A red-black tree is a binary balanced lookup tree in which each node has a storage bit to represent the color of the node, either RED or BLACK.Red-black trees have the following properties:
(1) Each node is red or black
(2) The root node is black
(3) If a node is red, both of its sons are black
(4) For each node, all paths from that node to its descendants contain the same number of black nodes
By the nature of the red-black tree, all implementations based on it can be guaranteed to run logarithmically (except for range lookup).The extra time it takes is proportional to the number of keys returned.
Java's TreeMap is implemented using red and black trees.
The operation of red and black trees can be confusing without drawing them. The insertion of red and black trees is illustrated below.
After inserting a red node into the red-black tree, there are six situations: N represents the inserted node, P represents the parent node, U represents the uncle node, G represents the grandparent node, X represents the current operation node.
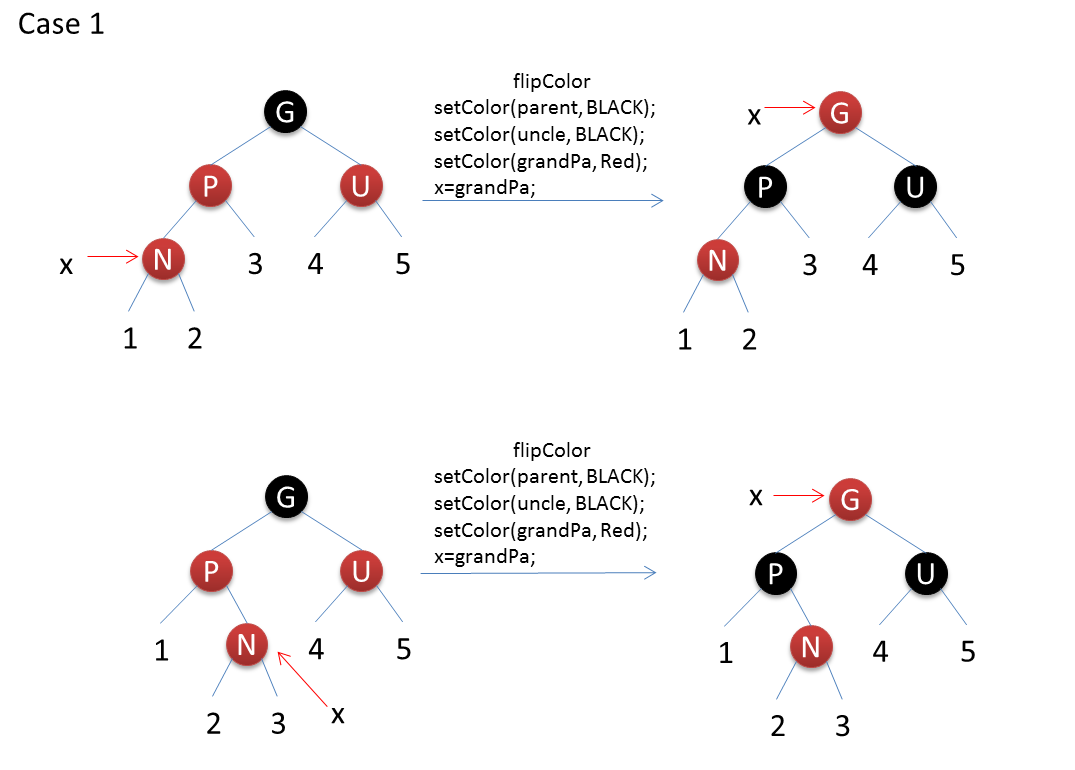
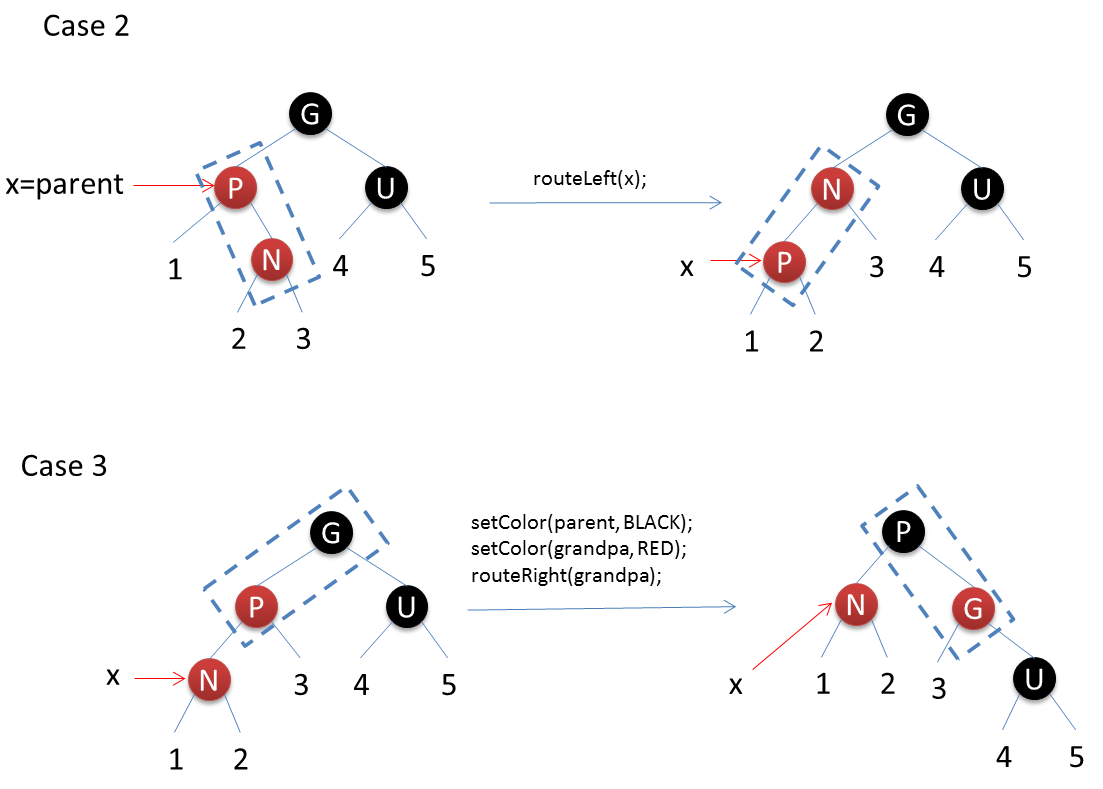
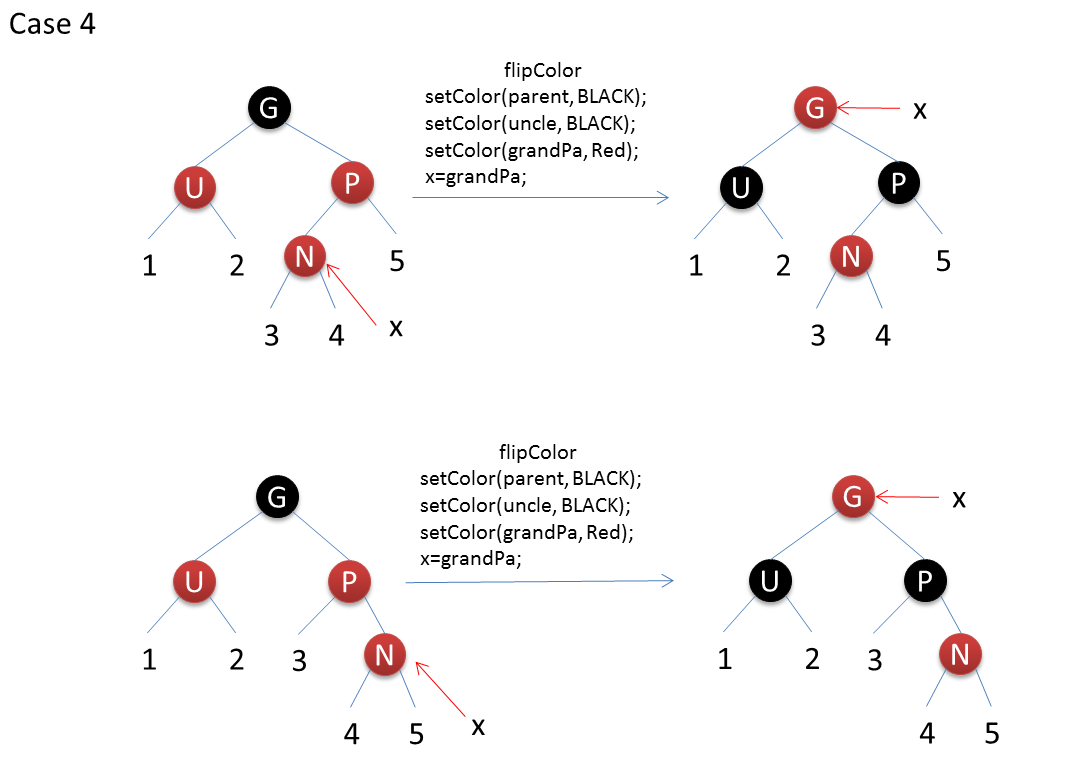
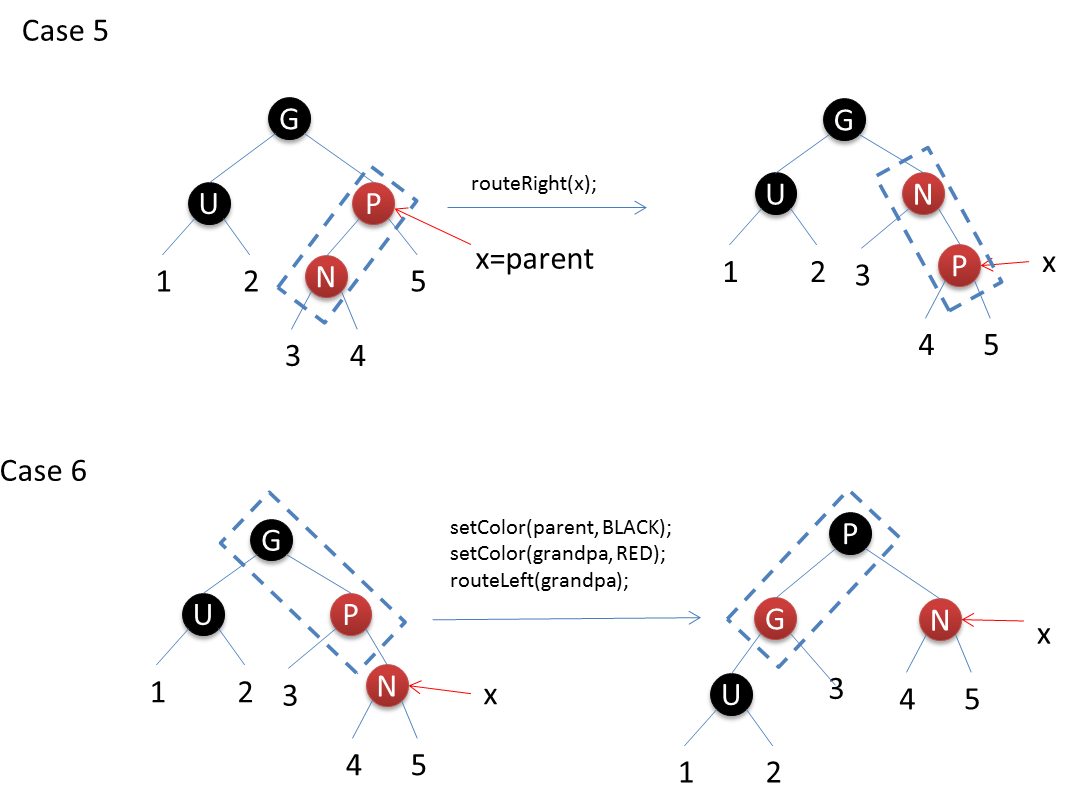
The code is as follows:
1 public class RedBlackBST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> { 2 private Node root; 3 private static final boolean RED = true; 4 private static final boolean BLACK = false; 5 private class Node{ 6 private Key key; //key 7 private Value val; //value 8 private Node left, right, parent; //Left and right subtrees and parent nodes 9 private boolean color; //The color of the link pointed to by its parent node 10 11 public Node(Key key, Value val,Node parent, boolean color){ 12 this.key = key; 13 this.val = val; 14 this.color = color; 15 } 16 } 17 18 public Value get(Key key){ 19 Node x = root; 20 while(x!=null){ 21 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 22 if(cmp < 0 ) x = x.left; 23 else if(cmp > 0) x = x.right; 24 else return x.val; 25 } 26 return null; 27 } 28 29 public void put(Key key, Value val){ 30 if(root==null) { //If it is the root node, create a new black node 31 root = new Node(key,val,null,BLACK); 32 return; 33 } 34 //Find a suitable insertion location 35 Node parent = null; 36 Node cur = root; 37 while(cur!=null) { 38 parent = cur; 39 if(key.compareTo(cur.key)>0) cur=cur.right; 40 else cur = cur.left; 41 } 42 Node n = new Node(key,val,parent,RED); //Common new node is red 43 //Insert a new node parent lower 44 if(key.compareTo(parent.key) > 0) parent.right = n; 45 else parent.left = n; 46 //After inserting a new node, adjust the color and attributes of some nodes in the tree to ensure that the characteristics of the red-black tree are not destroyed 47 fixAfterInsertion(n); 48 } 49 private Node parentOf(Node x) { 50 return (x==null ? null : x.parent); 51 } 52 private boolean colorOf(Node x) { 53 return (x==null ? BLACK : x.color); 54 } 55 private Node leftOf(Node x) { 56 return (x==null ? null : x.left); 57 } 58 private Node rightOf(Node x) { 59 return(x==null ? null : x.right); 60 } 61 private void setColor(Node x, boolean color) { 62 if(x!=null) 63 x.color = color; 64 } 65 66 private void fixAfterInsertion(Node x) { 67 while(x!=null && colorOf(parentOf(x)) == RED) { 68 Node grandPa = parentOf(parentOf(x)); 69 Node parent = parentOf(x); 70 if(parent == leftOf(grandPa)) {//case 1 || case2 || case3 71 Node uncle = rightOf(grandPa); 72 if(colorOf(uncle) == RED) {//case1, uncle is red 73 setColor(parent,BLACK); //Black parent node 74 setColor(uncle, BLACK); //Uncle node blackened 75 setColor(grandPa,RED); //Grandfather Node Red 76 x = grandPa; //Since the grandparent node goes from black to red, the red and black attributes of the parent node and its ancestors are readjusted 77 }else {//case2 || case3,uncle is black 78 if(x==rightOf(parent)) { //case2 79 x = parent; 80 rotateLeft(x); 81 } 82 //case3 83 setColor(parent,BLACK); 84 setColor(grandPa, RED); 85 rotateRight(grandPa); 86 } 87 88 }else {//case4 || case 5 || case6 89 Node uncle = leftOf(grandPa); 90 if(colorOf(uncle) == RED) { //case4 || case5 || case6 91 setColor(parent,BLACK); 92 setColor(uncle, BLACK); 93 setColor(grandPa,RED); 94 x = grandPa; 95 }else{ //case5 || case6, uncle is black 96 if(x==leftOf(parent)) { //case5 97 x = parent; 98 rotateRight(x); 99 } 100 //case6 101 setColor(parent,BLACK); 102 setColor(grandPa, RED); 103 rotateLeft(grandPa); 104 } 105 } 106 } 107 } 108 private void rotateLeft(Node x) { 109 if(x==null) return; 110 Node y = x.right; 111 x.right = y.left; 112 if(y.left!=null) 113 y.left.parent = x; 114 y.left = x; 115 y.parent = x.parent; 116 if(x.parent == null) { 117 root = y; 118 } 119 else if(x.parent.left == x) { 120 x.parent.left = y; 121 }else { 122 x.parent.right = y; 123 } 124 x.parent = y; 125 } 126 private void rotateRight(Node x) { 127 if(x==null) return; 128 Node y = x.left; 129 x.left = y.right; 130 if(y.right != null) 131 y.right.parent = x; 132 y.right = x; 133 y.parent = x.parent; 134 if(x.parent == null) { 135 root = y; 136 }else if(x.parent.left==x) { 137 x.parent.left = y; 138 }else { 139 x.parent.right=y; 140 } 141 x.parent = y; 142 } 143 144 }
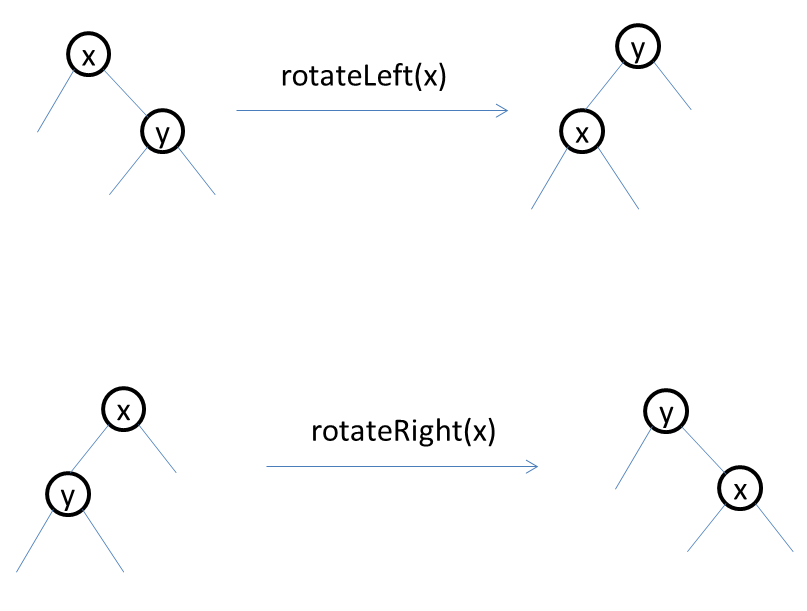
The rotateLeft and rotateRight above need to be illustrated: