1. Scenario Display
Regular expressions and corresponding functions are the same in oracle and mysql.
Introduction to regular expression symbols:
'^' Matches the start position of the input string, used in a square bracket expression, where it indicates that the character set is not accepted.
'$' Matches the end of the input string. If set RegExp Object Multiline Property, then $ Also match '\n' or '\r'.
'.' Matches any single character except the newline character.
'?' Matches the previous subexpression zero or once.
'+' Matches the previous subexpression one or more times.
'*' Matches the previous subexpression zero or more times.
'|' Indicates a choice between two items. example'^([a-z]+|[0-9]+)$'Represents a string composed of all lowercase letters or numbers.
'( )' Marks the beginning and end of a subexpression.
'[]' Mark a bracket expression.
'{m,n}' A precise range of occurrences, m=<Number of occurrences<=n,'{m}'Indicates presence m Times,'{m,}'Indicates that at least m Times.
\num matching num,among num Is a positive integer. A reference to the match obtained.
Character cluster:
[[:alpha:]] Any letter.
[[:digit:]] Any number.
[[:alnum:]] Any letters and numbers.
[[:space:]] Any white characters.
[[:upper:]] Any capital letter.
[[:lower:]] Any lowercase letter.
[[:punct:]] Any punctuation.
[[:xdigit:]] Any hexadecimal number, equivalent to[0-9a-fA-F]. Operation priority of various operators:
\Escape character
(), (?:), (? =), [] parentheses and square brackets
*, +, ?, {n}, {n,}, {n,m} qualifiers
^, $, anymetacharacter position and order
|
*/
2.REGEXP_LIKE()
Similar to the function of LIKE, the difference is that regular expressions can be used;
Basic usage:
-- query THEMECODE The field value contains 36 records select * from meta_theme where regexp_like(THEMECODE,'36');
amount to:
select * from meta_theme where THEMECODE like '%36%';
Contains only numbers 0-9 or decimal points
regexp_like(str,'^[0-9\.]+$')
Four implementations containing only pure numbers
regexp_like(str,'^[0-9]+[0-9]$'); regexp_like(str,'^[0-9]+$'); regexp_like(str,'^[[:digit:]]+$'); not regexp_like(str,'[^0-9]');
'+' matches the previous subexpression one or more times;
^Indicates exclusion.
Not two implementations of pure numbers 0-9
regexp_like(str,'[^0-9]'); -- ^Indicates exclusion not regexp_like(str,'^[[:digit:]]+$');
Two implementations containing only 0-9 and - characters
regexp_like(str,'[0-9-]'); regexp_like(str,'^[0-9]|[-]$');
'|' indicates a choice between two items, equivalent to or.
Five implementations that contain only 0-9, - characters, or spaces
regexp_like(str,'^[0-9]|[-]$') or regexp_like(str,'^[ ]$'); regexp_like(str,'^[0-9]|[-]$|^[ ]$'); regexp_like(str,'(^[0-9]|[-]$)|(^[ ]$)'); regexp_like(str,'^[0-9]|[-]|[ ]$'); regexp_like(str,'[0-9- ]');
3.REGEXP_INSTR()
Similar to INSTR(), the difference is that regular expressions can be used;
4.REGEXP_SUBSTR()
Similar to SUBSTR(), the difference is that regular expressions can be used;
5.REGEXP_REPLACE()
Similar to REPLACE(), the difference is that regular expressions can be used;
Regular expressions can be used to replace or extract the contents of fields.
-- replace
select regexp_replace('hjbfgcoqwue8723r8fhescb938r','[^0-9]','-');
-- extract
select regexp_replace('hjbfgcoqwue8723r8fhescb938r','[^0-9]','') from dual;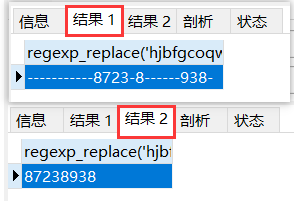
6. Common regular expressions
Match number
^[1-9]\d*$ -- Match positive integer ^-[1-9]\d*$ -- Match negative integer ^-?[1-9]\d*$ -- Match integer ^[1-9]\d*|0$ -- Match nonnegative (positive) integers + 0) ^-[1-9]\d*|0$ -- Match non positive (negative) integers + 0) ^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*$ -- Match positive floating point number ^-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*)$ -- Match negative floating point number ^-?([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0)$ -- Matching floating point numbers ^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0$ -- Match non negative floating point number (positive floating point number) + 0) ^(-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*))|0?\.0+|0$ -- Matching non positive floating point numbers (negative floating point numbers) + 0)
Match character
^[A-Za-z]+$ -- Matches a string of 26 English letters ^[A-Z]+$ -- Matches a string of 26 uppercase letters ^[a-z]+$ -- Matches a string of 26 lowercase letters ^[A-Za-z0-9]+$ -- Matches a string of numbers and 26 English letters ^\w+$ -- Matches a string of numbers, 26 letters, or underscores
Hex value: / ^#? ([a-f0-9]{6}|[a-f0-9]{3})$/
Email: / ^ ([a-z0-9 \. -] +) @ ([\ da-z \. -] +) \. ([A-Z \.] {2,6})$/
URL: /^(https?:\/\/)?([\da-z\.-]+)\.([a-z\.]{2,6})([\/\w \.-]*)*\/?$/
IP address: / ^ (?: (?: 25 [0-5] | 2 [0-4] [0-9] | [01]? [0-9] [0-9]?) \) {3} (?: 25 [0-5] | 2 [0-4] [0-9] | [01]? [0-9] [0-9]?)$/
HTML tag: / ^ < ([A-Z] +) ([^ <] +) * (?: > (. *) < \ / \ 1 > | \ S + \ / >)$/
Chinese character range in Unicode encoding: / ^ [u4e00-u9fa5],{0,}$/
Regular expression matching Chinese characters: [\ u4e00-\u9fa5]
Regular expressions that match blank lines: \ n\s*\r
Regular expressions matching HTML Tags: < (\ s *?) [^ >] * >. *? | <. *? / >
Note: the above can only match parts, and there is still nothing to do with complex nested tags
Regular expression matching leading and trailing whitespace characters: ^ \ s*|\s*$
Note: it can be used to delete white space characters at the beginning and end of a line (including spaces, tabs, page breaks, etc.), which is a very useful expression
Regular expression matching Email address: \ w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w +)*
Note: form verification is very practical
Regular expression matching URL of web address: [a-zA-z]+://[^\s]*
Match domestic phone number: \ d{3}-\d{8}|\d{4}-\d{7}
Note: the matching form is 0511-4405222 or 021-87888822
Match Tencent QQ number: [1-9] [0-9] {4,}
Note: Tencent QQ number starts from 10000
Encoding Chinese mainland postal code: [1-9]\d{5}(?!\d)
Explanation: Chinese mainland postal encoding is 6 digit.
Matching ID card: \ d{15}|\d{18}
Matching ip addresses: \ d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+
Write at the end
If you find any mistakes in the article or need to add more content, please leave a message!!!