Nuxt.js(4) ajax operation for programmers
1, Integrate axiox
- When building a project, if you select the axios component, nuxt.js will automatically integrate with axios.
- Integration effect:
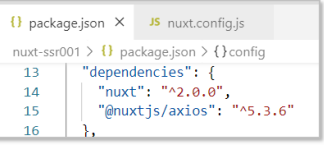
- 1) package.json has axios version
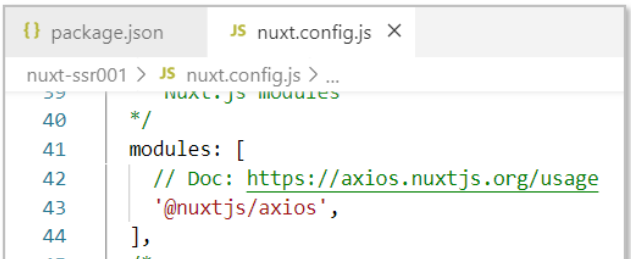
- 2) nuxt.config.js add axios as a module
- Common configuration, modify nuxt.config.js to configure the baseURL (change according to your background configuration path)
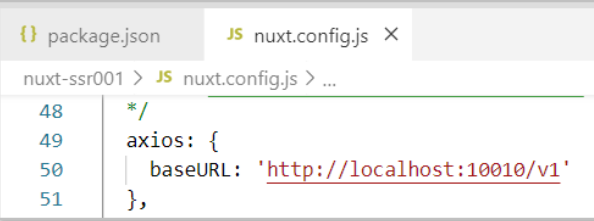
axios: { baseURL:'http://localhost:10010/api '/ / configure the gateway address },
2, Normal ajax (nuxt and axios integration)
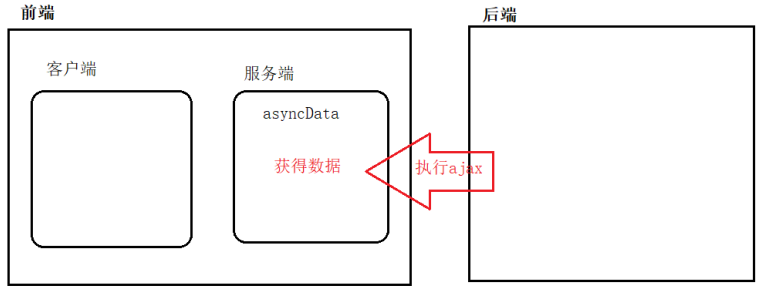
this.$axios can get the axios instance and send ajax |
|---|
For example:
<template> <div> //Normal ajax (nuxt integrates axios) < br / > <!-- Provide button, click button, send ajax Query the result and display it under the button --> <input type="button" @click="findAllFn" value="Click to send"> {{pageInfo}} </div> </template> <script> export default { methods: { async findAllFn() { //Send ajax let { data } = await this.$axios.get('/userservice/user/list') //Save data this.pageInfo = data.data } }, data() { return { pageInfo: '' } }, } </script> <style> </style>
3, Sending asynchronous data using asyncData
1. use asyncData-- one request
ajax in asyncData will be executed in the "front-end server", and the browser will see that it is the data, not the ajax program.
|
|---|
-
asyncData syntax 1: use context object
- For example:
<template> {{Name}} </template> <script> export default { //asyncData cannot use this (current component) //Provide the first parameter context to represent the context (all functions of nuxt) asyncData( context ) { //Send ajax let data = context.$axios.get('','') // Combine data and return return { //Name: Data } } } </script>
• asyncData syntax 2: deconstruct the context object, context. $Axios -- > {$Axios}
<script> export default { async asyncData( {$axios} ) { //Send ajax let { data } = await $axios.get('Route') //encapsulation return { //Variables: querying data } } } </script> •Example <template> <div> {{pageInfo}} </div> </template> <script> export default { async asyncData( context ) { //Send ajax let { data } = await context.$axios.get('/userservice/user/list') //Composite data return { pageInfo: data.data } }, } </script> <style> </style>
Comparison between ajax and asyncData
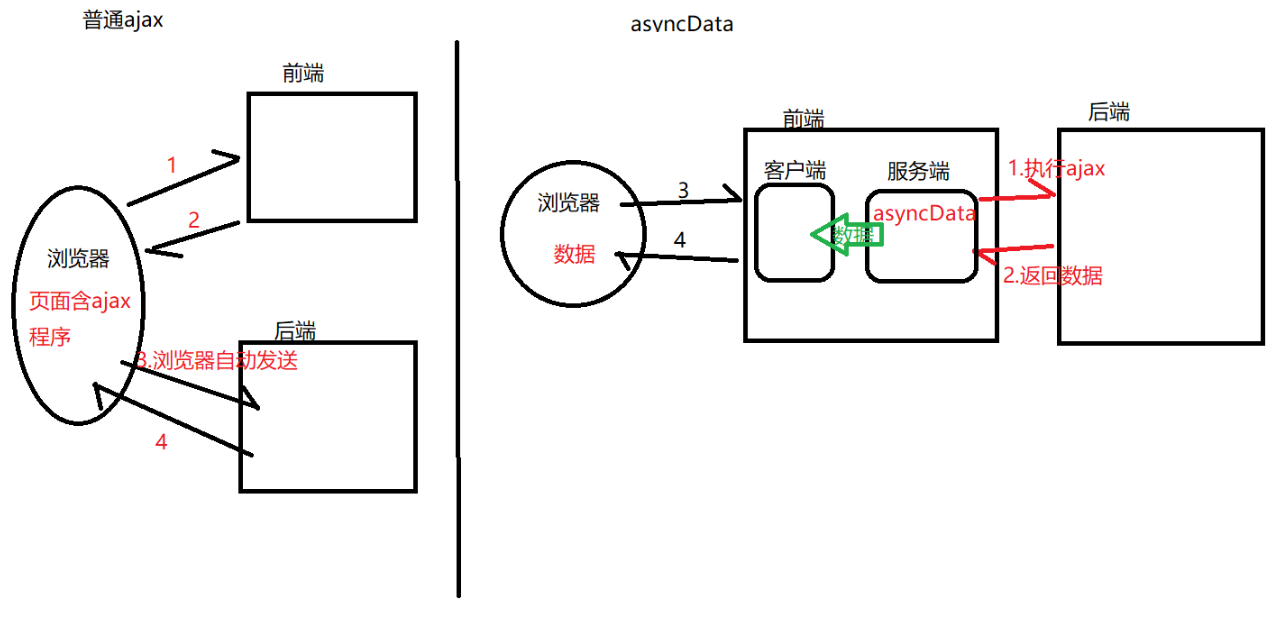
2. Using asyncData -- multiple requests
- Multiple requests require Promise ($axios.get() to return Promise object)
<script>
//Rarely use response objects directly
export default {
async asyncData( {$axios} ) {
//Send multiple requests
let [response 1, response 2] = await Promise.all([request 1, request 2])
//Return data
return {
Variable 1: response 1,
Variable 2: response 2
}
}
}
</script>//Deconstruct the response object response 1 -- > {data} //Both "response 1" and "response 2" can deconstruct data with duplicate variable names. It is recommended to use the alias {data: alias} export default { async asyncData( {$axios} ) { //Send multiple requests let [ { data: d1 }, {data:d2} ] = await Promise.all([Request 1, Request 2]) //Return data return { //Variable 1: d1.data, //Variable 2: d2.data } } } </script>
- Instance 1: Promise.all sends 1 request
<template> <div> {{pageInfo}} </div> </template> <script> export default { async asyncData({ $axios }) { //Send ajax let [ {data} ] = await Promise.all([ $axios.get('/userservice/user/list') ]) //Return return { pageInfo : data.data } }, } </script> <style> </style>
- Example 2: Promise.all sends 2 requests
<template> <div> {{pageInfo}} {{list}} </div> </template> <script> export default { async asyncData({ $axios }) { //Send ajax let [ {data : d1 }, {data : d2} ] = await Promise.all([ $axios.get('/userservice/user/list'), $axios.get('/userservice/user/list2') ]) //Return return { pageInfo : d1.data, list : d2.data } }, } </script> <style> </style>
3, fetch send ajax
- The fetch method is used to fill the application's state tree data before rendering the page. Similar to the asyncData method, it does not set the component's data.
- Comparison map
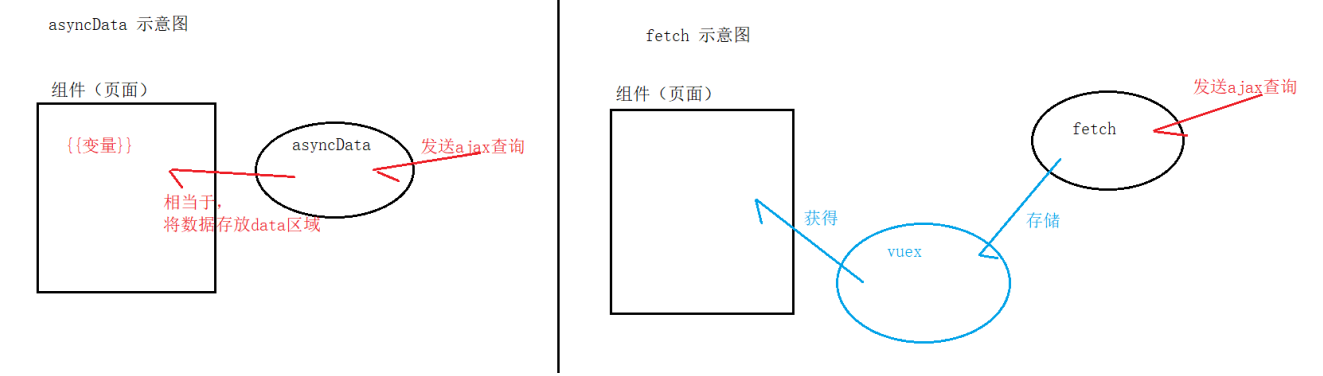
Of course, to send ajax using fetch, you need to learn to integrate vuex (state tree)
- In nuxt, only the core content of vuex is written.
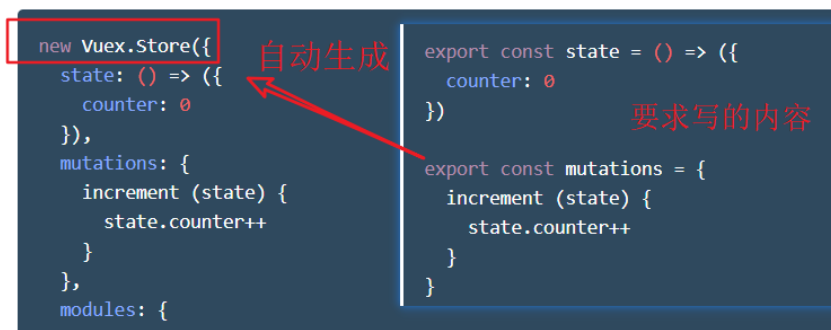
- Compiling content
//state area, equivalent to defining variables
export const state = () => ({
})
//Regions for modifying data
export const mutations = {
Method name (state, value){
}
}
– pay attention to the implementation of the state area
//state area, equivalent to defining variables
export const state = ()=> {
return {
}
}
//Ellipsis
export const state = () => ({
})
For example:
- 1) Create ~ / store/index.js and write the following
//state area, equivalent to defining variables export const state = () => ({ pageInfo: '' }) //Regions for modifying data export const mutations = { setData( state , value) { state.pageInfo = value } }
- 2) Complete the fetch operation
<template> <div> {{ this.$store.state.pageInfo }} </div> </template> <script> export default { async fetch( {$axios, store } ) { //Send ajax let { data } = await $axios.get('/userservice/user/list') console.info( data ) //Save query results to vuex store.commit('setData', data.data ) } } </script> <style> </style>
At the same time, we need to pay attention to the following small knowledge points:
localStorage and sessionStorage cannot be used here. An error will appear
- Both localStorage and sessionStorage are browser side objects, which are not available on the front-end server. If the above two variables are used in created(), the program will throw an exception (the object is not declared)

Conclusion;
In nuxt.js, migrate the code previously stored in created() to mounted()
<template> </template> <script> export default { /* //created()The function is called on both the client and the server. localStorage can only be used on the client created() { localStorage.setItem('name','Test data ') }, */ mounted() { localStorage.setItem('name','test data') }, } </script>
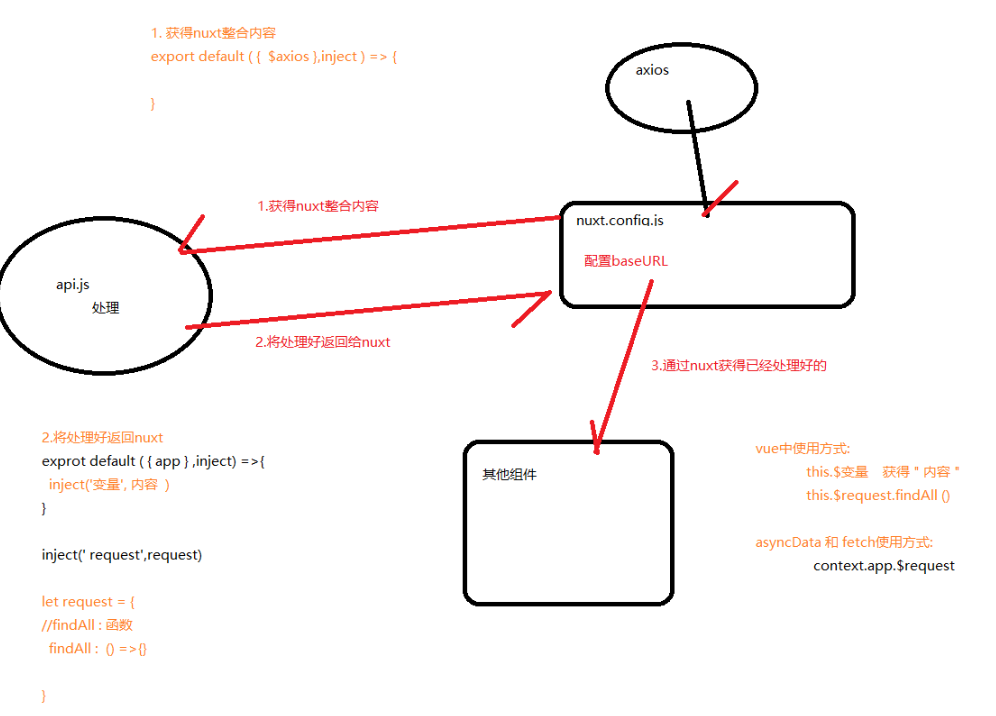
4, Customize axios
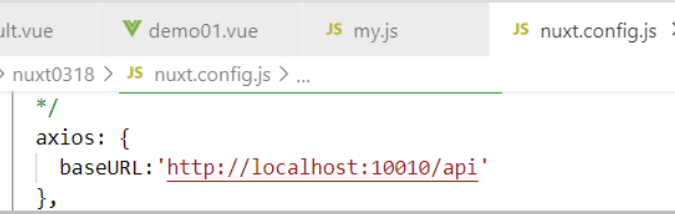
- Purpose of customizing axios: write an api.js file for unified maintenance of request path
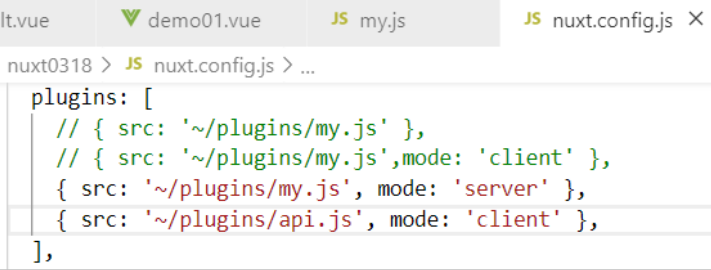
- Step 1: modify nuxt.config.js and write axios baseURL
- Step 2: create ~ / plugins/api.js file and configure it in nuxt.config.js file (only available to clients)
plugins: [ // { src: '~/plugins/my.js' }, // { src: '~/plugins/my.js',mode: 'client' }, { src: '~/plugins/my.js', mode: 'server' }, { src: '~/plugins/api.js', mode: 'client' }, ],
- Step 3: modify api.js and copy fixed content
//Custom function const request = { test : (params) => { return axios.get('/web-service/test',{ params }) }, } var axios = null export default ({ $axios }, inject) => { //3) Save built-in axios axios = $axios //4) Hand over custom function to nuxt // Usage 1: in vue, this.$request.xxx() // Usage 2: in asyncData of nuxt, content.app.$request.xxx() inject('request', request) }
- Step 4: send ajax in other components
-
<template> <div> </div> </template> <script> export default { //Page loaded successfully async mounted() { //Send ajax let { data } = await this.$request.findAll() console.info( data ) }, } </script> <style> </style>
- Step 5: modify api.js to write specific functions
//Custom function const request = { test : (params) => { return axios.get('/web-service/test',{ params }) }, //Method name: function findAll : () => { return axios.get('/userservice/user/list') } }
Custom axios: Principle Analysis
After learning this, you can almost come and go freely in Nuxt.js
Can operate to write some pages, quickly try it!
Please give yourself a compliment!
Make a little progress every day`~~~~~