DNFS is a new feature introduced by Oracle 11g to improve the IO performance of the system with NFS. Compared with system level NFS, DNFS reduces the consumption of network and IO transmission. The reasons for the low IO capacity of normal NFS are:
1. Low efficiency data transmission, multi link implementation is difficult;
2. The system's RPC stack IO is implemented in the form of queue, which limits the data sent to the TCP layer.
3. The IO transfer from Oracle instance to nfs client is inefficient.
Path for NFS and DNFS data transfer:
Ordinary NFS: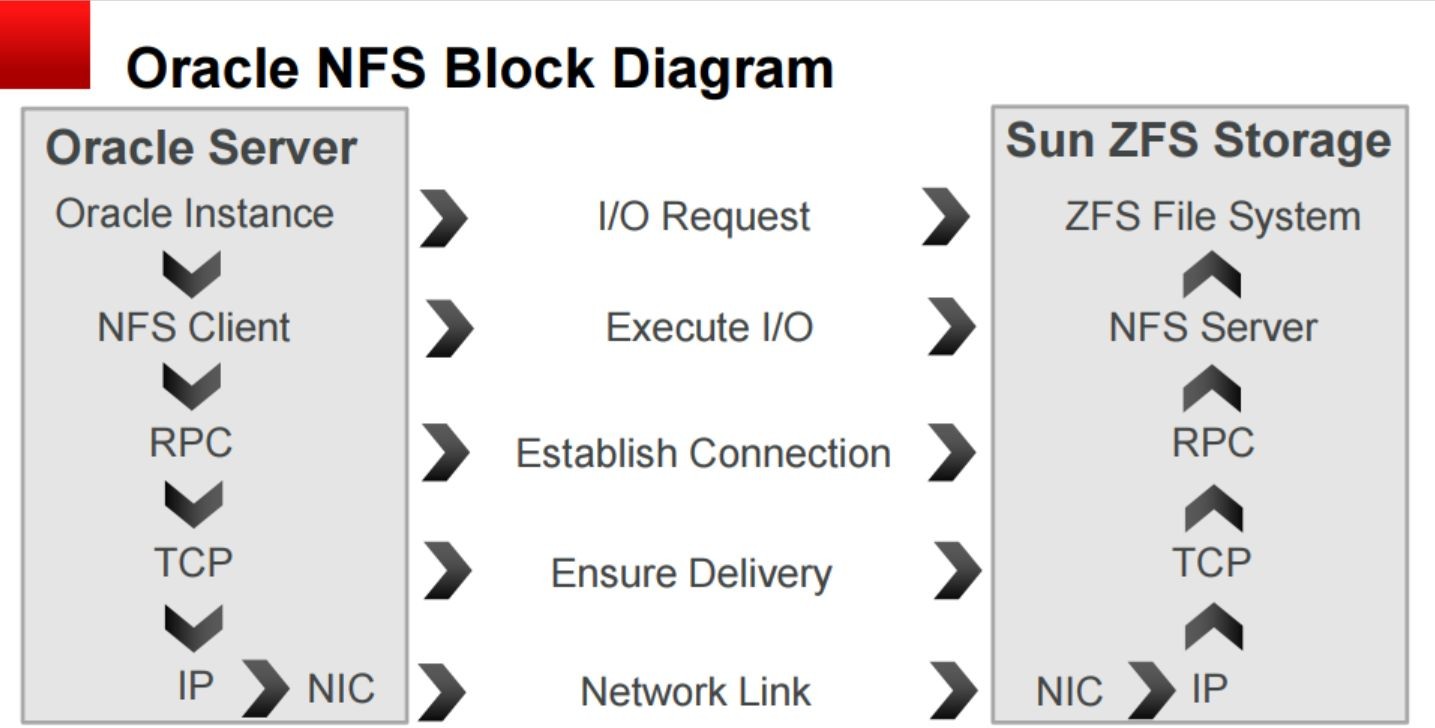
DNFS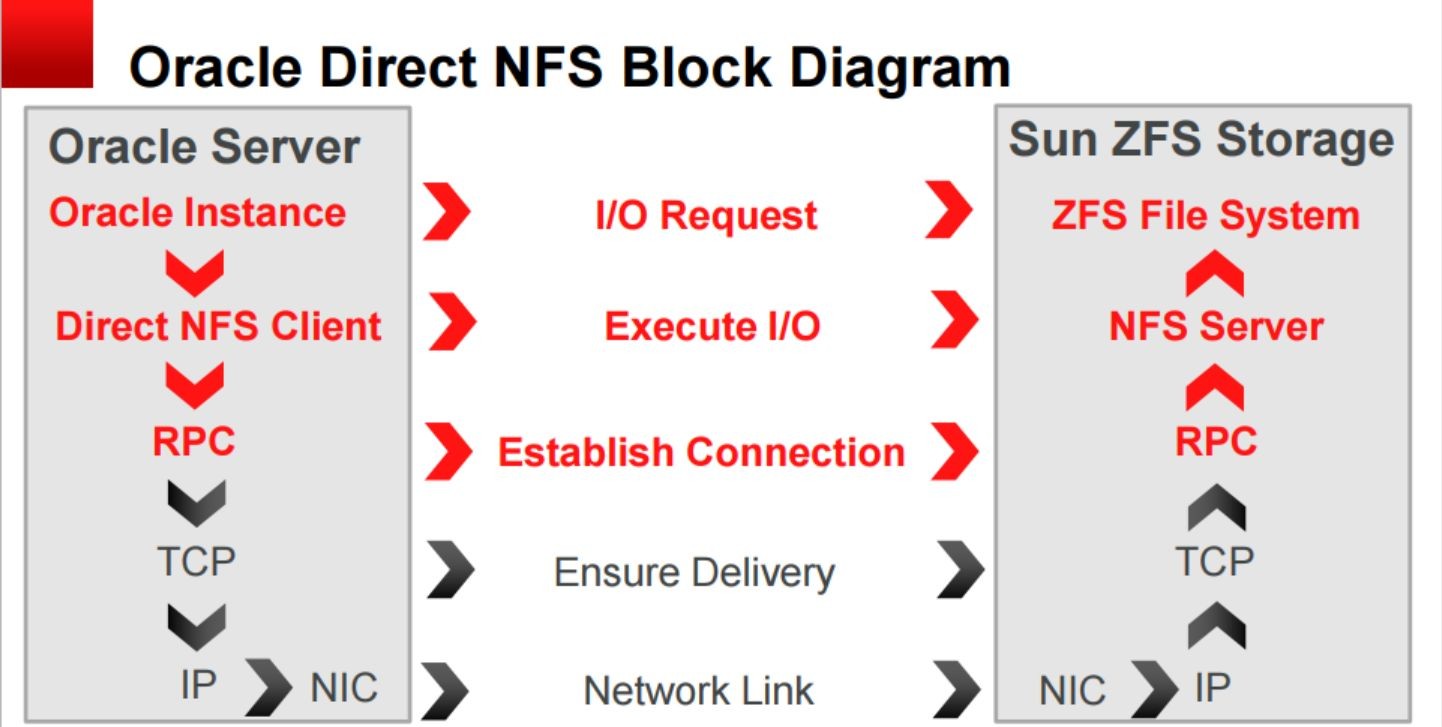
It can be seen that dnfs is less than nfs in the data transmission stage of TCP - > IP, and it connects directly through RPC.
Installation process:
Environmental Science NFS SERVER: 172.10.10.10 PROD2 NFS CLIENT: 172.10.10.20 PROD1
nfs Please refer to: https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E37670_01/E37355/html/ol_setupnfssvr_btrfs.html
1. Install software
PROD2#yum install nfs-utils -y
2. Configure SERVER
1)PROD2 Create shared directory on PROD2#mkdir -p /u01/nfs_torage PROD2#vi /etc/exports
2)modify exports PROD2#cat /etc/exports /u01/nfs_torage *(rw,sync,no_wdelay,insecure,insecure_locks,no_root_squash)
Mount options:
a.https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/install.112/e47689/post_inst_task.htm#LADBI1297
b.Mount Options for Oracle files for RAC databases and Clusterware when used with NFS on NAS devices (Doc ID 359515.1)
3)Startup service PROD2# service rpcbind start PROD2# service nfs start PROD2# service nfslock start PROD2# chkconfig rpcbind on PROD2# chkconfig nfs on PROD2# chkconfig nfslock on
4)Check configuration PROD2# exportfs -rv PROD2# showmount -e localhost
3. Configure client
1)Create mount path PROD1# mkdir -p /vol/nfs_oradta PROD1# chown -R oracle:oinstall /vol/nfs_oradata PROD1# chmod -R 755 /vol/nfs_oradata
2)Startup service PROD1# service rpcbind status PROD1# chkconfig rpcbind on PROD1# service restart rpcbind
3)View server information PROD1#showmount -e PROD2
4)Manual mount //Format: Mount - t NFS < nfs-server-ip >: < export-location > < local-mount-location > PROD1#mount -t nfs PROD2:/u01/nfs_storage /vol/nfs_oradata
5)Configure auto mount PROD1#cat /etc/fstab PROD2:/u01/nfs_storage /vol/nfs_oradata nfs rw,bg,hard,nointr,tcp,vers=3,timeo=300,rsize=32768,wsize=32768,actimeo=0 0 0 //perhaps PROD1#vi /etc/rc.local mount -o rw,bg,hard,nointr,rsize=32768,wsize=32768,tcp,vers=3,timeo=600,actimeo=0,suid PROD2:/u01/nfs_storage /vol/nfs_oradata
4. configure DNFS
1)DNFS configuration file When mounting, dnfs determines the mount point information by looking up the following files: $ORCLE_HOME/dbs/oranfstab /etc/orafnstab /etc/mtab The content format is as follows: Server:NFS server name Path:NFS server IP or host name Export: path to export from NFS server Mount: local mount point for NFS $vi /etc/oranfstab server:PROD2 path:172.10.10.10 export:/u01/nfs_storage mount:/vol/nfs_oradata
2)modify odm library $sqlplus / as sysdba sql>shutdown immediate; $cd $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib $make -f ins_rdbms.mk dnfs_on sql>startup
3)Create tablespace sql>create tablespace testnfs datfile '/u01/nfs_oradta/PROD1/testnfs01.dbf' size 100m;
4)inspect dnfs Is it effective? $grep NFS /u01/ap/oracle/diag/rdbms/prod1/PROD1/trace/alert_PROD1.log
5. Views related to dsnfs
v$dnfs_servers; v$dnfs_files; v$dnfs_chanels; v$dnfs_tas;
6. disable dnfs
1).Delete tablespace, stop Library drop tablespace testnfs including contents andatfiles; shutdown imediate 2).Prohibit dnfs: cd $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib make -f ins_rdbms.mk dnfs_of 3).Start database startup 4).Delete related nfs To configure
Reference resources:
Step by Step - Configure Direct NFS Client (DNFS) on Linux (Doc ID 762374.1)