Experiment 1 command interpreter
Experimental content
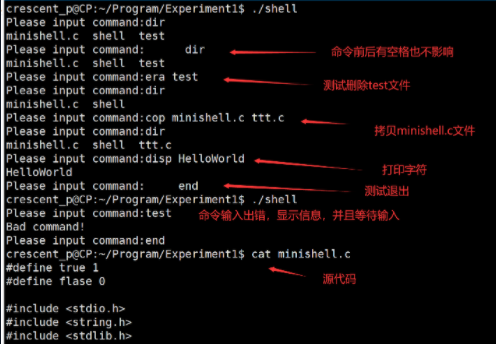
Write a micro command interpreter minishell.c in C language, which can receive and interpret the following commands:
(1) dir lists the current directory
(2) cop file1 file2 copy files
(3) era filename delete file
(4) disp string display string
(5) end end, exit
requirement:
(1) Check the validity of the command. If there is an error, display the error message and wait for re-entry;
(2) A space before and after the command indicates a legal command.
Experimental preparation
- gets() reads the string until the end of carriage return, but does not include carriage return
- strcspn(str1,str2) returns a string beginning with str1 that does not contain str2
- strncpy(str1,str2,n) copies the first n str2 strings into str1
- strcmp(str1,str2) compares str1 and str2
- Return value is less than 0, STR1 < STR2
- Equal to zero str1 == str2
- Greater than zero STR1 > STR2
- system(command) execute command
Sample program
#define true 1
#define false 0
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
char cmdl[80];
char *scwt[] = {"exit","dir","time"};
static int cmdnum = 3; // Number of commands available
char cmd[80];
int j,n;
while(true){
printf("Please input command:");
gets(cmdl); // Take command line input
n = strcspn(cmdl," ");// Fetch command part
if(n > 0 || strlen(cmdl) > 0){
strncpy(cmd,cmdl,n);
// Composition string
cmd[n] = '\0';
for(j = 0;j < cmdnum;j++){
if(strcmp(cmdl,scwt[j]) == 0) break;
}
if(j == 0) exit(0);
if(j < cmdnum){
system(cmdl);
continue;
}
printf("Bad command!\n");
}
}
}
Experimental code
Don't let it out for the time being
Experiment 2 process management
Experimental content
1. Process creation
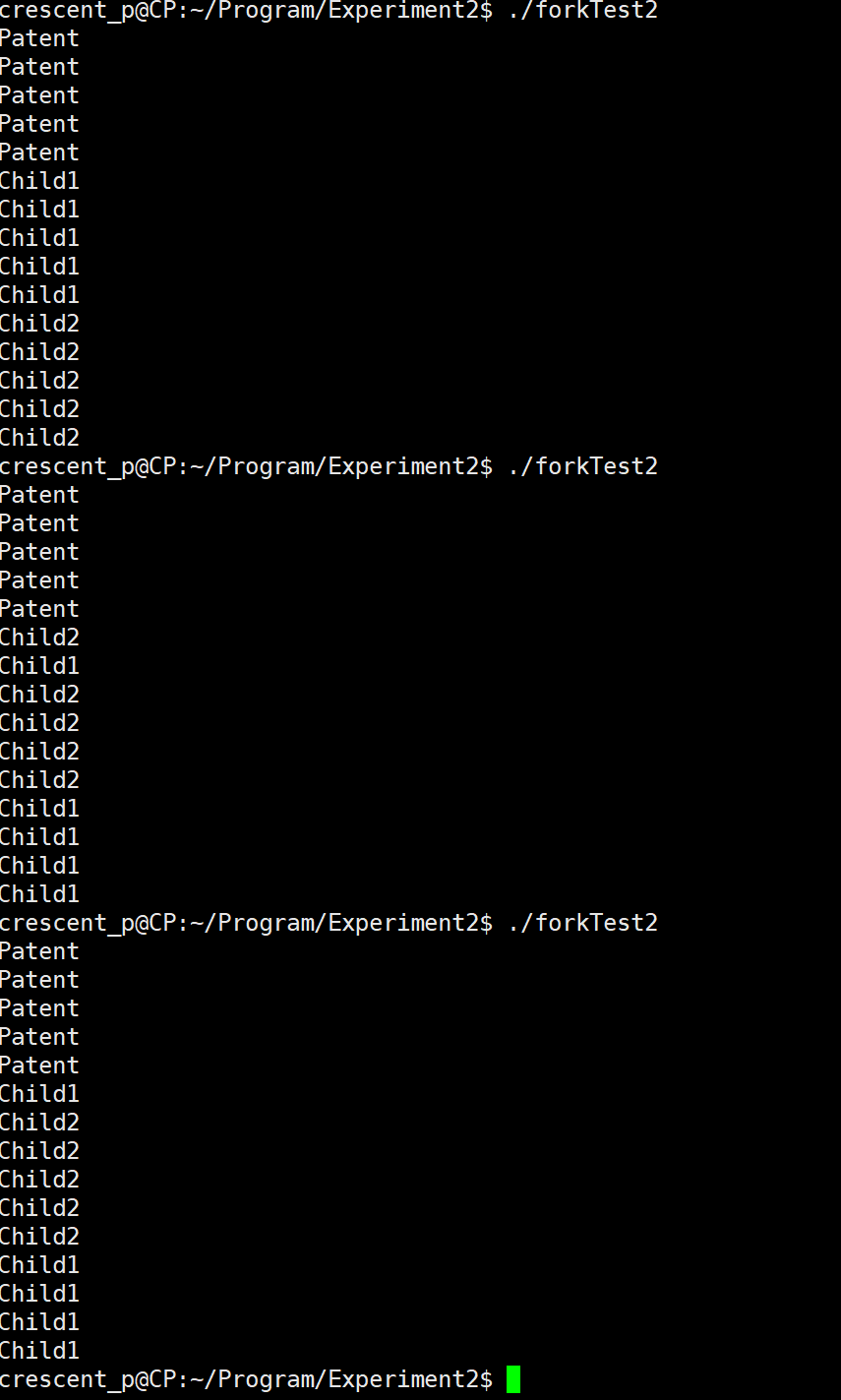
Write a program that uses the system call fork() to create two sub processes. Let the Parent process display the string 'Parent:'; The two subprocesses display the strings' Child1: 'and' Child2: 'respectively. Run this program several times, observe the results displayed on the screen, and analyze the causes.
2. Process control
Modify the written program, output a sentence repeated many times, observe the results displayed on the screen when the program is executed, and analyze the reasons.
If the system call lockf() is used to lock each process in the program, the mutual exclusion between processes can be realized, the results displayed on the screen can be observed, and the causes can be analyzed.
Experimental preparation content and sample program
fork test
Function description of fork:
- fork() creates a new process by copying the process. A child process is similar to a copy of the current process, but:
- The child process has its own unique process ID, and the PID of this process is different from that of any process
- The parent process ID of the child process is equal to the process ID of the parent process
- Return value:
- If successful, return the PID of the child process in the parent process and 0 in the child process
- Failed, returned - 1 in the parent process, no child process was created
crescent_p@CP:~/Program/Experiment2$ gcc -o fork1 forkTest1.c crescent_p@CP:~/Program/Experiment2$ ./fork1 fork test fork test
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
fork();
printf("fork test\n");
return 0;
}
Analysis: why is it output twice?
- A process is created at the beginning of the program
- When the process fork s, a child process is created
- The code of the child process is a copy of the code of the parent process
- The code execution progress of the child process is consistent with that of the parent process when creating the child process
Test 2:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
// Parent process
if(pid > 0){
printf("I am father\n");
}
if(pid == 0){
printf("I an son\n");
}
if(pid < 0){
printf("fork error\n");
}
printf("main over\n");
return 0;
}
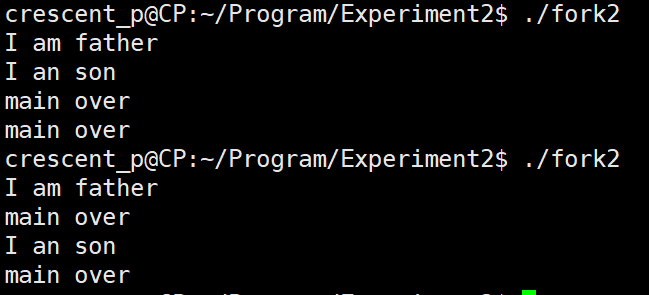
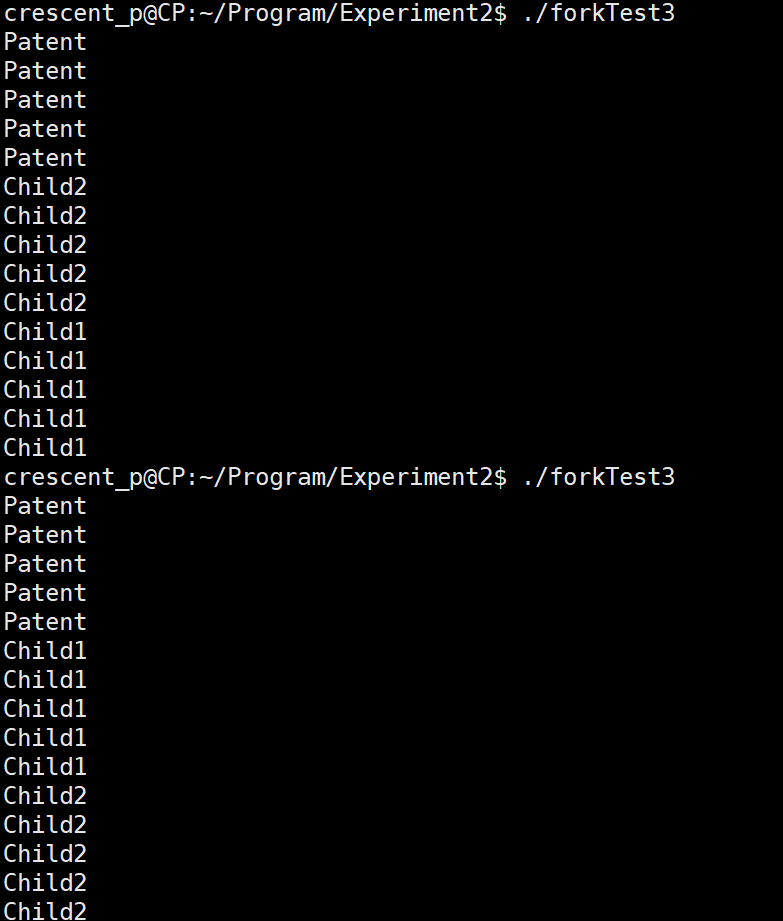
Why the analysis results are different:
- Why is there son and father again?
- In the parent process, fork() returns the PID of the child process, which is greater than 0, so the first if will be executed
- In the child process, fork() returns the PID of the child process, equal to 0, so the second if will be executed
- Why does the result of executing this executable file twice differ?
- For the asynchrony of processes, we set the parent process as p1 and the child process as p2
- First execution:
- After p1 executes the first if, it is p2's turn to run the processor
- Second execution:
- After p1 is executed, it is p2's turn to the processor
Test 3:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
printf("Execute to fork Function whose process was %d,Its parent process is %d\n",getpid(),getppid());
sleep(1);
fork();
printf("This process id by:%d,Its parent process is%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
return 0;
}
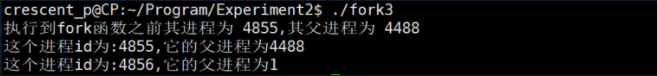
Test 4:
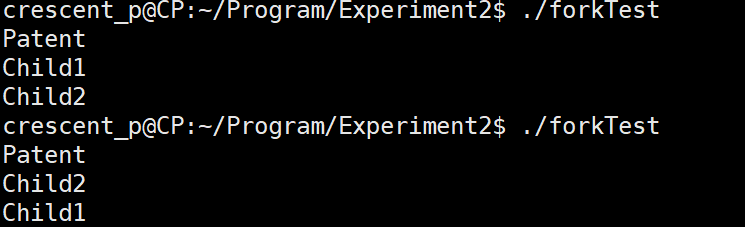
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
pid_t p1,p2;
while((p1 = fork()) == -1);
// Subprocess
if(p1 == 0) {
puts("b");
}
else {
puts("a");
}
return 0;
}
Experimental code
Don't let it out for the time being
Experiment 3 communication between processes
pipeline communication
Experimental preparation content and sample program
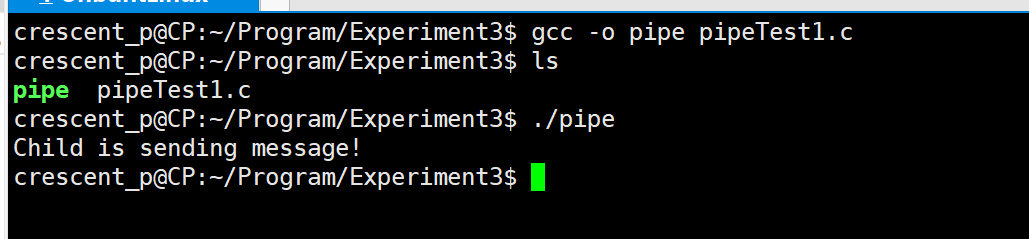
Test pipe():
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(){
pid_t pid;
int fd[2];
char buf[50],s[50];
// Created pipe, half duplex
pipe(fd);
while((pid = fork()) == -1);
// Subprocess
if(pid == 0){
sprintf(buf,"Child is sending message!");
// fd[1] write pipeline
write(fd[1],buf,50);
// exit also writes the contents of the file buffer back to the file before exiting
// Exiting the process is actually a zombie process
exit(0);
}else{
// Once a process calls wait, it blocks itself immediately
// wait automatically analyzes whether a child process of the current process has exited
// If it finds such a sub process that has become a zombie
// wait will collect the information of the child process, destroy it completely and return
// If such a child process is not found, the wait will block here until one appears.
wait(0);
// fd[0] reads the pipeline and reads the contents of the pipeline into s
read(fd[0],s,50);
printf("%s\n",s);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
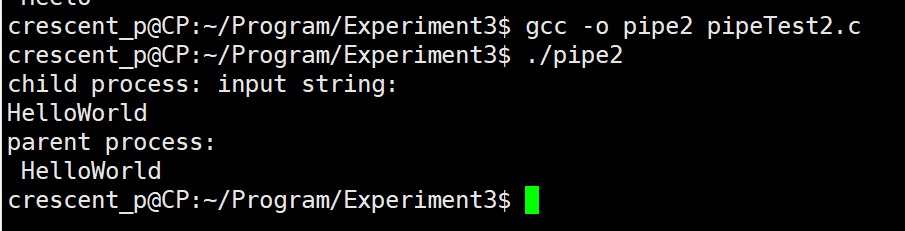
A pipe
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
// Channel array
int fd[2];
pid_t pid;
// Be sure to create the pipeline first, otherwise the child process out of fork will also create the key pipeline
pipe(fd);
while((pid = fork()) == -1);
// Subprocess
if(pid == 0){
char str[100] = {0};
printf("child process: input string:\n");
scanf("%s",str);
// Write to pipe
write(fd[1],str,strlen(str));
exit(0);
// Parent process
}else{
wait(0);
char buf[30] = {0};
// Read from pipe to buf
read(fd[0],buf,30);
printf("parent process:\n %s\n",buf);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
Dual channel:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
// Two pipes
int fd1[2],fd2[2];
// Create two channels
pipe(fd1),pipe(fd2);
pid_t pid;
while((pid = fork()) != -1);
// Subprocess
if(pid == 0){
char read_buf1[100] = {0};
char write_buf1[100] = {0};
printf("child process write:\n")
scanf("%s",write_buf1);
// write in
write(fd1[1],write_buf1,strlen(write_buf1));
// dormancy
sleep(10);
// Read in
read(fd2[0],read_buf1,100);
printf("child process read:\n %s\n",read_buf1);
exit(0);
// Parent process
}else{
sleep(5);
char read_buf2[100] = {0};
char write_buf2[100] = {0};
read(fd1[0],read_buf2,100);
printf("parent process read:\n %s\n",read_buf2);
printf("parent process write:\n")
scanf("%s",write_buf2);
// write in
write(fd2[1],write_buf2,strlen(write_buf2));
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
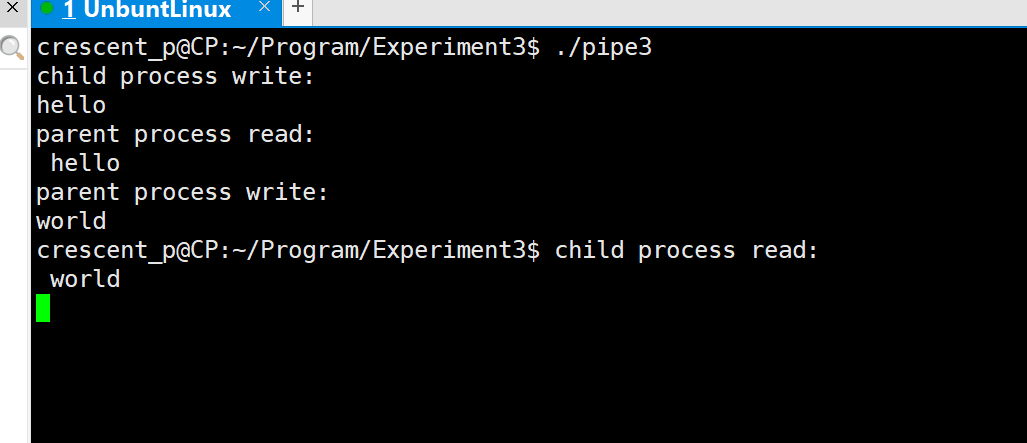
Experimental code
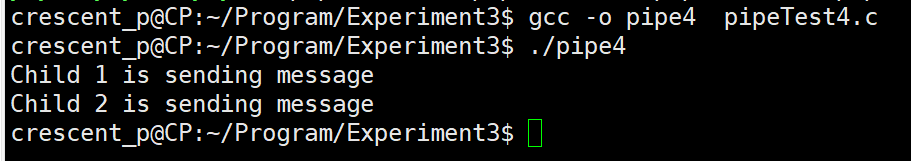
Don't let it out for the time being
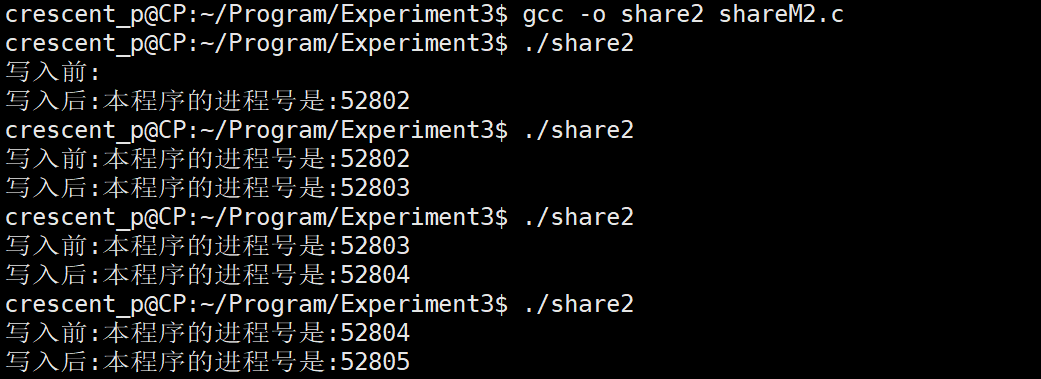
Shared memory
Experimental preparation content and sample program
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
// Shared memory identifier
int shmid;
// Create shared memory
if((shmid = shmget((key_t)0x5005,1024,0666|IPC_CREAT)) == -1){
printf("shmat(0x5005) failed\n");
return -1;
}
// Pointer to shared memory
char *ptext = 0;
// Connect the shared memory to the address space of the current process, and point to it by ptext
ptext = (char *)shmat(shmid,0,0);
// Operating the ptext pointer of this program is to operate the shared memory
printf("Before writing:%s\n",ptext);
sprintf(ptext,"The process number of this program is:%d",getpid());
printf("After writing:%s\n",ptext);
// Separates shared memory from the current process
shmdt(shmid);
// Delete shared memory
if(shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,0) == -1){
printf("shmctl(0x5005) failed\n");
return -1;
}
}
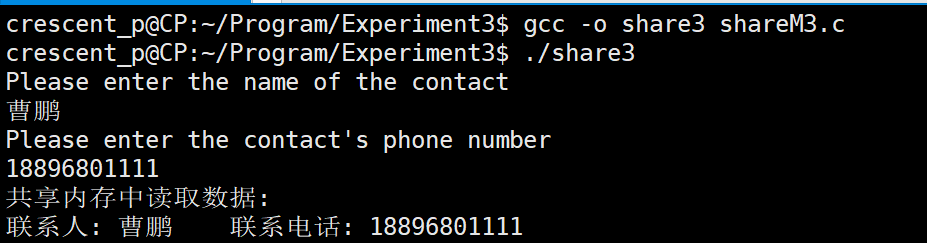
Experimental code
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
// Shared memory identifier
int shmid;
// Create shared memory
if((shmid = shmget((key_t)0x5005,1024,0666|IPC_CREAT)) == -1){
printf("shmat(0x5005) failed\n");
return -1;
}
// Pointer to shared memory
char *ptext = 0;
// Connect the shared memory to the address space of the current process, and point to it by ptext
ptext = (char *)shmat(shmid,0,0);
printf("Please enter the name of the contact\n");
char name[50];
scanf("%s",name);
printf("Please enter the contact's phone number\n");
long long tel;
scanf("%lld",&tel);
// Operating the ptext pointer of this program is to operate the shared memory
// Send message to shared memory
sprintf(ptext,"contacts: %s\t contact number: %lld\n",name,tel);
// Read from shared memory
printf("Read data from shared memory:\n%s\n",ptext);
// Separates shared memory from the current process
shmdt(ptext);
// Delete shared memory
if(shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,0) == -1){
printf("shmctl(0x5005) failed\n");
return -1;
}
}
Message queue
Experimental preparation content and sample program
message.h
#ifndef MESSAGE_H
#define MESSAGE_H
struct mymsgbuf
{
long mtype;
char mtext[256];
};
#endif
msg_server.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include "message.h"
int msqid = -1;
// Soft terminal
void sig_handle(int signo){
if(msqid != -1) msgctl(msqid,IPC_RMID,NULL); // delete
printf("server quit...\n");
exit(0);
}
int main(){
struct mymsgbuf msgbuf;
int left,right;
char c;
int length;
if((msqid = msgget(999,0666)) != -1){
msgctl(msqid,IPC_RMID,NULL); // delete
}
if((msqid = msgget(999,IPC_CREAT|0666)) == -1 ){
printf("error:getmsg\n");
exit(1);
}
signal(SIGINT,sig_handle); // Register soft interrupt
for(;;){
if(msgrcv(msqid,&msgbuf,256,1L,0) == -1){
printf("error:msgrcv\n");
exit(1);
}
length = strlen(msgbuf.mtext);
left = 0;
right = length - 1;
while (left < right)
{
c = msgbuf.mtext[left];
msgbuf.mtext[left] = msgbuf.mtext[right];
msgbuf.mtext[right] = c;
left++;
right--;
}
msgbuf.mtext[length] = '\0';
msgbuf.mtype = 2; // Change type to 2
if(msgsnd(msqid,&msgbuf,256,0) == -1){
printf("error:msgsnd");
exit(1);
}
}
msgctl(msqid,IPC_RMID,NULL);
exit(0);
}
msg_client.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include "message.h"
int main(){
struct mymsgbuf msgbuf;
int msqid;
if((msqid = msgget(999,0666)) == -1){
printf("Server is not running\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("Input a line:");
scanf("%s",msgbuf.mtext);
msgbuf.mtype = 1;
if(msgsnd(msqid,&msgbuf,256,0)==-1){
printf("error:msgsnd\n");
exit(1);
}
if(msgrcv(msqid,&msgbuf,256,2L,0) == -1){
printf("error:msgrcv\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("The reversed line is :%s\n",msgbuf.mtext);
exit(0);
}


msgsend.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// Message types, enumerating
enum MT{MI=1,MD,MS,MSTU,MEMP};
#define QUIT 0
#define MSG_MAX_LEN 1024
#define NAME_LEN 48
typedef struct Msg{
int msgtype; //Type of message
char msg[MSG_MAX_LEN]; // Content of message
}Msg;
typedef struct Stu{
int id;
char name[NAME_LEN];
int s[3]; // Three grades
}Stu;
typedef struct Emp
{
int id;
char name[NAME_LEN];
float salary;
}Emp;
void menu(void){
printf("***Message queue sending test interface***\n");
printf("*** %d.int Type of data\n",MI);
printf("*** %d.double Type of data\n",MD);
printf("*** %d.character string\n",MS);
printf("*** %d.Student information\n",MSTU);
printf("*** %d.Employee information\n",MEMP);
printf("*** %d.sign out\n",QUIT);
printf(">>>");
}
size_t readInt(Msg *msg){
// Sets the type of message
msg->msgtype = MI;
printf("input integer:");
// Read the message into the msg attribute of the message structure
scanf("%d",(int*)msg->msg);
return sizeof(int);
}
size_t readDouble(Msg *msg){
msg->msgtype = MD;
printf("input double:");
scanf("%lf",(double*)msg->msg);
return sizeof(double);
}
size_t readString(Msg *msg){
msg->msgtype = MS;
printf("input string:");
// Read wrap
scanf("%*c");
gets(msg->msg); // gets is not safe
// Add \ 0
return strlen(msg->msg)+1;
}
size_t readStu(Msg *msg){
msg->msgtype = MSTU;
// Strong rotation
Stu *pstu = (Stu*)msg->msg;
printf("input stu's id:");
scanf("%d",&pstu->id);
printf("input stu's name:");
scanf("%s",pstu->name);
printf("input three score:");
scanf("%d %d %d",&pstu->s[0],&pstu->s[1],&pstu->s[2]);
return sizeof(Stu);
}
size_t readEmp(Msg *msg){
msg->msgtype = MEMP;
Emp *pe = (Emp*)msg->msg;
printf("input emp's id:");
scanf("%d",&pe->id);
printf("input emp's name:");
scanf("%s",pe->name);
printf("input emp's salary:");
scanf("%f",&pe->salary);
return sizeof(Emp);
}
int main(){
key_t keyid = ftok(".",250);
if(keyid == -1){
perror("ftok");
return -1;
}
// Create message queue
int msgid = msgget(keyid,IPC_CREAT|0666);
if(msgid == -1){
perror("msgget");
return -1;
}
// Create message
Msg msg = {};
bool run = true;
size_t msgsz = 0;
while(run){
menu();
int opt = 0;
scanf("%d",&opt);
switch (opt)
{
case MI:msgsz = readInt(&msg);break;
case MD:msgsz = readDouble(&msg);break;
case MS:msgsz = readString(&msg);break;
case MSTU:msgsz = readStu(&msg);break;
case MEMP:msgsz = readEmp(&msg);break;
case QUIT:run = false;break;
default:
printf("error operation!\n");
}
// msgsz is the length of the message, excluding the length of the message type
int ret = msgsnd(msgid,&msg,msgsz,0); //0: blocking IPC_NOWAIT is not blocked
if(ret == -1){
perror("msgend");
run = false;
}
}
return 0;
}
msgrecive.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// Message types, enumerating
enum MT{MI=1,MD,MS,MSTU,MEMP,FIRST,ABSL};
#define QUIT 0
#define MSG_MAX_LEN 1024
#define NAME_LEN 48
typedef struct Msg{
int msgtype; //Type of message
char msg[MSG_MAX_LEN]; // Content of message
}Msg;
typedef struct Stu{
int id;
char name[NAME_LEN];
int s[3]; // Three grades
}Stu;
typedef struct Emp
{
int id;
char name[NAME_LEN];
float salary;
}Emp;
void menu(void){
printf("***Message queue acceptance test interface***\n");
printf("*** %d.int Type of data\n",MI);
printf("*** %d.double Type of data\n",MD);
printf("*** %d.character string\n",MS);
printf("*** %d.Student information\n",MSTU);
printf("*** %d.Employee information\n",MEMP);
printf("*** %d.Accept the first message \n",FIRST);
printf("*** %d.Accepts messages whose specified message is less than the minimum absolute value \n",ABSL);
printf("*** %d.sign out\n",QUIT);
printf(">>>");
}
void showMsg(Msg *msg){
switch (msg->msgtype)
{
case MI:printf("recv:%d\n",*(int*)msg->msg);break;
case MD:printf("recv:%f\n",*(double*)msg->msg);break;
case MS:printf("recv:%s\n",msg->msg);break;
case MSTU:{
Stu *ps = (Stu *)msg->msg;
printf("recv:%d %s %d %d %d\n",ps->id,ps->name,ps->s[0],ps->s[1],ps->s[2]);
break;
}
case MEMP:{
Emp *pe = (Emp *)msg->msg;
printf("recv:%d %s %f\n",pe->id,pe->name,pe->salary);
break;
}
}
}
int main(){
key_t keyid = ftok(".",250);
if(keyid == -1){
perror("ftok");
return -1;
}
// Create message queue
int msgid = msgget(keyid,IPC_CREAT|0666);
if(msgid == -1){
perror("msgget");
return -1;
}
// Create message
Msg msg = {};
bool run = true;
size_t msgsz = 0;
// Type of message read
int msgtype = 0;
while(run){
menu();
int opt = 0;
scanf("%d",&opt);
if(opt >= MI && opt <=MEMP){
msgtype = opt;
}else if(opt == FIRST){
msgtype = 0;
}else if(opt == ABSL){
printf("input masgtype(<0):");
scanf("%d",&msgtype);
if(msgtype > 0) msgtype *= -1;
}else if(opt == 0){
run = false;
break;
}
int ret = msgrcv(msgid,&msg,MSG_MAX_LEN-1,msgtype,IPC_NOWAIT);
if(ret == -1){
if(errno == EAGAIN){
printf("no this type message");
}else{
perror("msgend");
run = false;
}
}else{
// Display message content
showMsg(&msg);
}
}
return 0;
}
Experimental code
Don't let it out for the time being