Oracle advanced query
Advanced query is widely used in database development. This paper introduces Oracle advanced query from three aspects: grouping query, multi table query and sub query.
Grouping query
Grouping query is to group according to certain rules. After grouping, data will be aggregated, and aggregation function is required. However, grouping is not necessary to use aggregation function. The grouping keyword is group by.
Common aggregation functions are: max(), min(), avg(), sum(), count()
The count function automatically ignores null values when using column names
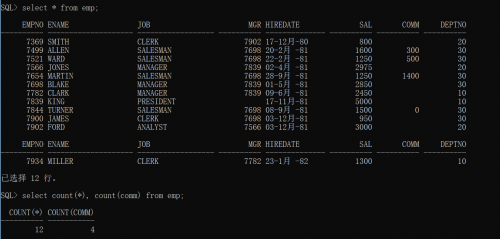
nvl function can prevent count from automatically ignoring null values. Its function is to return 0 when comm is empty. Because 0 is not empty, it will enter the total statistics.

group by subquery
In the select list, all columns not included in the aggregate function should be included in the group by clause.
Single column grouping
Find the average salary of each department, display the department number and the average salary of the Department.
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno order by deptno
Multi column grouping
Calculate the total salary of employees by department and position
select detpno,job,sum(sal) from emp group by deptno,job order by deptno
Filter grouping
Use of having clause
The difference between where and having
- Aggregate functions cannot be used in the where clause. Filter first and then group
- Aggregation functions can be used in the having clause to group first and then filter
Note: from the perspective of SQL optimization, try to use where, because where greatly reduces the number of grouping records and improves efficiency.
Seek departments with an average wage greater than 2000
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp where(avg(sal)) > 2000 group by deptno
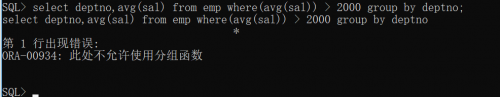
Aggregate functions cannot be used in the where clause, so an error is reported. Change to the having xxx clause.
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno having(avg(sal)) > 2000
Use order by in grouping queries
Calculate the average salary of each department, display the department number and the average salary of the Department, and arrange them in ascending order.
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno order by avg(sal)
You can also sort by column alias
select deptno,avg(sal) avgsal from emp group by deptno order by avgsal
You can also sort by column serial number. The average salary is column 2
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno order by 2
In descending order, add desc
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno order by 2 desc
Nesting of grouping functions
Find the maximum average wage of the Department
select max(avg(sal)) from emp group by deptno
group by statement enhancement
It is mainly used in the group by statement report function
For each department, install different positions, calculate the total salary, department summary and summary.
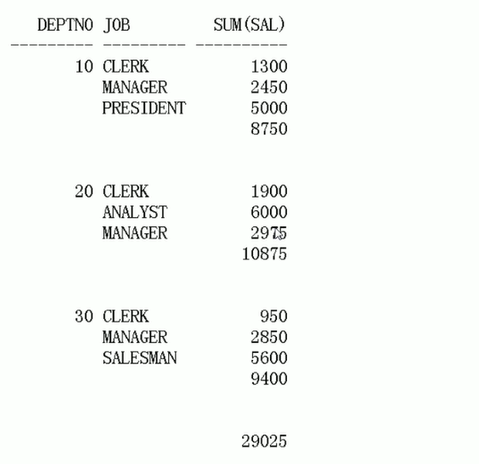
You can use the rollup function
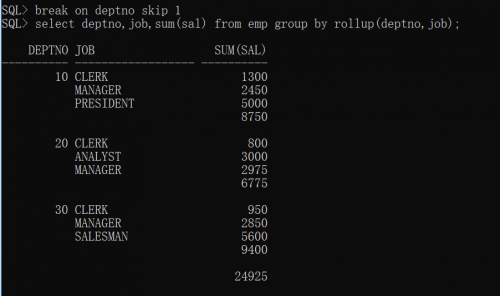
select deptno,job,sum(sal) from emp group by rollup(deptno,job)
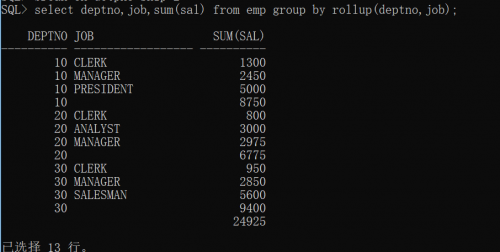
Set the display format again. break on deptno means that only one department number is displayed for the same department number, and skip 1 means that there is a blank line between different department numbers.
Improve report display
Add title, page number, etc
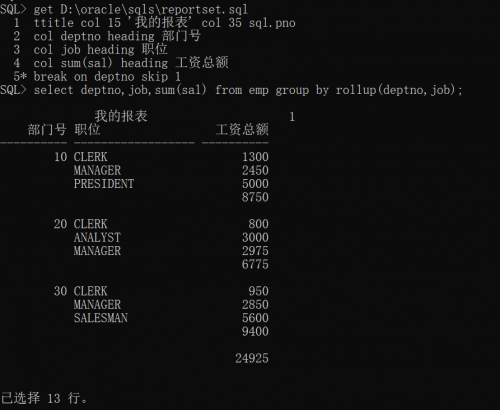
ttitle col 15 'my report' col 35 sql.pno
Set the title, and the empty 15 columns display my report, and then the empty 35 columns display the page number
col deptno heading department number
col job heading
col sum(sal) heading payroll
Set column headings in the above 3 rows
break on deptno skip 1
Set the display format. Only one department number is displayed for the same department number, and one line is blank between different department numbers
Save these settings to an sql file (pay attention to change to ANSI code, otherwise there will be garbled code and the settings will be invalid), and then read and execute through the get command. Execute the query statement again to get the following report. If there are multiple pages, you can set one page to display more rows for beautiful display. For example, set pagesize 100 to display 100 rows per page
multi-table query
The above examples all query data from a single table, and the following will explain how to query data from multiple tables.
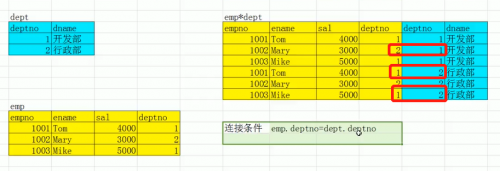
In order to avoid Cartesian sets, effective connection conditions can be added in where. Under the actual allowable environment, Cartesian complete sets should be avoided.
Equivalent connection
Example: query employee information. It is required to display: employee number, name, monthly salary and department name
You need to query the employee table and department table, and perform equivalent connection query through the department number, where xxx=xxx
select e.empno,e.ename,e.sal,d.dname from emp e,dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno
Unequal value connection
Example: query employee information and display employee number, name, monthly salary and salary level
You need to query the employee table and salary grade table, and perform unequal connection query through the upper and lower limits of salary grade. where xxx between xxx and xxx, note: small values precede between and large values follow between
select e.empno,e.ename,e.sal,s.grade from emp e,salgrade s where e.sal between s.losal and s.hisal
External connection
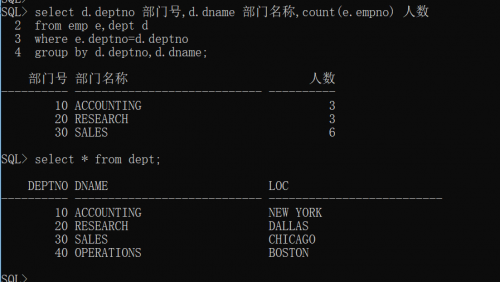
Example: count the number of employees by department. It is required to display: department number, department name and number of employees
You need to query department table and employee table
The following is a query through equivalent connection. Although there is no problem with the total number of people, one department is missing because there are no employees in one department.
select d.deptno Department number,d.dname Department name,count(e.empno) Number of people from emp e,dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno group by d.deptno,d.dname
External connections are generally realized through joins. You can understand various join usages of SQL in one diagram.
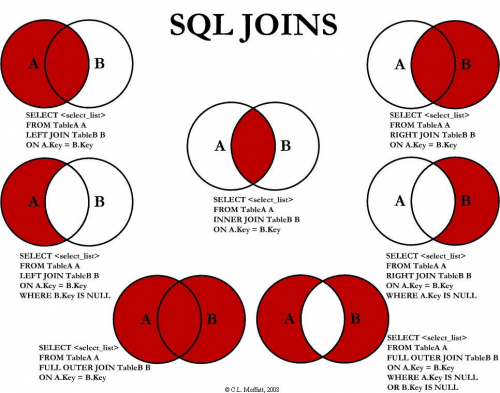
Re implement the sample functionality using the join statement
select d.deptno Department number,d.dname Department name,count(e.empno) Number of people from dept d left join emp e on d.deptno=e.deptno group by d.deptno,d.dname
Self connection
Example: query employee name and employee's boss name
Core: treat the same table as multiple tables by alias
select e.ename Employee name,b.ename Boss name from emp e, emp b where e.mgr=b.empno
This method will produce Cartesian sets, which is not suitable for large table queries. Hierarchical queries can be used to solve them. connect by xxx start with xxx
level is a pseudo column provided by hierarchical query. This pseudo column can be queried only when it is displayed and used.
select level,empno,ename,sal,mgr from emp connect by prior empno=mgr start with mgr is null order by 1
Subquery
Parentheses in subquery syntax
There must be small brackets and the writing style should be clear, as shown in the figure below:
Example: query employees with higher wages than FORD
select * from emp where sal > (select sal from emp where ename='FORD')
Locations where subqueries can be used
select,from,where,having
The sub query at the select position can only be a single line sub query, that is, only one result can be returned
select empno,ename,sal,(select job from emp where empno='7839') job from emp
Subquery of having location
Example: find the department number and its average salary whose average Department salary is greater than the maximum salary of department No. 30
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno having avg(sal) > (select max(sal) from emp where deptno=30)
Subquery from location
Query results can also be used as tables
select * from (select empno,ename,sal from emp)
Add 1 column of annual salary and use sal*12 to get the annual salary
select * from (select empno,ename,sal,sal*12 annsal from emp)
The main query and sub query can not be the same table
Example: query employee information whose department name is SALES
How to use subquery:
select * from emp where deptno=(select deptno from dept where dname='SALES')
How to use multi table query:
select e.* from emp e, dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno and d.dname='SALES'
Sorting of subqueries
Generally, sorting is not used in sub queries; However, in the Top-N analysis problem, sub queries must be sorted
Example: find the top three with the highest salary in the employee table, in the following format:

rownum, row number, pseudo column automatically assigned by oracle to the table.
- Line numbers are always generated in the default order
- Line number can only use <, < =; Cannot use >, >=
select rownum,empno,ename,sal from (select * from emp order by sal desc) where rownum<=3
Subquery execution order
Generally, the sub query is executed first, and then the main query is executed; Single phase subquery exception.
Example of related sub query: find employees whose salary in the employee table is greater than the average salary of the Department
select empno,ename,sal,(select avg(sal) from emp where deptno=e.deptno) avgsal from emp e where sal > (select avg(sal) from emp where deptno=e.deptno)
Single row subquery and multi row subquery
A single line sub query returns a result. Only single line operators can be used;
A multi row subquery returns multiple results. Only multi row operators can be used.
Single line operator:
| Operator | meaning |
|---|---|
| = | be equal to |
| > | greater than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| < | less than |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| <> | Not equal to |
Multiline operator:
| Operator | meaning |
|---|---|
| in | Equal to any one in the list |
| any | And any value returned by the subquery |
| all | Compare with the left and right values returned by subquery |
Single line sub query example 1:
To query employee information, please:
The position is the same as that of 7566 employees, and the salary is greater than that of 7782 employees
select * from emp where job=(select job from emp where empno=7566) and sal >(select sal from emp where empno=7782)
Single line sub query example 2:
Query the department number and the minimum wage of the Department whose minimum wage is greater than the minimum wage of No. 20 department
select deptno,min(sal) from emp group by deptno having min(sal) > (select min(sal) from emp where deptno=20)
Example of multiline subquery:
Query employee information whose department names are SALES and ACCOUNTING
How to use multi row subqueries:
select * from emp where deptno in (select deptno from dept where dname='SALES' or dname='ACCOUNTING')
How to use multi table query:
select e.* from emp e, dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno and (d.dname='SALES' or d.dname='ACCOUNTING')
Null value problem in subquery
Query employees who are not the boss
Note: do not use not in when the subquery contains null values.
a not in (10,20,null)
a != 10 and a != 20 and a != null, a != null never holds, so the entire expression always returns false.
You can filter out null values in the subquery and then use not in.
select * from emp where empno not in (select mgr from emp where mgr is not null)