summary:
PL/SQL(Procedural Language/SQL) is a special application development language of Oracle database. It is a programming language formed after the process expansion of the standard SQL language.
- PL/SQL Oracle extends SQL procedure.
- PL/SQL database programming
- Benefits: simple, efficient, flexible and practical
1. Grammar
- Basic syntax:
-- Basic grammar( declare,exception Can be omitted) declare -- Declaration, defining variables begin -- code exception --exception handling end;
- Instance: instance 1, define variable i, assign 'hello', output
declare i varchar2(20); begin i := 'Hello'; dbms_output.put_line('The output content is:' || i); end;
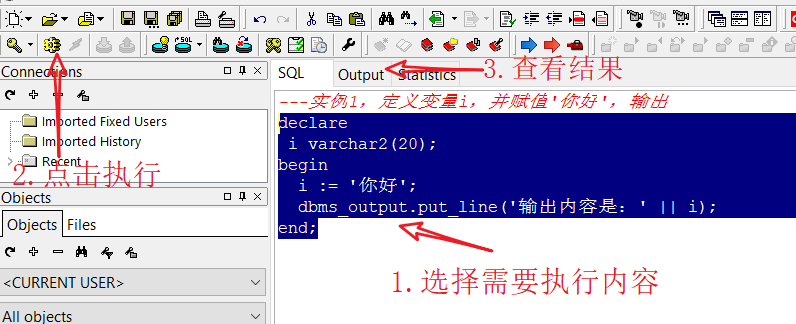
2. Entry case
-- PL/SQL Getting started exercise 1: printing“ welcome !!!" begin dbms_output.put_line('welcome !!!'); end; -- PL/SQL Getting started exercise 2: defining variables v_i ,And assign a value“ welcome !!!",Reprint variables -- The type of variable must support the length of assignment content declare v_i varchar2(40); begin v_i := 'welcome welcome !!!'; dbms_output.put_line(v_i); end;
3. Assignment + type
3.1 assignment into
-
Exercise 1: print the name of the owner
-- Exercise 1: print the name of the owner declare -- Declare variables to hold name Value of begin -- Execute query statement, get name And assign the variable -- Print variables end; -
realization
-- Exercise 1: print the name of the owner declare -- Declare variables to hold name Value of v_name varchar2(50); begin -- Execute query statement, get name And assign the variable select name into v_name from t_owners where id = 11; -- Print variables dbms_output.put_line(v_name); end;
3.2. Variable type% type
-
Exercise 2: print the owner name and declare the variable type
--Grammar Variable name table name. Column name% type; --Examples v_name towners.name%type;
-- Exercise 2: print owner name, variable type declare -- Declare variables to hold name Value of v_name t_owners.name%type; begin -- Execute query statement, get name And assign the variable select name into v_name from t_owners where id = 11; -- Print variables dbms_output.put_line(v_name); end;
3.3 variable type exercise
- Exercise 3: demand: calculate the water consumption amount of the current month for the user with No. 1 in the account.
- Required output: unit price, tonnage, amount, water consumption of last month, water consumption of this month
-- Exercise 3: demand: calculate the water consumption amount of the current month for the user with No. 1 in the account table. ---- Required output: unit price, tonnage, amount, water consumption of last month, water consumption of this month declare v_price number; --Accumulated water consumption of last month t_account.num0%type v_num0 number; --Accumulated water consumption of this month t_account.num1%type v_num1 number; --Usage t_account.usenum%type v_usenum number; --amount of money v_money number; -- Tonnage v_usenum2 number; begin -- Unit Price v_price := 3.45; -- Query data to obtain water consumption and amount select num0,num1,usenum,money into v_num0,v_num1,v_usenum,v_money from t_account where id = 1; -- Tons 19920 --> /1000 --> 19.920 --> 19.92 v_usenum2 := round(v_usenum / 1000 , 2 ); -- Printing dbms_output.put_line('Unit Price' || v_price || ',Tonnage'|| v_usenum2 ||',amount of money'|| v_money ||',Water consumption of last month'|| v_num0 ||',Water consumption of this month'|| v_num1); end;
3.4. Variable type% rowtype
-
Get all types of a row through% rowtype, which is equivalent to an object and holds a record
-
Declare variables
--Grammar Variable table name% rowtype; --Examples v_account t_account%rowtype;
-
assignment
--Single column select column name, column name 2,... into variable. Column name, variable. Column name 2,... From table name; --All select * into variable from table name;
-
-
Instance: Rewrite exercise 3: use% rowtype
-- Rewrite exercise 3: Using%rowtype declare -- Unit Price v_price number; -- Declare line variables v_account t_account%rowtype; begin -- Unit Price v_price := 3.45; -- Save one line select * into v_account from t_account where id = 1; -- Printing dbms_output.put_line('Unit Price' || v_price ||',amount of money'|| v_account.money ||',Water consumption of last month'|| v_account.num0 ||',Water consumption of this month'|| v_account.num1); end;
4. Abnormal
--Grammar declare begin --Normal code --Abnormal block exception when exception type then handle when exception type then handle .... end; --Common exception types: no_date_found, no data exception, query result is null too_many_rows, too many rows, query result greater than 1
-
Exercise 4: query the account table, all information with id 1, and print part - normal situation
-- exception handling -- Exercise 4: query the account table, id For 1 all information and print part declare v_account t_account%rowtype; begin --query select * into v_account from t_account where id = 1; --Printing dbms_output.put_line('Water consumption of last month' || v_account.num0 || 'Water consumption of this month' || v_account.num1); -- exception handling exception when no_data_found then dbms_output.put_line('No data found'); when too_many_rows then dbms_output.put_line('More than 1 query result'); end; -
Exercise 4: query the account table, all the information with id 1, and print the part - exception - no data
-- exception handling -- Exercise 4: query the account table, id For 1 all information and print part declare v_account t_account%rowtype; begin --query select * into v_account from t_account where id = 999; --Printing dbms_output.put_line('Water consumption of last month' || v_account.num0 || 'Water consumption of this month' || v_account.num1); -- exception handling exception when no_data_found then dbms_output.put_line('No data found'); when too_many_rows then dbms_output.put_line('More than 1 query result'); end; -
Exercise 4: query the account table, all the information with id 1, and print the part - exception - query multiple pieces of data
-- Exercise 4: query the account table, id For 1 all information and print part declare v_account t_account%rowtype; begin --query select * into v_account from t_account; --Printing dbms_output.put_line('Water consumption of last month' || v_account.num0 || 'Water consumption of this month' || v_account.num1); -- exception handling exception when no_data_found then dbms_output.put_line('No data found'); when too_many_rows then dbms_output.put_line('More than 1 query result'); end;
5. Judgment statement if
-
if syntax
if condition then elsif Condition 2 then els if Condition 3 then ... else end if; -
Example: set three levels of water charge: 2.45 yuan / ton for less than 5 tons, 3.45 yuan / ton for 5 tons to 10 tons, 4.45 yuan / ton for more than 10 tons, and calculate the step water charge according to the amount of water charge
-- Demand: set three levels of water charge below 5 tons 2.45 element/Tons 5 to 10 tons Part 3.45 element/Tons, over 10 tons 4.45 ,The step water charge is calculated according to the amount of water used. declare -- Define 3 water prices v_price1 number; v_price2 number; v_price3 number; -- Standing book record v_account t_account%rowtype; -- Usage(Tonnage) v_usenum2 number; -- amount of money v_money number; begin -- Determine water price v_price1 := 2.45; v_price2 := 3.45; v_price3 := 4.45; -- Query record select * into v_account from t_account where id = 4; -- Calculate usage v_usenum2 := round(v_account.usenum / 1000 , 2); -- Calculation of step water charge according to usage if v_usenum2 <= 5 then --- Less than 5 tons: Usage * 2.45 v_money := v_usenum2 * 2.45; elsif v_usenum2 <= 10 then --- Less than 10 tons: 5 * 2.45 + (Usage - 5) * 3.45 v_money := 5 * 2.45 + (v_usenum2 - 5) * 3.45; else --- More than 10 tons: 5 * 2.45 + 5 * 3.45 + (Usage - 10) * 4.45 v_money := 5 * 2.45 + 5 * 3.45 + (v_usenum2 - 10) * 4.45; end if; -- Print water charge dbms_output.put_line(v_money); end;
6. Cycle
6.1. Unconditional cycle
--grammar loop -- code -- End cycle exit; end loop;
- Lesson: output 100 numbers from 1
--Exercise: output 100 numbers from 1 declare v_i int := 1 ; begin loop dbms_output.put_line(v_i); -- accumulation v_i := v_i + 1; -- sign out if v_i > 100 then exit; end if; end loop; end;
6.2 while cycle
--grammar while condition loop --content end loop;
- Lesson exercise: 1-100 sum and print
-- Exercise: find 1-100 And print declare --Counter v_i int := 1; --Summation variable v_sum int := 0; begin while v_i <= 100 loop --Summation v_sum := v_sum + v_i; --accumulation v_i := v_i + 1; end loop; --Printing dbms_output.put_line(v_sum); end;
6.3 for cycle
-
grammar
for variable in Starting value..Termination value loop -- Circulatory body end loop; -
Exercise 1:
-- Exercise 1: print 1--100 number declare v_i int; begin for v_i in 1..100 loop dbms_output.put_line(v_i); end loop; end; -
Exercise 2:
-- Exercise 2: find 1-100 All even sum and print declare -- Count variable v_i int; -- Summation variable v_sum int := 0; begin for v_i in 1..100 loop -- mod() For redundancy if mod(v_i,2) = 0 then v_sum := v_sum + v_i; end if; end loop; dbms_output.put_line(v_sum); end; -
Exercise 3:99 multiplication table
-- Exercise 3:99 multiplication table --- Output content, wrap or not declare begin -- One line output dbms_output.put('abc'); -- Line feed output dbms_output.put_line('123'); end; -------- Common cycle declare v_i int; begin -- loop for v_i in 1..9 loop dbms_output.put_line(v_i); end loop; end; -------- Nested loop declare v_i int; v_j int; begin -- Nested loop for v_i in 1..9 loop -- Internal circulation for v_j in 1..9 loop dbms_output.put_line(v_i || v_j); end loop; end loop; end; -------99 multiplication table declare v_i int; v_j int; begin -- Nested loop for v_i in 1..9 loop -- Internal circulation for v_j in 1..v_i loop dbms_output.put(v_j || ' * ' || v_i || ' = ' || (v_i * v_j) ); dbms_output.put(' '); end loop; dbms_output.put_line(''); end loop; end;