1, Introduction of database and related concepts
Database: warehouse for storing data;
1.DB(DateBase)
data base
A collection of data organized according to a data model and placed in storage
2.DBMS(DateBase Management System)
Database management system
Service software for manipulating and managing databases
3.DBS(DataBase System)
Database system: DB+DBMS
A computer system with a database and integrated database management software
Typical application environment
LAMP platform, combined with Apache HTTP Server
LNMP platform, combined with Nginx
Installation software
[root@proxy ~]# systemctl start mysqld #Startup service [root@proxy ~]# ss -auntlp | grep 3306 #See if the service has started
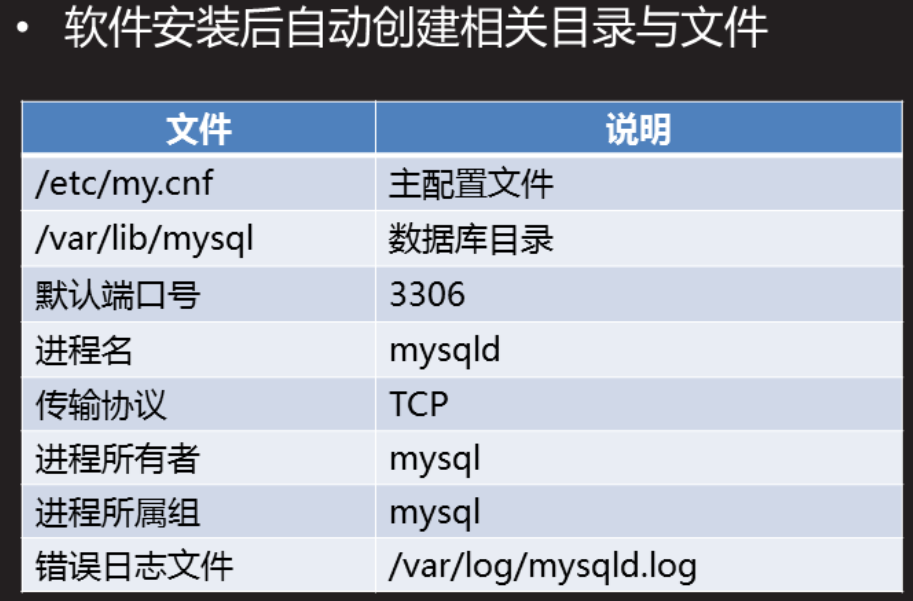
information is not available in mysql directory. It belongs to virtual database and data exists
In memory, read-only, cannot be deleted. Server parameter settings are stored
2, Basic operations related to database
1. Change login password
First, find the initial password and go to the log to find it. If there are special symbols, you need to add single quotation marks
[root@proxy ~]# grep password /var/log/mysqld.log [root@proxy ~]# mysql -uroot -p'vcY;pJT,f8Es' mysql> alter user root@"localhost" identified by "123qqq...A";
If the log does not have an initial password, delete the mysql directory and restart the service (you can also do this if you forget the password)
1.1 change password policy
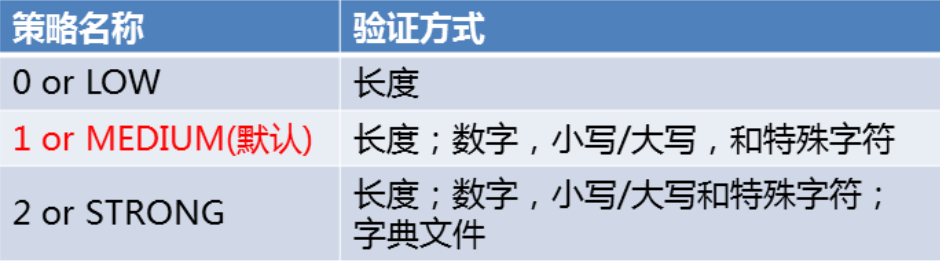
Temporary modification
mysql> show variables like "%password%"; #View variables mysql> set global validate_password_policy=0; #Modify password policy mysql> set global validate_password_length=6; #Change password length
Permanent modification
[root@proxy ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] .... validate_password_policy=0 validate_password_length=6
2. Common SQL command classifications

2.1 warehouse management command

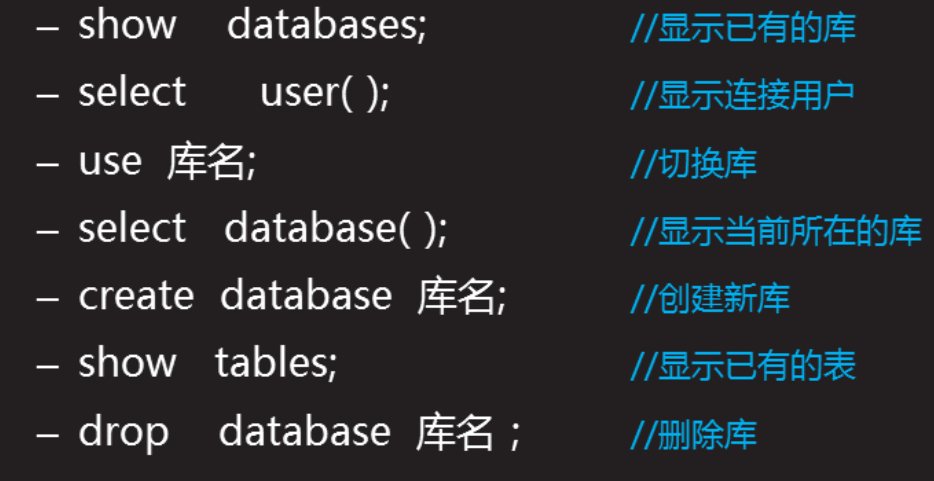
2.2 table management command
mysql> create database db1; #Create Library mysql> create table db1.sun(name char(10),homeadd char(20)); #Create table mysql> create table db1.yun(password char(50),name char(5))default charset=utf8; #Create tables and support Chinese mysql> use db1 #Enter the Library Directory mysql> show tables; #View all tables under the library mysql> desc db1.sun; #View table structure mysql> drop table db1.sun; #Delete table
2.3 record management command

mysql> insert into db1.yun values("jie","mao"),("f760","Li Feng"); #Add two lines, separated by commas mysql> select * from db1.yun; #View table contents mysql> select name from yun; #View the name column content of the table mysql> update db1.yun set name="Li Feng" where password="f760"; #Modify the contents of the table mysql> select * from db1.yun\G; #When there are too many contents in the table, you can use \ G to look vertically mysql> delete from yun; #Delete the contents of the table. Do not delete the table. You can also use it to delete rows. Conditional deletion is required
3. MySQL data type

3.1 character type
Fixed length: char (number of characters)
Maximum characters 255
Insufficient specified number of characters is filled with spaces on the right
Cannot write data when the number of characters exceeds
Side length: varchar (number of characters)
Allocate storage space according to actual data size
Cannot write data when the number of characters exceeds (65535)
Large text type: text/bob
Use when the number of characters is greater than 65535
3.2 value type
3.2.1 integer type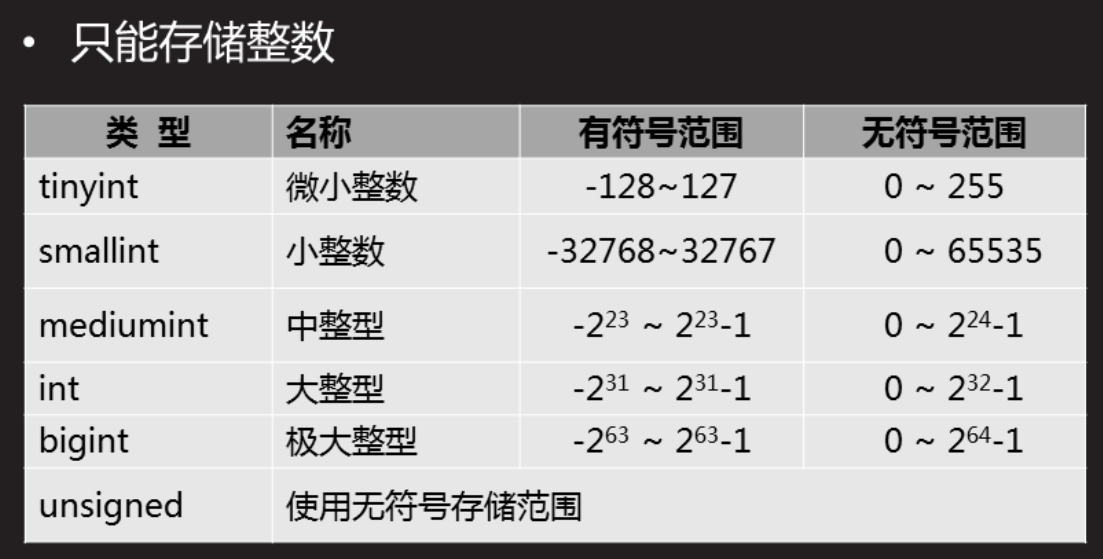
mysql> create table db1.t1(name char(10),age tinyint unsigned); #Value type of age and use unsigned storage range mysql> insert into t1 values("jack","19.4"); #When the input number has decimal point, it will be rounded
3.2.2 floating point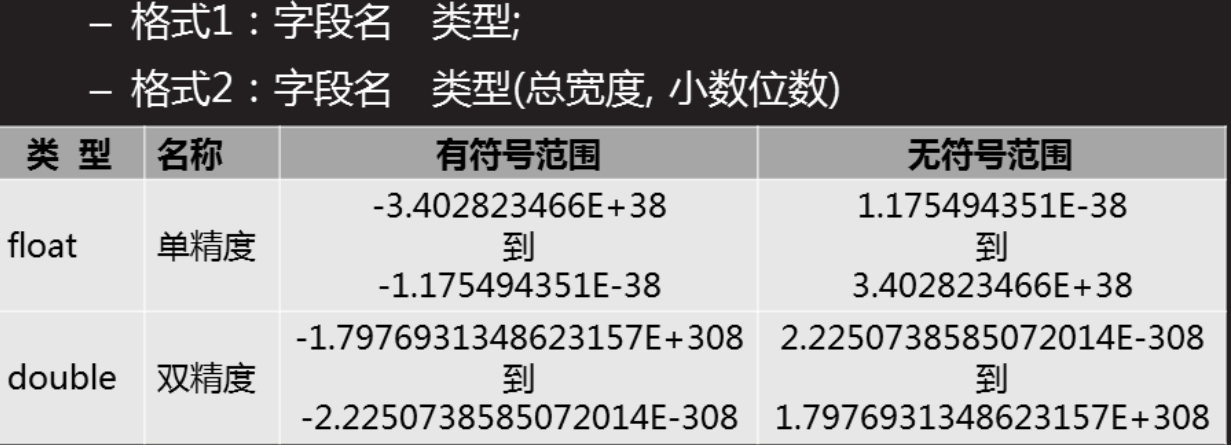
Field name float (n, m) xxx.xx 999.99 ~ -999.99
Field name double(n,m) xxxxx.xx 99999.99 ~ -99999.99
n represents the total number of digits
m is the number of decimal places
mysql> create table t2(name char(10),gz float(7,2)); mysql> insert into t2 values("jack","77777"); mysql> select * from t2; +------+----------+ | name | gz | +------+----------+ | jack | 77777.00 | +------+----------+
3.3 date time type
-datetime
1. Range: 1000-01-01 00:00:00 ~ 9999-12-31 23:59:59 2. Format: yyyymmddhhmms
-Date time timestamp
1. Range: 1970-01-01 00:00:00 ~ 2038-01-19 00:00:00 2. Format: yyyymmddhhmms
PS: when the timestamp field is assigned, the current system time is assigned automatically, and the datetime value is null (empty)
- date date
1. Range: 0001-01-01 ~ 9999-12-31 2. Format: yyyymmdd
- year year
1. Range: 1901-2155 2. Format: yyyy
PS: when 2-digit assignment is used: 01-69 is regarded as 2001-2069, 70-99 as 1970-1999
- time time
Format: HH:MM:SS
mysql> create table db2.t11(name char(15),csnf year,birthday date,up_class time,party datetime); mysql> insert into db2.t11 values("bob",2020,20200214,090000,20200214090000); mysql> create table db3.t1(name char(10),meetting datetime,party timestamp); #See the difference between timestamp and datetime mysql> insert into db3.t1(name,meetting) values("mao",20200214090000); mysql> insert into db3.t1(name,party) values("jie",20200214090000);
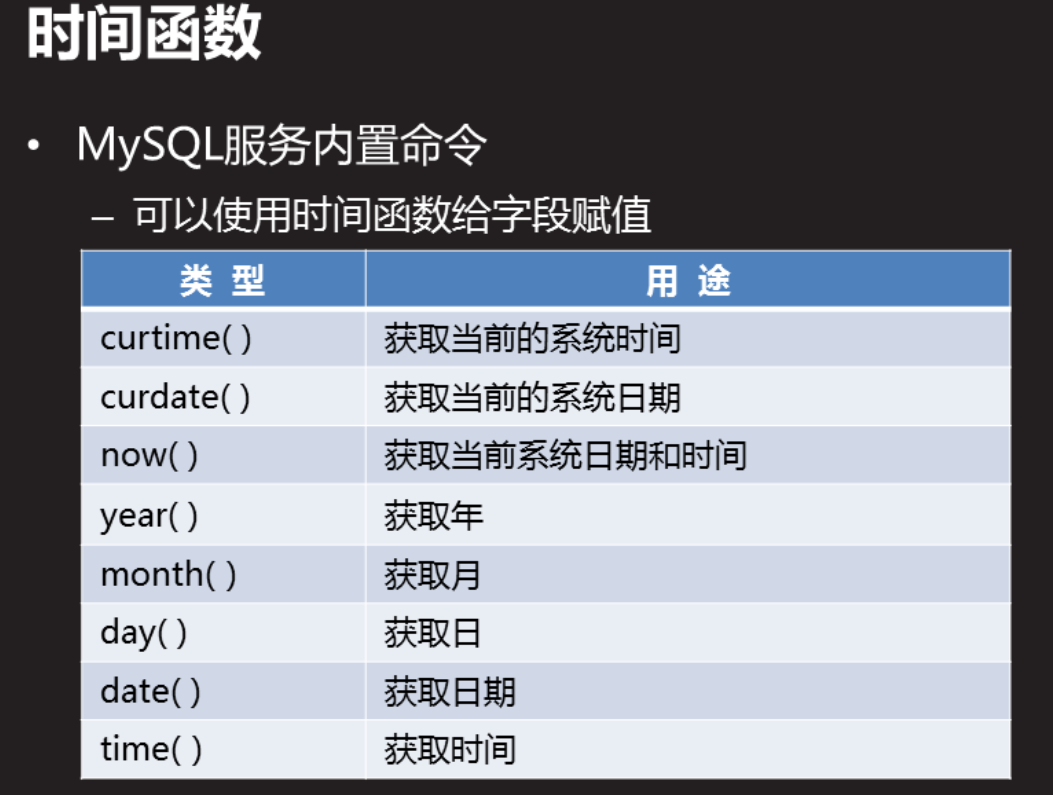
mysql> select curtime(); mysql> select curdate; mysql> select time(now()); mysql> insert into db2.t11 values("jack",year(now()),date(now()),time(now()),now()); #Insert current system time
3.4 enumeration type
enum single election
1. Format: field name enum (value 1, value 2, value N)
2. Only one value can be selected
3. Field value must be selected in the list
set multiple selection
1. Format: field name set (value 1, value 2, value N)
2. Select one or more values
3. Field value must be selected in the list
mysql> create table db1.t7(name char(15),sex enum("boy","girl"),likes set("eat","game","it")); mysql> insert into db1.t7 values("mao","boy","eat,it");

