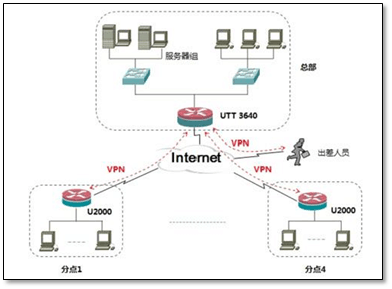
Service concept:
Virtual private network, in fact, is to open up a virtual private line in the network
Application classification:
1. Host remote access * * * service
2. Services between enterprise networks
3. Services between IDC rooms of Internet companies
Transmission data protocol mode:
Establishment between PPTP terminal and terminal
L2TP: layer 2 Tunneling Protocol L2TP can provide tunnel validation, but not PPTP does not support tunnel validation
Special encapsulation technology for IPsec to guarantee the encryption characteristics of data packets
SSL guarantees that the data packet encryption communication mode encrypts the data information (public key certificate private key key)
Principle of service architecture:
By using virtual private network, the external network host can obtain the internal network address information in the architecture, and realize the data transmission by using the internal network address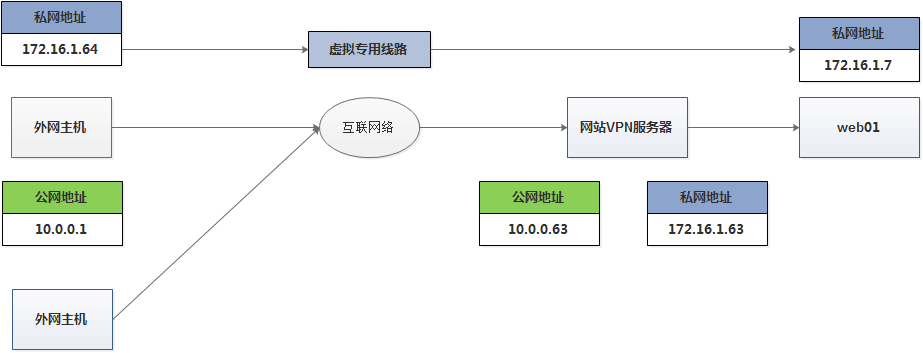
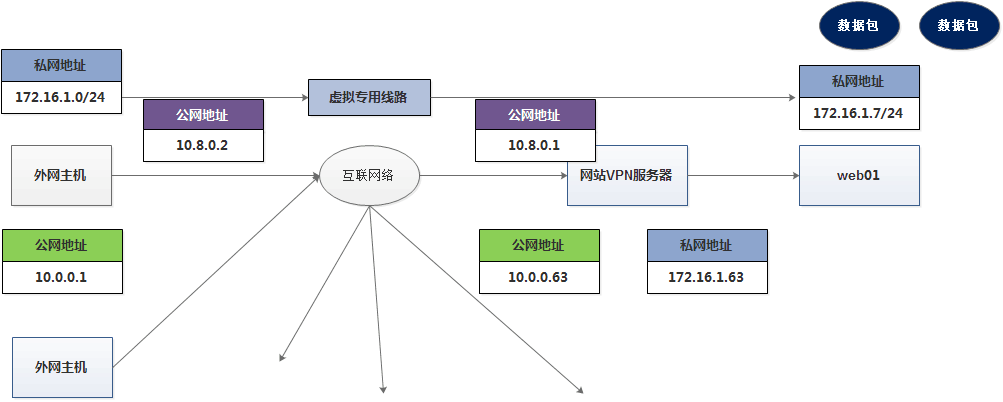
Service architecture environment
windows host external network host 10.0.0.1 (analog public network address)
v*nserver host 10.0.0.63 (analog public network address) 172.16.1.41 (analog private network address)
Web01 172.16.1.7 (analog private network address)
PS: ensure that the time of each host is properly synchronized
Service deployment process
The first process: Download and install the required software programs
yum install -y openv*n easy-rsa
open vipne: service package
Easy RSA: can be used to generate Certificate (public key) and secret key information = = similar to SSH keygen, which generates private key and public key information
The second process: create the certificate and key information required by the server
cp -r /usr/share/easy-rsa/ /etc/openv*n/ cp /usr/share/doc/easy-rsa-3.0.6/vars.example /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/vars --- Enterprise company information record file cd /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/
./easyrsa init-pki --- Create a directory environment for saving certificates and secret key information Your newly created PKI dir is: /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki
# Create server ca certificate?? Public key? ./easyrsa build-ca nopass /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/ca.crt
# Create server certificate similar to server public key and private key ./easyrsa gen-req openv*n nopass /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/openv*n.key --- Generate secret key information ./easyrsa sign server openv*n /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/issued/openv*n.crt --- Generate certificate file information
#Generate Diffie Hellman data file . / easyrsa Gen DH -- generate key exchange file /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/dh.pem
========================================================= //Summary: after the above operations are completed, the following file information is generated cp /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/ca.crt /etc/openv*n/server cp /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/openv*n.key /etc/openv*n/server cp /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/issued/openv*n.crt /etc/openv*n/server cp /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/dh.pem /etc/openv*n/server =========================================================
The third process: writing an open configuration file
cp /usr/share/doc/openvn-2.4.8/sample/sample-config-files/server.conf /etc/openvn/
vim /etc/openvn/server.conf
[root@v*n openv*n]# grep ^[a-Z] server.conf local 10.0.0.41 port 1194 proto tcp dev tun ca /etc/openv*n/server/ca.crt cert /etc/openv*n/server/openv*n.crt key /etc/openv*n/server/openv*n.key # This file should be kept secret dh /etc/openv*n/server/dh.pem topology subnet server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0 ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt push "route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0" keepalive 10 120 cipher AES-256-CBC persist-key persist-tun status /var/log/openv*n-status.log log-append /var/log/openv*n.log verb 3 mute 20
Interpretation:
25 local 10.0.0.63 -- set V*N service to listen to address information
32 port 1194 -- set the service port number, which is 1194 by default
35 proto TCP -- V * n link communication protocol uses TCP protocol to ensure data transmission security
53 dev tun -- use tunnel to transfer data
78 ca /etc/openv*n/server/ca.crt
79 cert /etc/openv*n/server/openv*n.crt
80 key /etc/openv*n/server/openv*n.key
85 dh /etc/openv*n/server/dh.pem
92 topology subnet -- identify correct mask information
101 server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0 - set a direct communication address between a client and v*n server
141 push "route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0" -- client pushes an intranet segment route entry information
231 keepalive 10 120 -- TCP long connection timeout
244 ;tls-auth ta.key 0 --- !!! Be sure to turn off the TLS function
287 status /var/log/openv*n-status.log --- generate an openv*n service status log information file
297 log append / var / log / openv*n.log -- generate an openv*n service running log information file
315 ;explicit-exit-notify 1 --- !!! Be sure to turn off this function
The fourth process: start the service program (start in the mode of daemons)
# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/openv*n.service [Unit] Description=openv*n service After=network-online.target Wants=network-online.target [Service] Type=forking User=root Group=root ExecStart=/usr/sbin/openv*n --daemon --config /etc/openv*n/server.conf ExecStop=/bin/kill -9 $MAINPID Restart=on-failure PrivateTmp=true [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start openvn
systemctl enable openvn
================================================================ The first big hole of openv*n service: service cannot be started Step 1: use the command to test whether the configuration file information is correct openv*n /etc/openv*n/server.conf netstat -lntup|grep 1194 Step 2: view profile configuration information Step 3: confirm whether the preparation of startup file is correct ================================================================
windows host configuration deployment process (* * client deployment process)
The first process: Download and install the open client software
D:\Program Files (x86)\OpenV*N\config --- clients can be configured in this directory
Tip: it is in the config directory, not subdirectory, as long as it is in config
The second process: generate client certificate and key file
cd /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/ ./easyrsa gen-req client01 nopass /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/client01.key ./easyrsa sign client client01 /etc/openvp*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/issued/client01.crt
Organize data files in client directory
cp /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/client01.key /etc/openv*n/client/ cp /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/issued/client01.crt /etc/openv*n/client/ cp /etc/openv*n/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/ca.crt /etc/openv8n/client
The third process: import the client certificate or key file into Windows
cd /etc/openv*n/client/ sz -y client01.key client01.crt ca.crt
Build profile in Windows
Under the openn program directory – \ sample config - get client.ovn and put it into the corresponding subdirectory of the – config directory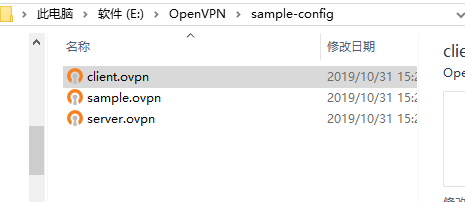
Copy to the following figure: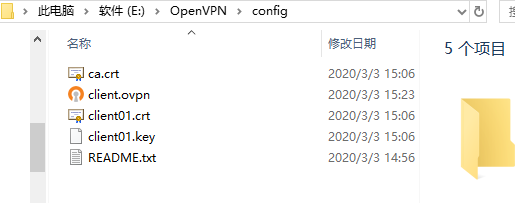
The rest of the client files are generated and exported here in linux
The fourth process: write and modify the client configuration file
Write client.ov*n client configuration file
client dev tun proto tcp remote 10.0.0.63 1194 resolv-retry infinite nobind persist-key persist-tun ca ca.crt cert client01.crt key client01.key cipher AES-256-CBC verb 3
The fifth process: start the open client program
Double click to run the openVNgui program on the Windows host -- find the run openvn icon in the lower right corner -- right click the input connection
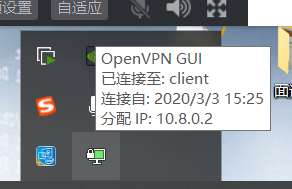
The sixth process: Test and verify:
Verification 1: conduct address test of 10.0.0.1

Verification 2: ping the intranet address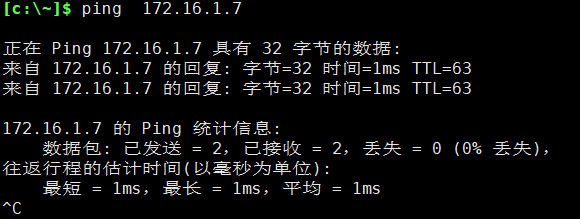
Confirm 01: whether the intranet host of the server can enable the configuration of return route information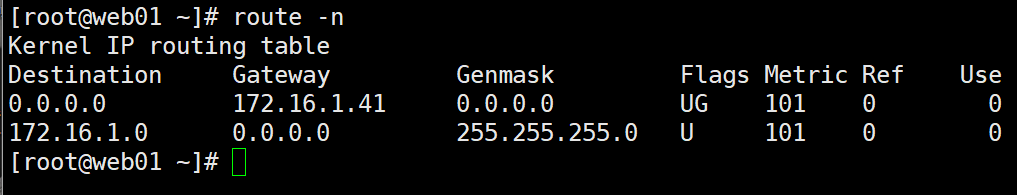
Confirm 02: confirm whether openV*N turns on kernel forwarding function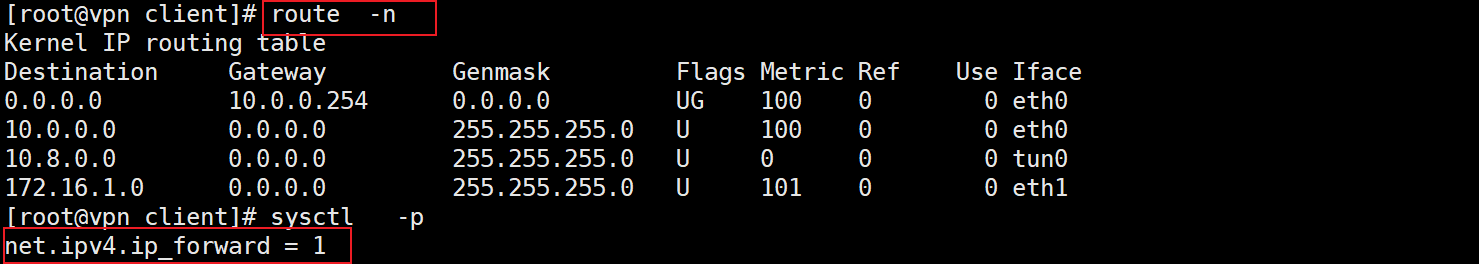
Pits encountered during deployment:
Verify that the certificate and private key files are created correctly If private key or certificate file creation is abnormal --- delete pki directory and recreate pki directory to generate certificate and private key file

