Spring Data JPA is a sub-project of Spring Data. By providing JPA-based Repository, it greatly reduces the amount of code JPA is used as a data access scheme. You only need to write an interface defined within Spring Data JPA under interface integration to complete simple CRUD operations.
Preface
This article guides you through Spring Boot, Spring Data JPA and MySQL to map one-to-one foreign keys, one-to-one primary keys, one-to-many, many-to-many, many-to-many, many-to-many additional columns.
Get ready
- JDK 1.8 or later
- Maven 3 or later
- MySQL Server 5.6
technology stack
- Spring Data JPA
- Spring Boot
- MySQL
directory structure
Father pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>cn.merryyou</groupId> <artifactId>jpa-example</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <modules> <module>one-to-one-foreignkey</module> <module>one-to-one-primarykey</module> <module>one-to-many</module> <module>many-to-many</module> <module>many-to-many-extra-columns</module> </modules> <packaging>pom</packaging> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.spring.platform</groupId> <artifactId>platform-bom</artifactId> <version>Brussels-SR6</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> </project>
One-to-one foreign key
directory structure
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>jpa-example</artifactId> <groupId>cn.merryyou</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>one-to-one-foreignkey</artifactId> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.6.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
One-to-one relationship
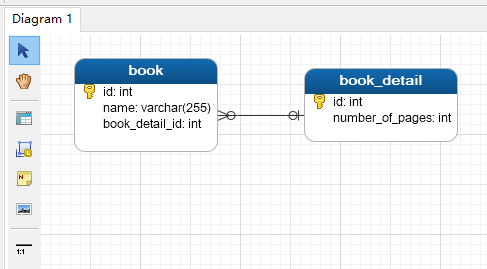
book.book_detail_id and book_detail.id
db.sql
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `jpa_onetoone_foreignkey`; USE `jpa_onetoone_foreignkey`; -- -- Table structure for table `book_detail` -- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `book_detail`; CREATE TABLE `book_detail` ( `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `number_of_pages` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- -- Table structure for table `book` -- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `book`; CREATE TABLE `book` ( `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `book_detail_id` int(11) unsigned DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `fk_book_bookdetail` (`book_detail_id`), CONSTRAINT `fk_book_bookdetail` FOREIGN KEY (`book_detail_id`) REFERENCES `book_detail` (`id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Entity class
Book
@Entity @Data @Table(name = "book") public class Book { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "id") private int id; @Column(name = "name") private String name; @OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL) @JoinColumn(name = "book_detail_id") // @Lazy(false) private BookDetail bookDetail; public Book() { } public Book(String name, BookDetail bookDetail) { this.name = name; this.bookDetail = bookDetail; } }
BookDetail
@Entity @Table(name = "book_detail") @Data public class BookDetail { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "id") private Integer id; @Column(name = "number_of_pages") private Integer numberOfPages; @OneToOne(mappedBy = "bookDetail") private Book book; public BookDetail() { } public BookDetail(Integer numberOfPages) { this.numberOfPages = numberOfPages; } }
-
The @Table declares that this object maps to the database's data tables by which the names of tables (talbe), catalogs, and schema s can be specified for entities. This annotation is not required, and if not, the system uses the default value (the short class name of the entity).
-
Id declares this property as the primary key. This attribute value can be created by itself, but Hibernate recommends that it be generated by Hibernate
-
GeneratedValue specifies the primary key generation strategy.
- TABLE: Save id values with tables
- IDENTITY: identitycolumn
- SEQUENCR : sequence
- AUTO: The three above are used differently depending on the database.
-
Column declares the mapping relationship between the attribute and the database field.
-
OneToOne One One-to-one Association
-
JoinColumn specifies the associated fields
Spring Data JPA Repository
public interface BookRepository extends JpaRepository<Book, Integer> { }
Spring Data JPA includes some built-in Repository and implements some commonly used methods: findone, findall, save, etc.
application.yml
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost/jpa_onetoone_foreignkey username: root password: admin driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jpa: show-sql: true
BookRepositoryTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest @Slf4j public class BookRepositoryTest { @Autowired private BookRepository bookRepository; @Test public void saveTest() throws Exception { List<Book> books = new ArrayList<>(); books.add(new Book("Book one", new BookDetail(1))); books.add(new Book("Book two", new BookDetail(2))); books.add(new Book("Book three", new BookDetail(3))); List<Book> bookList = bookRepository.save(books); Assert.assertNotNull(bookList); Assert.assertEquals(3, bookList.size()); } @Test public void findBooksTest() throws Exception{ List<Book> books = bookRepository.findAll(); for (Book book: books) { log.info(book.toString()); } } }
Other
The remaining one-to-one primary key, one-to-many, many-to-one, many-to-many, many-to-many additional column references are as above.
Code download
Download it from my github. https://github.com/longfeizheng/jpa-example