Value based and decision based
In reinforcement learning, there are two kinds of methods, one is based on value and the other is based on policy
- The typical representative of the value based algorithm is Q-learning and SARS a, which optimizes the Q function to the best, and then selects the best strategy according to the Q function.
- The typical representative of policy based algorithm is Policy Gradient, which directly optimizes the policy function.
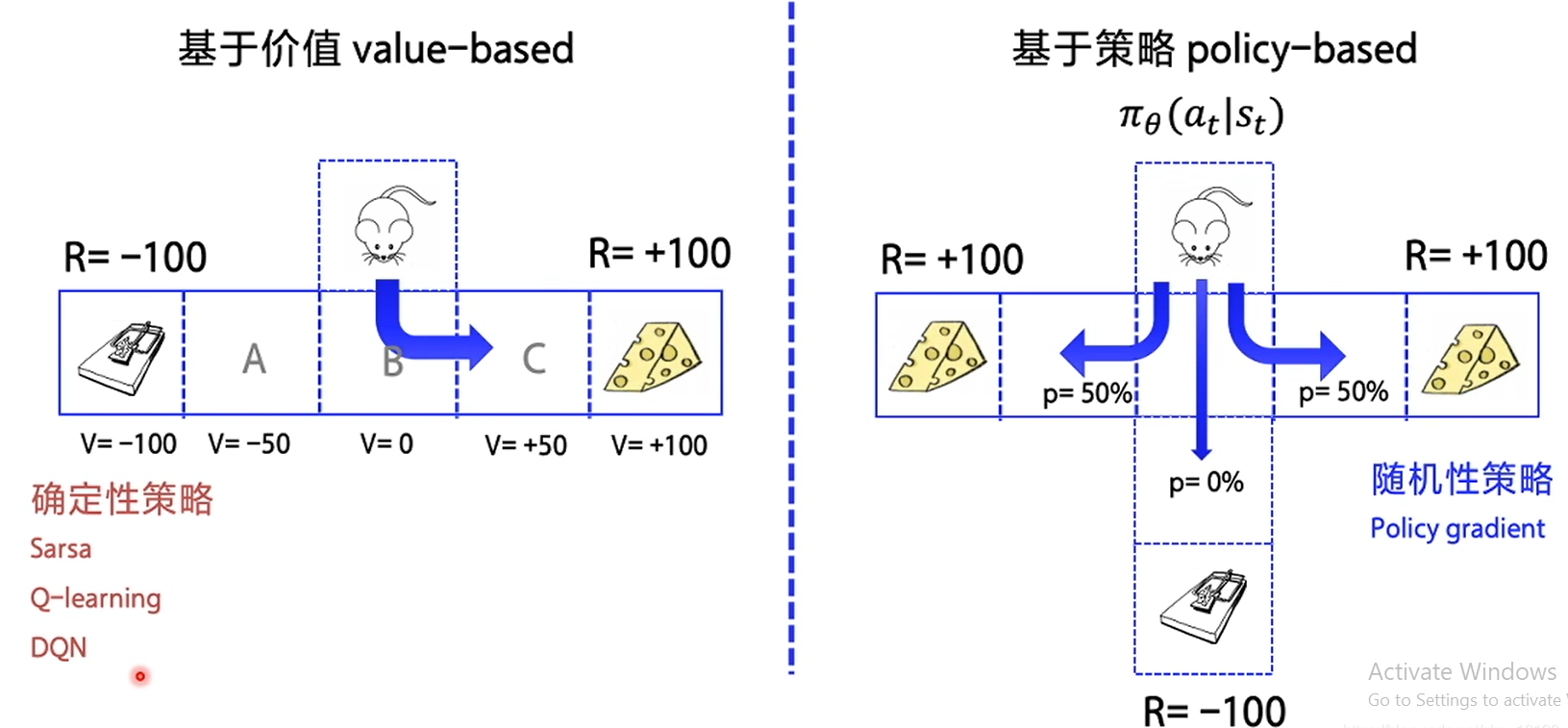
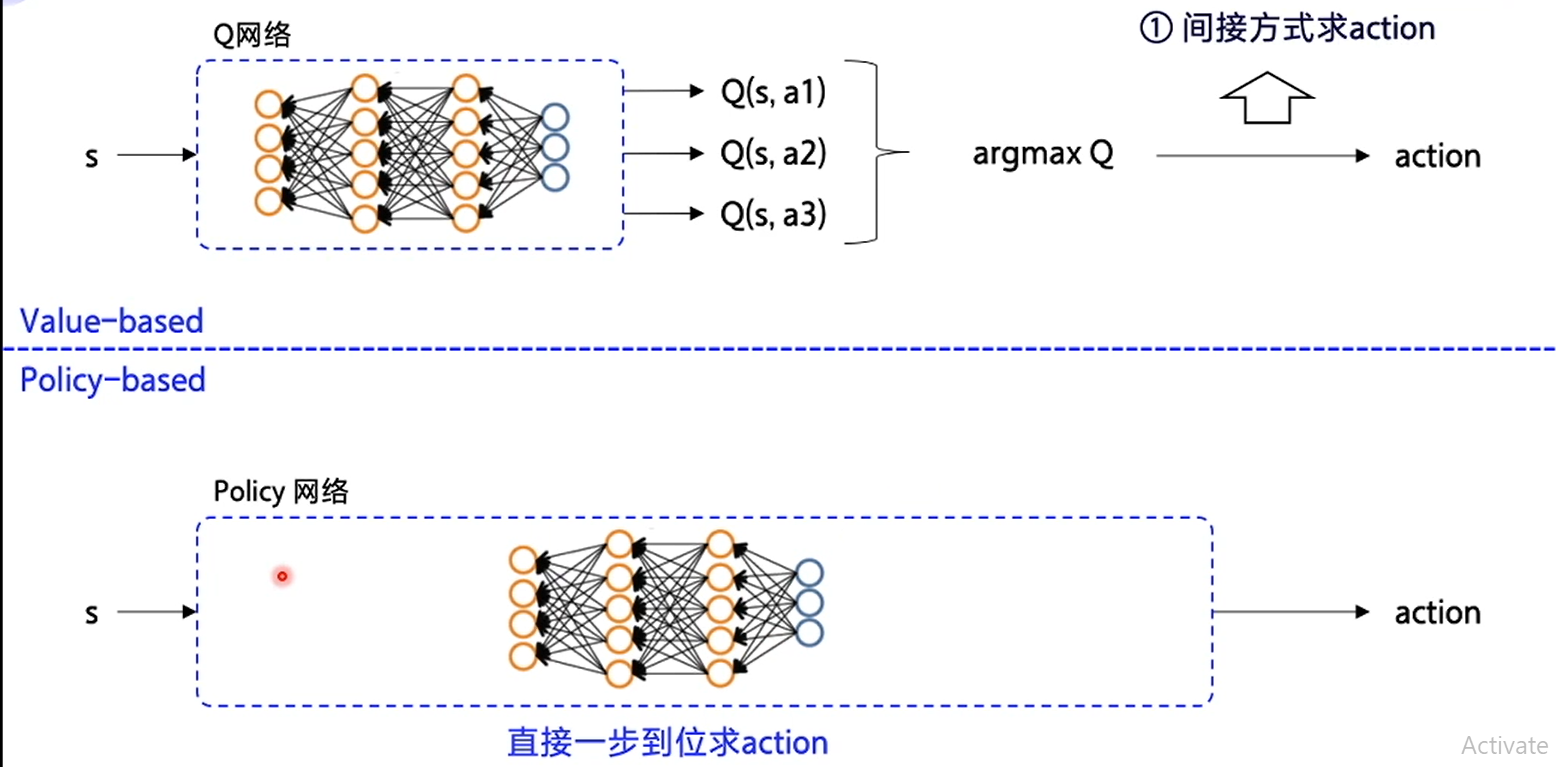
The difference between the two is clear at a glance, that is, one is to make decision according to the scheme determined by value, the other is to get the result of decision directly in place, rather than to make decision step by step after calculating the reward of each state in turn.
Random strategy
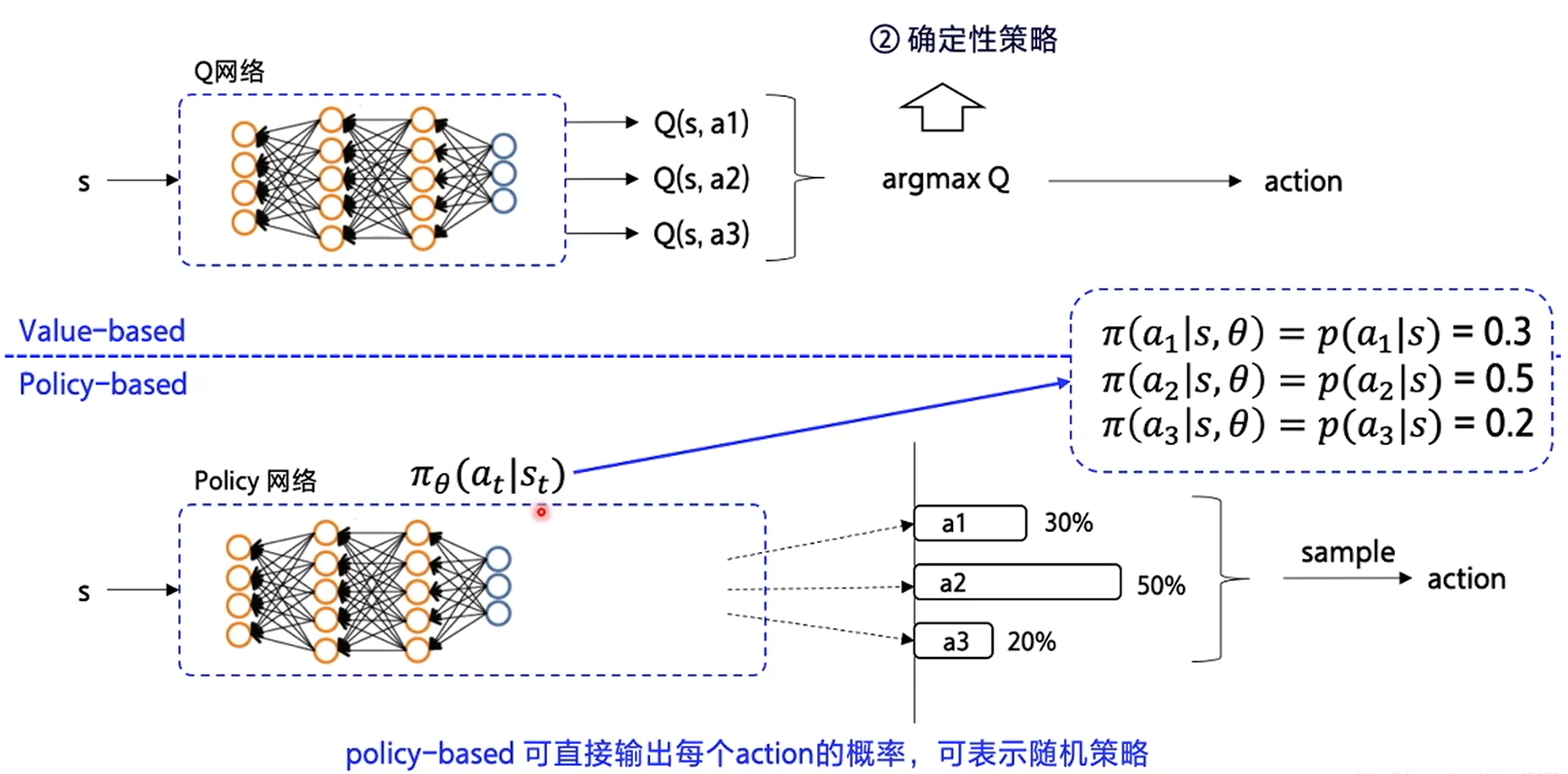
In the decision-making strategy, the output of neural network is the Q value calculated according to the state, and then we make decisions according to the Q value with a fixed strategy.
In the random strategy, we input different states, then calculate the probability of making a decision directly, learn to make a decision directly in one step, and no longer generate Q value.
After doing so, we are faced with a problem that is how to optimize our network, how to evaluate the quality of the network?
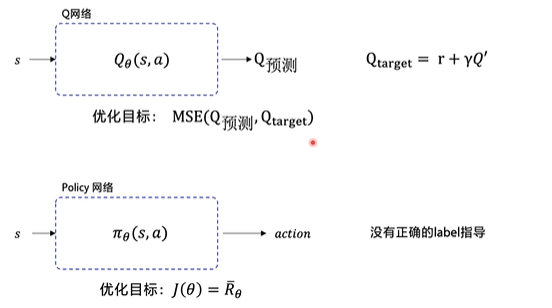
The strategy based model can't carry out back propagation to the neural network after one calculation, because its result is generated after many iterations, so its optimization is also different from the ordinary neural network.
Track expected return
Since our ultimate goal is to get the maximum expectation after decision-making, then we can calculate the expected return according to the final return and the probability of the decision trajectory to represent the return as a trajectory, then we can optimize the network according to the size of the return.
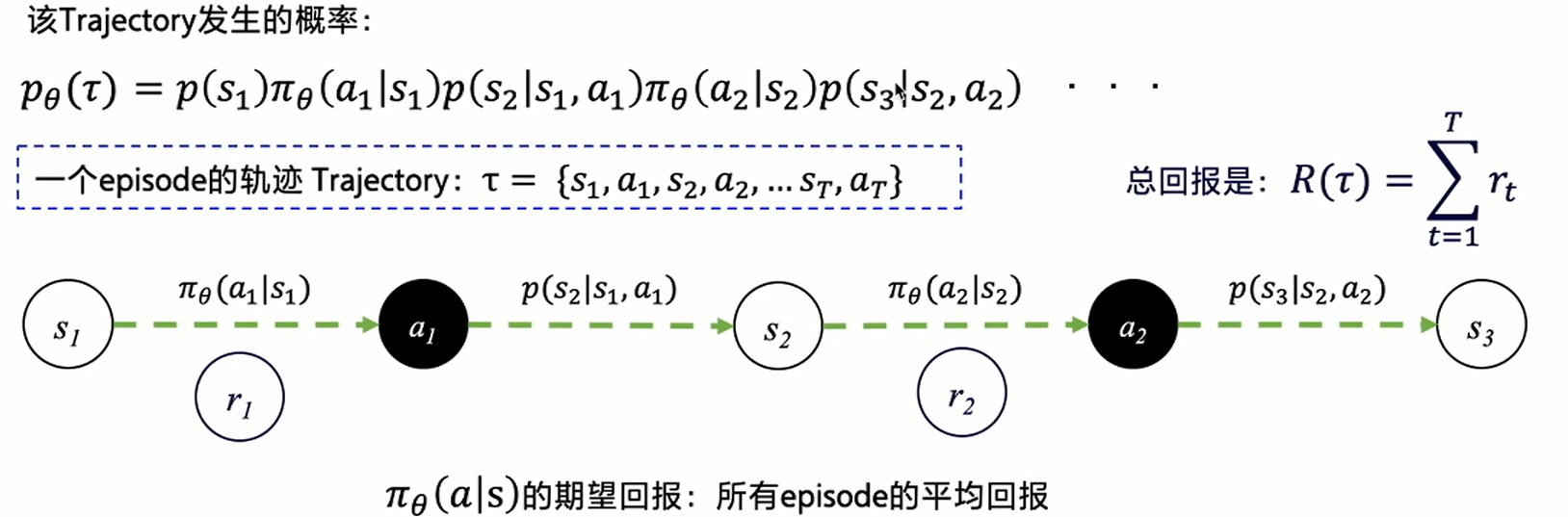
So, we have a strategy gradient, and take the strategy gradient as Loss to optimize the neural network
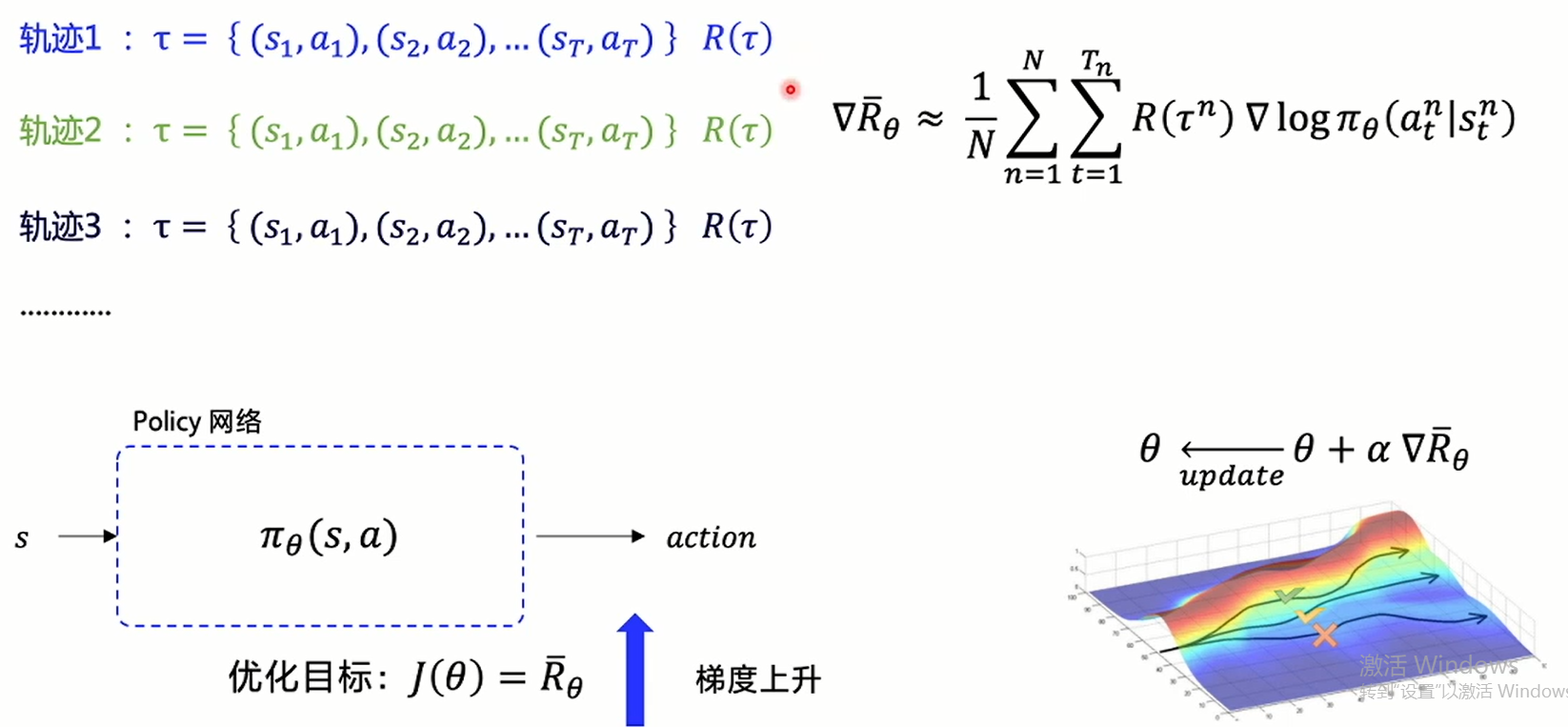
There are two ways to sample strategy gradients:
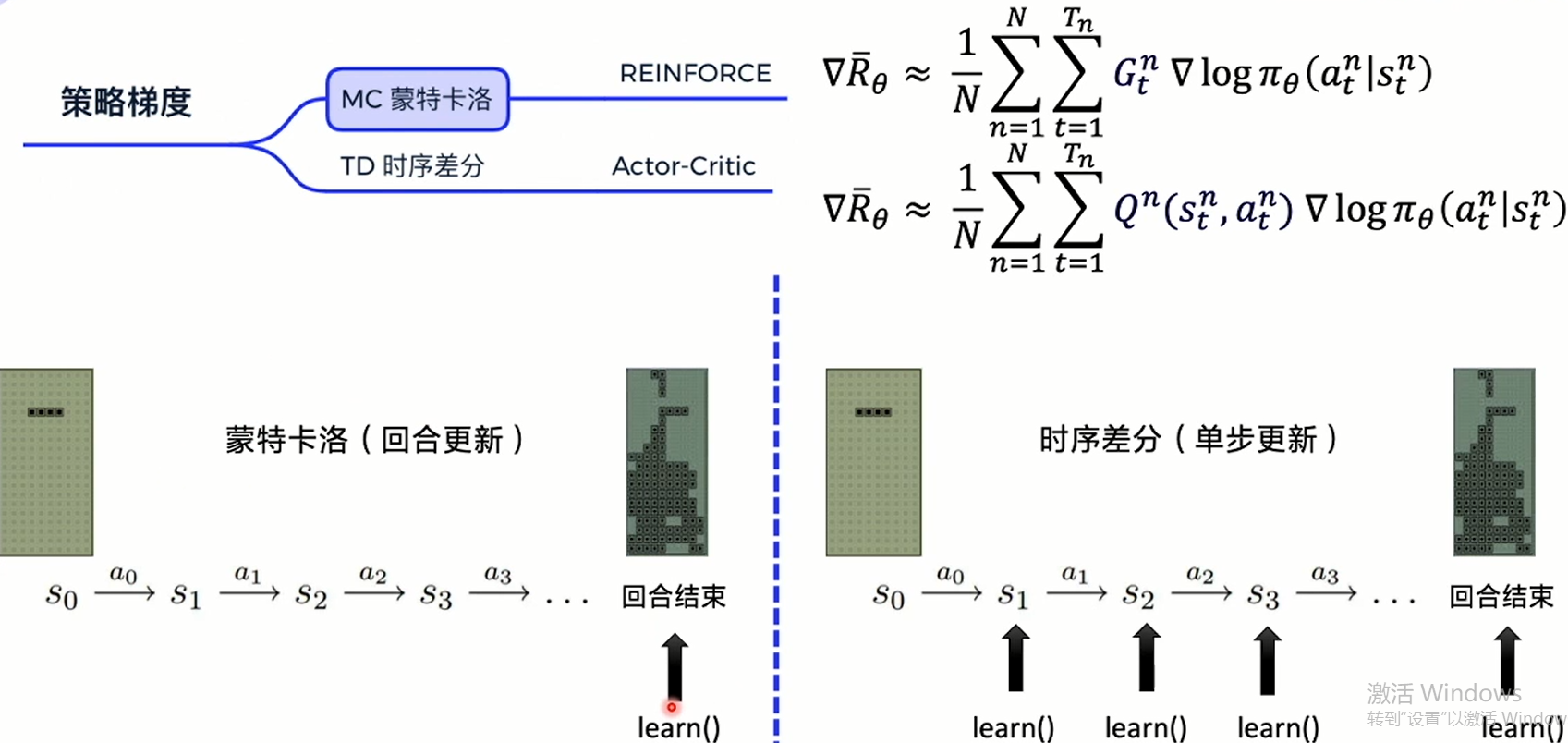
- Monte Carlo is to update the parameters at the end of each round
- Timing difference is to update parameters after each step, and its update frequency is higher (actor critical)
Reinforce
Algorithm core
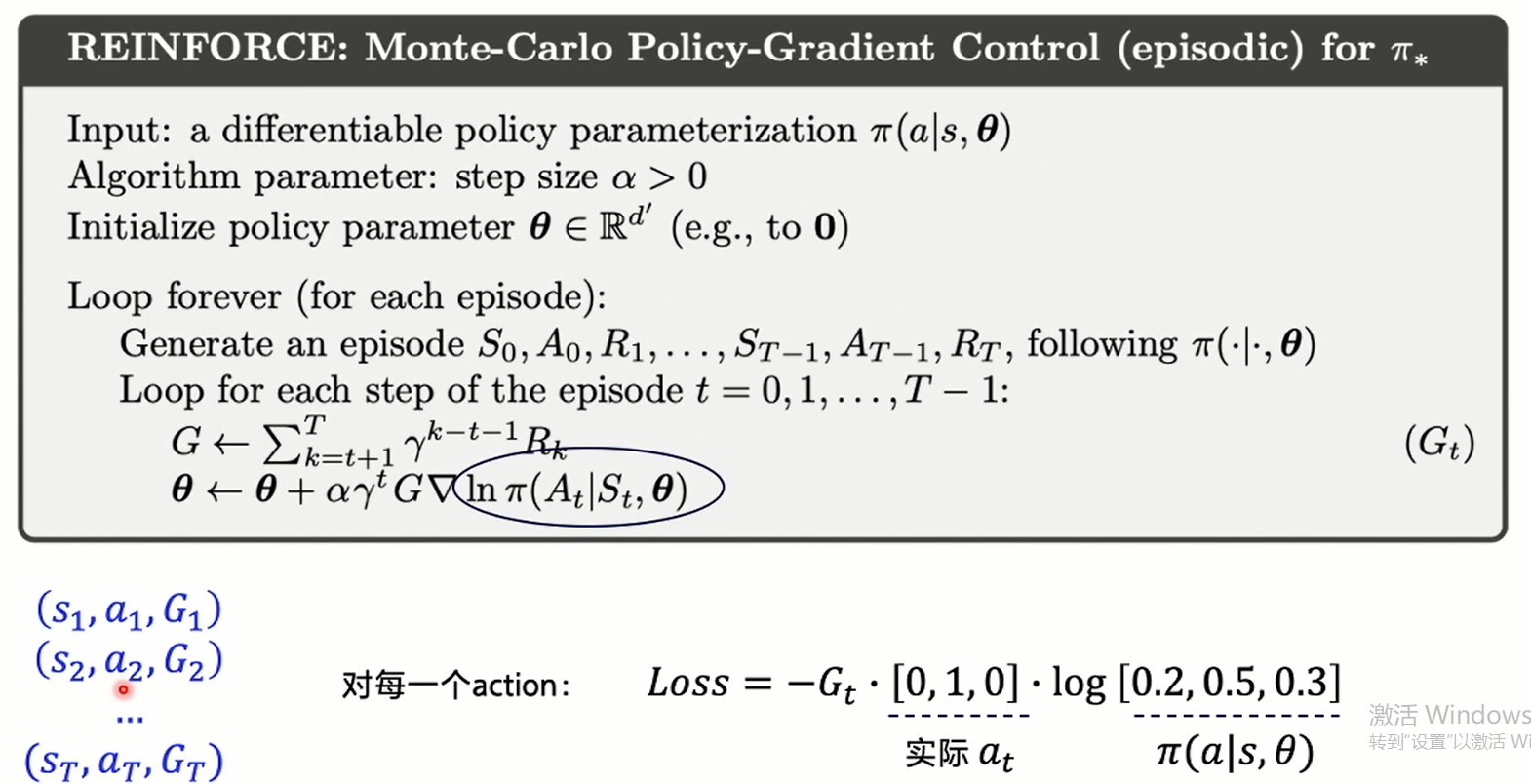
Practice as code

Algorithm flow
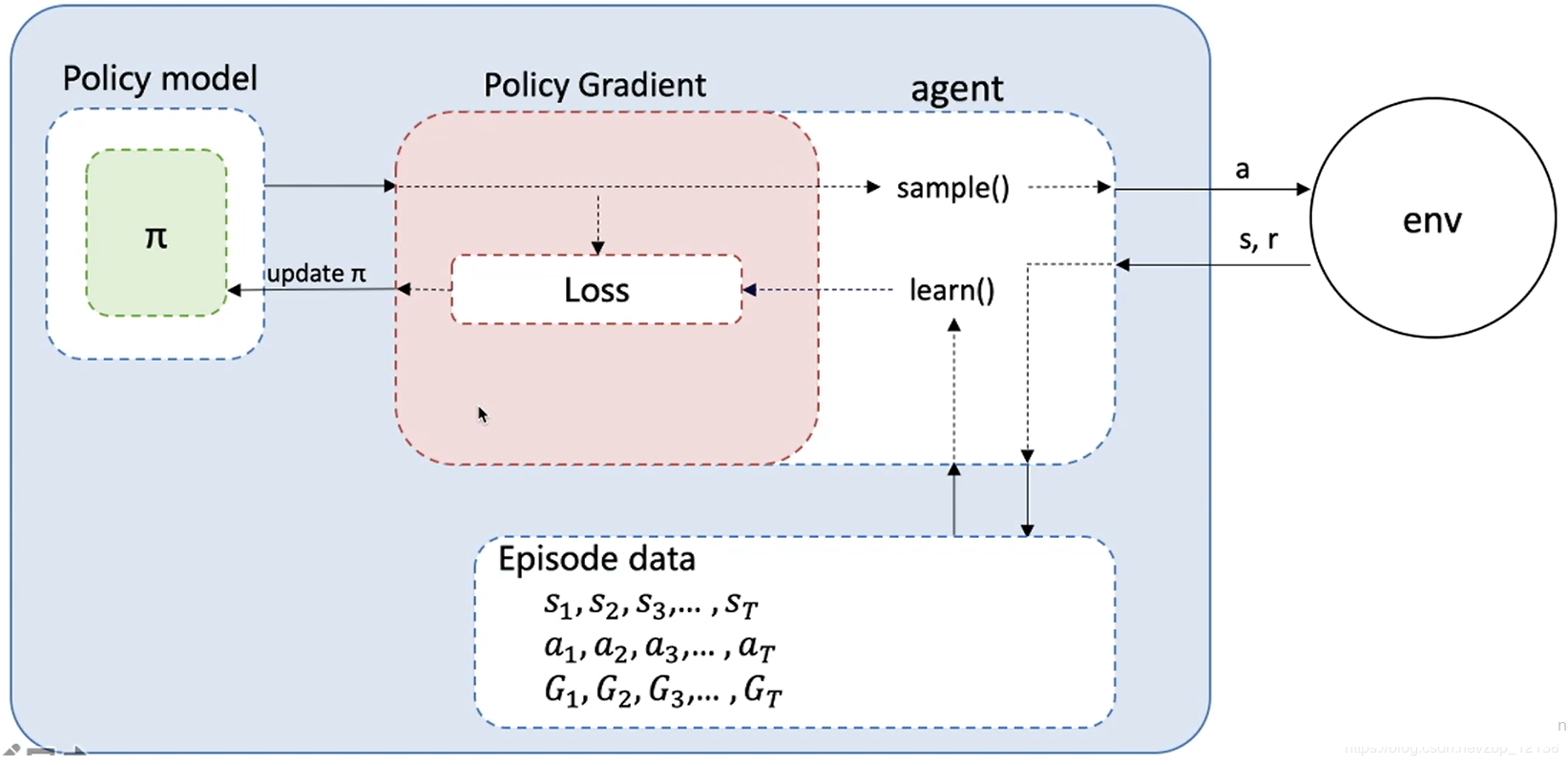
Code practice
Refer to the above figure
model
class Model(parl.Model):
def __init__(self, act_dim):
self.fc1 = layers.fc(size = 256,act='tanh')
self.fc2 = layers.fc(size = act_dim,act='softmax')#Output probability of actions
def forward(self, obs): # It can be called directly with model = Model(5); model(obs)
out = self.fc1(obs)
out = self.fc2(out)
return outAlgorithm
class PolicyGradient(parl.Algorithm):
def __init__(self, model, lr=None):
""" Policy Gradient algorithm
Args:
model (parl.Model): policy Forward network of.
lr (float): Learning rate.
"""
self.model = model
assert isinstance(lr, float)
self.lr = lr
def predict(self, obs):
""" use policy model Action probability of predicted output
"""
return self.model(obs)
def learn(self, obs, action, reward):
""" use policy gradient Algorithm update policy model
"""
act_prob = self.model(obs) # Get output action probability
# log_prob = layers.cross_entropy(act_prob, action) # Cross entropy
log_prob = layers.reduce_sum(
-1.0 * layers.log(act_prob) * layers.one_hot(
action, act_prob.shape[1]),
dim=1)
cost = log_prob * reward
cost = layers.reduce_mean(cost)
optimizer = fluid.optimizer.Adam(self.lr)
optimizer.minimize(cost)
return costAgent
class Agent(parl.Agent):
def __init__(self, algorithm, obs_dim, act_dim):
self.obs_dim = obs_dim
self.act_dim = act_dim
super(Agent, self).__init__(algorithm)
def build_program(self):
self.pred_program = fluid.Program()
self.learn_program = fluid.Program()
with fluid.program_guard(self.pred_program): # Build calculation chart to predict actions and define input and output variables
obs = layers.data(
name='obs', shape=[self.obs_dim], dtype='float32')
self.act_prob = self.alg.predict(obs)
with fluid.program_guard(
self.learn_program): # Build calculation chart to update policy network and define input and output variables
obs = layers.data(
name='obs', shape=[self.obs_dim], dtype='float32')
act = layers.data(name='act', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
reward = layers.data(name='reward', shape=[], dtype='float32')
self.cost = self.alg.learn(obs, act, reward)
def sample(self, obs):
obs = np.expand_dims(obs, axis=0) # Add one dimension
act_prob = self.fluid_executor.run(
self.pred_program,
feed={'obs': obs.astype('float32')},
fetch_list=[self.act_prob])[0]
act_prob = np.squeeze(act_prob, axis=0) # Reduce one dimension
act = np.random.choice(range(self.act_dim), p=act_prob) # Select actions according to action probability
return act
def predict(self, obs):
obs = np.expand_dims(obs, axis=0)
act_prob = self.fluid_executor.run(
self.pred_program,
feed={'obs': obs.astype('float32')},
fetch_list=[self.act_prob])[0]
act_prob = np.squeeze(act_prob, axis=0)
act = np.argmax(act_prob) # Select the action with the highest probability according to the action probability
return act
def learn(self, obs, act, reward):
act = np.expand_dims(act, axis=-1)
feed = {
'obs': obs.astype('float32'),
'act': act.astype('int64'),
'reward': reward.astype('float32')
}
cost = self.fluid_executor.run(
self.learn_program, feed=feed, fetch_list=[self.cost])[0]
return costTraining and testing
def run_episode(env, agent):
obs_list, action_list, reward_list = [], [], []
obs = env.reset()
while True:
obs = preprocess(obs) # from shape (210, 160, 3) to (100800,)
obs_list.append(obs)
action = agent.sample(obs) # Sampling action
action_list.append(action)
obs, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
reward_list.append(reward)
if done:
break
return obs_list, action_list, reward_list
# Evaluate the agent, run 5 episode s, and find the average
def evaluate(env, agent, render=False):
eval_reward = []
for i in range(5):
obs = env.reset()
episode_reward = 0
while True:
obs = preprocess(obs) # from shape (210, 160, 3) to (100800,)
action = agent.predict(obs) # Select the best action
obs, reward, isOver, _ = env.step(action)
episode_reward += reward
if render:
env.render()
if isOver:
break
eval_reward.append(episode_reward)
return np.mean(eval_reward)Preprocessing image input and calculating step return
def preprocess(image):
""" Pretreatment 210 x160x3 uint8 frame into 6400 (80x80) 1 dimension float vector """
image = image[35:195] # Crop
image = image[::2,::2,0] # Subsampling, 2x scaling
image[image == 144] = 0 # Erase background type 1
image[image == 109] = 0 # Erase background type 2
image[image != 0] = 1 # Turn to grayscale, white except black
return image.astype(np.float).ravel()
# According to the reward list of each step of an episode, calculate the Gt of each step
def calc_reward_to_go(reward_list, gamma=0.99):
"""calculate discounted reward"""
reward_arr = np.array(reward_list)
for i in range(len(reward_arr) - 2, -1, -1):
# G_t = r_t + γ·r_t+1 + ... = r_t + γ·G_t+1
reward_arr[i] += gamma * reward_arr[i + 1]
# normalize episode rewards
reward_arr -= np.mean(reward_arr)
reward_arr /= np.std(reward_arr)
return reward_arr
Environment configuration and process control
# Create environment
env = gym.make('Pong-v0')
obs_dim = 80 * 80
act_dim = env.action_space.n
logger.info('obs_dim {}, act_dim {}'.format(obs_dim, act_dim))
# Building agent based on parl framework
model = Model(act_dim=act_dim)
alg = PolicyGradient(model,lr = LEARNING_RATE)
agent = Agent(alg,obs_dim = obs_dim,act_dim =act_dim)
# Load model
if os.path.exists('./model.ckpt'):
agent.restore('./model.ckpt')
for i in range(3000):
obs_list, action_list, reward_list = run_episode(env, agent)
if i % 10 == 0:
logger.info("Train Episode {}, Reward Sum {}.".format(i,
sum(reward_list)))
batch_obs = np.array(obs_list)
batch_action = np.array(action_list)
batch_reward = calc_reward_to_go(reward_list)
agent.learn(batch_obs, batch_action, batch_reward)
if (i + 1) % 100 == 0:
total_reward = evaluate(env, agent, render=False)
logger.info('Episode {}, Test reward: {}'.format(i + 1,
total_reward))
agent.save('./model.ckpt')Results display
