarters.values()) {
if(q.getValue()==value){
return q.getDesc();
}
}
return "";
}
}
3. Override set method
What you want to add here is the value of quarterName to send to the front end. The premise that it has a value is that quarter has a value. Therefore, rewrite the set method of quarter to copy quarterName at the same time.

4. Add an annotation to identify that the user-defined attribute does not belong to the database
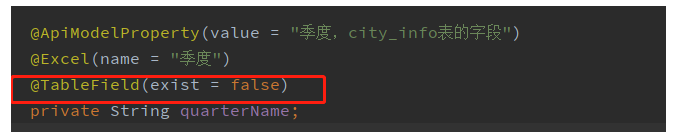
Without this annotation, when using an object to transfer values (for example, using the insert interface of mp), the transferred object will contain a quarterName attribute value, but it does not exist in the database. A field error appears.
Scheme 2: enumeration conversion using Mybatis
Single enumeration conversion
1. Define enumeration class
public enum QuarterType{
/**
* Q1(1, "Q1")
*/
Q1(1, "Q1"),
/**
* PRAISE(2L, "Q2")
*/
Q2(2, "Q2"),
/**
* COMPLAINT(3L, "Q3")
*/
Q3(3, "Q3"),
/**
* INCENTIVE(4L, "Q4")
*/
Q4(4, "Q4");
/**
* Quarter enumeration value, corresponding to QM_ accessories_ type field of info table
*/
private Integer value;
/**
* Quarter corresponding enumeration description
*/
private String desc;
QuarterType(Integer value, String desc) {
this.value = value;
this.desc = desc;
}
public Integer getValue() {
return value;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setValue(Integer value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
//Get the value according to the key
public static String getEnum(Integer value) {
for (QmMassIntegralStatVo.quarters q : QmMassIntegralStatVo.quarters.values()) {
if (q.getValue() == value) {
return q.getDesc();
}
}
return "";
}
}
2. Create entity class
@Data
@ApiModel(value="QmMassIntegralStat Return front end object", description="Statistical table of mass integral")
@ExcelTarget("Mass integral")
public class QmMassIntegralStatVo extends QmMassIntegralStat implements Serializable {
private QuarterType quarterType;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "QmMassIntegralStatVo{" +
"quarterType=" + quarterType +
'}';
}
}
3. Create enumeration conversion class
@Slf4j
@MappedTypes({QuarterType.class}) //The annotation here identifies which enumerations need to be used. It is required
public class QuarterTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<QuarterType> {
private Class<QuarterType> type;
private QuarterType[] enums;
/**
* Set the conversion class and enumeration class content set by the configuration file for more convenient and efficient implementation by other methods
* @param type Transformation class set in configuration file
*/
public QuarterTypeHandler(Class<QuarterType> type) {
if (type == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Type argument cannot be null");
this.type = type;
this.enums = type.getEnumConstants();
if (this.enums == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(type.getSimpleName()
+ " does not represent an enum type.");
}
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i, QuarterType quarterType, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
preparedStatement.setString(i,quarterType.getDesc());
}
@Override
public QuarterType getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, String s) throws SQLException {
// The acquisition type is determined according to the database storage type. In this example, the Integer type and the quarterly enumeration value in the corresponding enumeration class are stored in the database, the same below
Integer i = resultSet.getInt(s);
if (resultSet.wasNull()) {
return null;
}else {
return QuarterType.getEnum(i);
}
}
@Override
public QuarterType getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
Integer i = resultSet.getInt(columnIndex);
if (resultSet.wasNull()) {
return null;
}else {
return QuarterType.getEnum(i);
}
}
@Override
public QuarterType getNullableResult(CallableStatement callableStatement, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
Integer i = callableStatement.getInt(columnIndex);
if (callableStatement.wasNull()) {
return null;
}else {
return QuarterType.getEnum(i);
}
}
}
4. Writing xml
Type identification needs to be added when writing xml
Use when querying:
Use when adding:

5. Writing method
Just write the code of controller, service and mapper layers
Universal enumeration conversion (not fully implemented)
1. Define enumeration interface for easier management
public interface BaseEnum <E extends Enum<E>, T>{
Set<Class<?>> subClass = Sets.newConcurrentHashSet();
T getValue();
String getDesc();
}
2. The enumeration class is defined above, and the enumeration interface is implemented
3. Create an entity class as above
4. Write a general enumeration converter
@Slf4j
@MappedTypes({QuarterType.class})
public class QuarterTypeHandler<E extends BaseEnum> extends BaseTypeHandler<E> {
private Class<E> type;
private E[] enums;
/**
* Set the conversion class and enumeration class content set by the configuration file for more convenient and efficient implementation by other methods
* @param type Transformation class set in configuration file
*/
public QuarterTypeHandler(Class<E> type) {
if (type == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Type argument cannot be null");
System.out.println("1234567894512345623"+type);
this.type = type;
this.enums = type.getEnumConstants();
if (this.enums == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(type.getSimpleName()
+ " does not represent an enum type.");
}
/**
* Enumeration type conversion, because the constructor obtains the subclass enums of enumeration, which makes the traversal more efficient and fast
* @param value Custom value attribute stored in database
* @return value Corresponding enumeration class
*/
//The parameter passed in here should be the same as the parameter type of the enumeration value
private E locateEnumStatus(Integer value) {
for(E e : enums) {
if(e.getValue().equals(value)) {
return e;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown enumeration type:" + value + ",Please check" + type.getSimpleName());
}
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i, E e, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
preparedStatement.setString(i,e.getDesc());
}
@Override
public E getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, String s) throws SQLException {
Integer i = resultSet.getInt(s);
if (resultSet.wasNull()) {
return null;
}else {
return locateEnumStatus(i);
}
}
@Override
public E getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
Integer i = resultSet.getInt(columnIndex);
if (resultSet.wasNull()) {
return null;
}else {
return locateEnumStatus(i);
}
}
@Override
public E getNullableResult(CallableStatement callableStatement, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
Integer i = callableStatement.getInt(columnIndex);
if (callableStatement.wasNull()) {
return null;
}else {
return locateEnumStatus(i);
}
}
}
5. Write xml as above
6. Write as above
Mybatis Plus conversion method
https://www.cnblogs.com/dalianpai/p/11771269.html
Define enumeration class
- Add Getter annotation
- @EnumValue corresponds to the field name in the database
- @JsonValue corresponds to the value echoed on the page
@Getter
public enum StateEnum {
/**
*
*/
published(1,"Published"),
unpublished(0,"Unpublished");
@EnumValue
private final int startus;
@JsonValue
private final String desc;
StateEnum(int startus, String desc){
this.startus = startus;
this.desc = desc;
}
}
Entity class
- @Jsonfield (serializefeatures = serializerfeature. Writeenumusingtostring) identifies the transformation
- The entity parameter name here and the value name in the enumeration class are consistent with the field name in the database
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Status: 0 - Unpublished, 1 - Published") @JSONField(serialzeFeatures= SerializerFeature.WriteEnumUsingToString) private StateEnum startus;
to configure
- Scan enumerated packages
mybatis-plus: typeEnumsPackage: com.isoftstone.cloudmsp.channel.partner.policy.Enums;
Empty judgment of a large number of attributes
During development, the front end may encounter many required items when filling in the form. After the front end verification, in order to prevent sending data directly to the service, the back end also needs to verify to ensure accuracy.
Here, you can use a single judgment: user.name == null to verify.
However, once more values need to be verified, there will be a lot of if judgment redundancy, which will affect the speed and waste resources.
At this time, you can make judgment by annotation:
@NotBlank(message = "Partner type cannot be empty") @ApiModelProperty(value = "Partner type") @TableField(exist=false) private String partnerType;
- The @ NotBlank annotation here is javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank; Functions in
- @NotBlank:
This can only work on the received String type. Note that it can only be null, and the length must be greater than 0 after calling trim() - @NotNull:
Cannot be null, but can be empty("", "," "), which is generally used for non null verification of basic data types, and the marked field can use @ size/@Max/@Min to control the size of the field value
Prompt configuration
After using the annotation, you need to write the corresponding configuration class to prompt the corresponding message in the annotation
The configuration classes are as follows:
/**
* @author tingzhenge
* @date 2021/9/3
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class ControllerExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public RestResult exceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException e)
{
return new RestResult(RestResult.FAIL_CODE, null, e.getBindingResult().getFieldError().getDefaultMessage());
}
}
Other commonly used
Problems in Activiti workflow
User groups acquire and complete tasks
When the task node does not specify a person in charge, and the person who can operate the node is a certain role. For example, in the first step of approving a leave application, the approval of the Department Manager is generally required, but there may be multiple department managers. Everyone can operate the application, or if a new department manager is added, he should also be able to see and operate such a task belonging to the Department Manager.
In this scenario, we can use user groups to help us complete the above operations.
Now, when defining the process, we write the corresponding role ID on the user group definition.
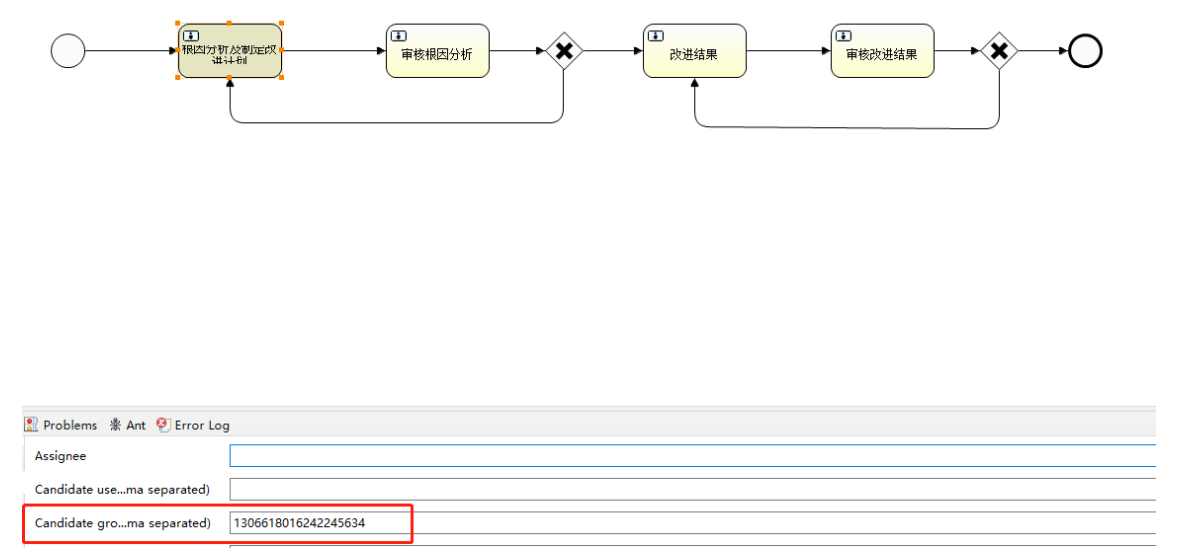
When completing the task, first judge whether the current user is the permission of the user group. Then let the processor pick up the task and complete the task. In this way, the current processor can be put into "act_hi_task" for subsequent query operations.
// First judge whether to change the task role
List<Task> taskList = processEngine.getTaskService().createTaskQuery()
.taskCandidateGroup(assignee)
.list();
if(!taskList.isEmpty()){
// Obtain the id and person in charge of the task parameter process instance through TaskService
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processInstanceId(processInstanceId)
.singleResult();
// Pick task
taskService.claim(task.getId(),userName);
System.out.println("Process instance id = "+task.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("Process task id = "+task.getId());
System.out.println("Task name = "+task.getName());
// Complete the task according to the id of the task
taskService.complete(task.getId());
Get previous task node information
To obtain the information of the previous node, we query through the information in "ACT_HI_TASKINST", use the process instance Id - processInstanceId to obtain the current task, then correct the fact that the unfinished tasks in the table have no end time feature, and flashback to find the latest information, that is, the information of the previous node.
/**
* Obtain the information of the previous node according to the process instance id
*
* @param proInsId
* @param historyService
* @return
*/
public static HistoricTaskInstance queryUpOneNodeMessage(String proInsId, HistoryService historyService) {
//Previous node
List<HistoricTaskInstance> list = historyService
.createHistoricTaskInstanceQuery()
.processInstanceId(proInsId)
.orderByHistoricTaskInstanceEndTime()
.desc()
.list();
HistoricTaskInstance taskInstance = null;
if (!list.isEmpty()) {
if (list.get(0).getEndTime() != null) {
taskInstance = list.get(0);
}
}
return taskInstance;
}
/**
* Obtain the information of the previous node according to the task id
*
* @param taskId
* @return
*/
public static HistoricTaskInstance queryUpOneNode(String taskId, HistoryService historyService) {
//Previous node
List<HistoricTaskInstance> list = historyService
.createHistoricTaskInstanceQuery()
.taskId(taskId).orderByHistoricTaskInstanceEndTime()
.desc()
.list();
HistoricTaskInstance taskInstance = null;
if (!list.isEmpty()) {
if (list.get(0).getEndTime() != null) {
taskInstance = list.get(0);
}
}
return taskInstance;
}
Use of Pair key value pairs
It can be used when there are only two return values of the function
Under the javax.util package, a simple Pair class can be called directly. The usage is to store the key and value of the attracted type directly through the constructor. There is no corresponding relationship between the key and value, and the type is arbitrary.
Usage:
Pair<String, String> pair = new Pair<>("aku", "female");
pair.getKey();
pair.getValue();
for example
taskInstance.getAssignee());
map.put("lastEndTime",taskInstance.getEndTime());
Pair<String, Date> pair = new Pair<>(taskInstance.getAssignee(),taskInstance.getEndTime());
// When used
Pair<String, Date> pair = taskService.findLastNodeInfo(businessKey);
qmRecallProcessInfoVo.setLastHandler(pair.getKey());
qmRecallProcessInfoVo.setLastHandleTime(pair.getValue());
That is, the two returned values are stored in pair in the form of keys and values respectively. You only need to obtain keys and values respectively.
RestTemplate send request
Params request
Use map to build request data
public void PostRequest() throws URISyntaxException {
URI uri = new URI("http://api.isoftstone.com/iSSC/msgServiceTest/1.0/msgOtherSystem/insertList");
String token = "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjNmNmU4ZDRlOTMzYTI2OGQxOGEzMTJlYzdiOWVlYjZhIiwidHlwIjoiSldUIn0.eyJuYmYiOjE2Mjk4OTY4NzQsImV4cCI6MTYyOTkwMDQ3NCwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9hcGkuaXNvZnRzdG9uZS5jb20vaWRzIiwiYXVkIjpbImh0dHBzOi8vYXBpLmlzb2Z0c3RvbmUuY29tL2lkcy9yZXNvdXJjZXMiLCJtc2dTZXJ2aWNlIiwibXNnU2VydmljZVRlc3QiXSwiY2xpZW50X2lkIjoiZjE3Njc3NDEtNmIzYS00ZmM3LThmMWQtNjYzNjJlY2RmODFhIiwic2NvcGUiOlsibXNnU2VydmljZSIsIm1zZ1NlcnZpY2VUZXN0Il19.RJUl87KfYJLwlPn9lN6zpVSH9vWQzTdP1q-KLYPJwWnMRACZeF0meTTPWpEq_P4Qwbof25ALhC2E8Njp3LzEblDGS8zWvhqzn0x8iT9Ikrjd2TGlMWlkUpM8qwUi2Hmd52E2eI86XRIXmUwCFVnuFJ44sFlxz2ovDjNoyGEdY3UqOfZ8LQmwlqrVluD4QHi7_a2esiexViwsXxJ7IJvrAwFNg0cKtx0C9-LWX65rS7CamAdMSOOlbKHQQreURkLluzLYauj0r2v9PSKFwCwz-3RiYvh-hnBRUKmhqNj5JC4f8lQZIyQTnZ-Pm27tjh7gTMONGF2OBn1oQr2CDCbdSg";
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
// Build request header
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
// Format request header
MediaType type = MediaType.parseMediaType("application/json");
headers.setContentType(type);
headers.add("Authorization","Bearer " + token);
// Map
Map<String, Object> param = new HashMap<String, Object>();
param.put("mobile","13016423117");
param.put("templateId","65e66878-2f21-4c12-853d-595156fa586e");
param.put("userDefinedParam","");
param.put("systemName","MSP Soft cloud");
HttpEntity<Map<String, Object>> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(param,headers);
String jsonObject = restTemplate.postForEntity(uri,httpEntity,String.class).getBody();
System.out.println(jsonObject);
// MultiValueMap
// MultiValueMap<String, Object> map = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
// map.add("mobile","13016423117");
// map.add("templateId","65e66878-2f21-4c12-853d-595156fa586e");
// map.add("userDefinedParam",content);
// map.add("systemName","MSP softcloud");
// HttpEntity<Object> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<>(map, headers);
// ResponseEntity<String> exchange = restTemplate.exchange(uri, HttpMethod.POST, requestEntity, String.class);
// JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(exchange.getBody());
// System.out.println(jsonObject);
}
JSON request
public void PostRequest() throws URISyntaxException {
URI uri = new URI("http://api.isoftstone.com/iSSC/msgServiceTest/1.0/msgOtherSystem/insertList");
String token = "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjNmNmU4ZDRlOTMzYTI2OGQxOGEzMTJlYzdiOWVlYjZhIiwidHlwIjoiSldUIn0.eyJuYmYiOjE2Mjk4OTY4NzQsImV4cCI6MTYyOTkwMDQ3NCwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9hcGkuaXNvZnRzdG9uZS5jb20vaWRzIiwiYXVkIjpbImh0dHBzOi8vYXBpLmlzb2Z0c3RvbmUuY29tL2lkcy9yZXNvdXJjZXMiLCJtc2dTZXJ2aWNlIiwibXNnU2VydmljZVRlc3QiXSwiY2xpZW50X2lkIjoiZjE3Njc3NDEtNmIzYS00ZmM3LThmMWQtNjYzNjJlY2RmODFhIiwic2NvcGUiOlsibXNnU2VydmljZSIsIm1zZ1NlcnZpY2VUZXN0Il19.RJUl87KfYJLwlPn9lN6zpVSH9vWQzTdP1q-KLYPJwWnMRACZeF0meTTPWpEq_P4Qwbof25ALhC2E8Njp3LzEblDGS8zWvhqzn0x8iT9Ikrjd2TGlMWlkUpM8qwUi2Hmd52E2eI86XRIXmUwCFVnuFJ44sFlxz2ovDjNoyGEdY3UqOfZ8LQmwlqrVluD4QHi7_a2esiexViwsXxJ7IJvrAwFNg0cKtx0C9-LWX65rS7CamAdMSOOlbKHQQreURkLluzLYauj0r2v9PSKFwCwz-3RiYvh-hnBRUKmhqNj5JC4f8lQZIyQTnZ-Pm27tjh7gTMONGF2OBn1oQr2CDCbdSg";
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
// Build request header
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
// Format request header
MediaType type = MediaType.parseMediaType("application/json");
headers.setContentType(type);
headers.add("Authorization","Bearer " + token);
// Building JSON
JSONObject content = new JSONObject();
content.put("checkCode","Off duty!!!");
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("mobile","13016431938");
json.put("templateId","65e66878-2f21-4c12-853d-595156fa586e");
json.put("userDefinedParam",content);
json.put("systemName","MSP Soft cloud");
JSONArray array = new JSONArray();
array.add(json);
// Build request body
HttpEntity<String> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<String>(array.toString(),headers);
String jsonObject = restTemplate.postForEntity(uri,httpEntity,String.class).getBody();
System.out.println(jsonObject);
}
-
notes
When requesting JSON as follows:

"[]" can only be found after building JSONObject and putting it into JSONArray. See the above code for details.
OkHttp send request
JSON request
public Boolean sendDriveMSG(String tel, String companyName) throws IOException {
//Look up the data from the database
SysSmsServerConfigVo sysSmsServerConfigVo = smsServerConfigMapper.querySmsConfig();
// Request address
String url = sysSmsServerConfigVo.getSendUrl();
// Get token
String token;
if (verifyToken()) {
token = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("token");
} else {
token = getToken();
}
// Set request header
Map header = new HashMap();
header.put("Authorization", "Bearer " + token);
// Assemble json requests
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
JSONObject content = new JSONObject();
json.put("mobile", tel);
json.put("systemName", "xxxx");
json.put("templateId", "xxxxxxx");
content.put("companyName", companyName);
json.put("userDefinedParam", content);
JSONArray array = new JSONArray();
array.add(json);
// Send request and get results
Response response = OkHttpUtil.post(url, array.toString(), header);
if (response.code() == 200) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
Form data format request
FormBody needs to be built to send
public String getToken() {
//Look up the data from the database
SysSmsServerConfigVo sysSmsServerConfigVo = smsServerConfigMapper.querySmsConfig();
OkHttpClient okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient();
String uri = "https://api.isoftstone.com/ids/connect/token";
FormBody formBody = new FormBody.Builder()
.add("client_id", sysSmsServerConfigVo.getAppKey())
.add("client_secret", sysSmsServerConfigVo.getAppSecret())
.add("grant_type", "client_credentials")
.add("scope", "msgService msgServiceTest")
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(uri)
.post(formBody)
.build();
try {
Response response = okHttpClient.newCall(request).execute();
String respBody = new String(response.body().bytes(), "gbk");
System.out.println(respBody);
// Add the token to Rides, which is valid for 10 minutes
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(respBody);
System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("access_token").toString());
String token = jsonObject.getString("access_token");
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("token", token, 3600, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return token;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("obtain Token fail");
}
return "";
}