Don't put in the question, put in the data range.
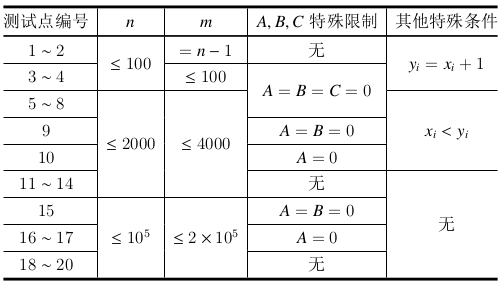
Seeing \ (n < = 2000, m < = 4000 \) and thinking of direct \ (dfs \) in the end, I actually passed the first \ (4 \) sample and the last \ (2s \). Later, I wrote \ (5 \) score of \ (A=B=0 \), and I knew whether it was wrong or handed in the following code. (LOJ data should be official data) score \ (70 \).
In the evening, I went to LOJ for a test, and found that if I ran directly, I had a score of \ (80 \), and then I read an excellent article in \ (AC \) record, which was changed to the back.
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cassert>
#include<queue>
#define debug(...) fprintf(stderr,__VA_ARGS__)
#define Debug(x) cout<<#x<<"="<<x<<endl
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF=1e9+7;
inline LL read(){
register LL x=0,f=1;register char c=getchar();
while(c<48||c>57){if(c=='-')f=-1;c=getchar();}
while(c>=48&&c<=57)x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c&15),c=getchar();
return f*x;
}
const int N=100005;
const int M=200005;
struct Edge{
int v,s,t,nxt;
}e[M];
int first[N],Ecnt=0;
inline void Add_edge(int u,int v,int s,int t){
e[++Ecnt]=(Edge){v,s,t,first[u]};
first[u]=Ecnt;
}
int n, m, A, B, C;
inline LL calc(int x){
return 1ll * A * x * x + 1ll * B * x + C;
}
namespace baoli{
LL ans = INF;
inline void dfs(int u, int time, LL cost){
if(u == n){
ans = min(ans, cost + time);
}
for(int i = first[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].v, s = e[i].s, t = e[i].t;
if(s < time) continue;
dfs(v, t, cost + calc(s - time));
}
}
inline void main(){
dfs(1, 0, 0);
printf("%lld\n", ans);
exit(0);
}
};
namespace Subtask1{ // A == 0 && B == 0
int dis[N], time[N];
queue <int> q;
LL ans = INF;
inline void Return(LL ans){
printf("%lld\n", ans);
exit(0);
}
inline void main(){
q.push(1);
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis);
dis[1] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i = first[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].v;
if(time[u] > e[i].s) continue;
if(dis[u] + 1 < dis[v]){
dis[v] = dis[u] + 1;
time[v] = e[i].t;
q.push(v);
}
if(v == n) ans = min(ans, 1ll * (dis[u] + 1 + 1) * C + e[i].t);
}
}
Return(ans);
assert(false);
}
/*inline void main(){
q.push((Node){1, 0, 0});
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front().x, d = q.front().dis, t = q.front().time; q.pop();
for(int i = first[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].v;
if(e[i].t < t) continue;
if(
}
}
}*/
};
int main(){
#ifndef file
freopen("route.in","r",stdin);
freopen("route.out","w",stdout);
#endif
n = read(), m = read(), A = read(), B = read(), C = read();
for(register int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
register int x = read(), y = read(), p = read(), q = read();
Add_edge(x, y, p, q);
}
if(n <= 2000 && m <= 4000)
baoli::main();
if(A == 0 && B == 0) Subtask1::main();
}
I didn't notice the time \ (Q < = 1000 \), so \ (O(nq)=O(1e8) \) should be able to get stuck?
Direct \ (dp \) someone got it 95 points . sort the trains by time, and then update them in turn, so that \ (1e8 \) is not satisfied with the running, and it will pass directly. You can use \ (vector \) to save the status.
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define debug(...) fprintf(stderr,__VA_ARGS__)
#define Debug(x) cout<<#x<<"="<<x<<endl
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const LL INF=1e18+7;
inline LL read(){
register LL x=0,f=1;register char c=getchar();
while(c<48||c>57){if(c=='-')f=-1;c=getchar();}
while(c>=48&&c<=57)x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c&15),c=getchar();
return f*x;
}
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
const int M = 2e5 + 5;
struct Node{
int x, y, p, q;
}a[M];
inline bool cmp1(Node a, Node b){
if(a.p == b.p) return a.q < b.q;
return a.p < b.p;
}
vector <LL> f[N];
vector <int> t[N];
int n, m, A, B, C;
inline LL calc(int x){
return 1ll * A * x * x + 1ll * B * x + C;
}
int main(){
#ifndef file
freopen("route.in","r",stdin);
freopen("route.out","w",stdout);
#endif
n = read(), m = read(), A = read(), B = read(), C = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
a[i].x = read(), a[i].y = read(), a[i].p = read(), a[i].q = read();
}
sort(a + 1, a + m + 1, cmp1);
f[1].push_back(0), t[1].push_back(0);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
int x = a[i].x, y = a[i].y, p = a[i].p, q = a[i].q;
int tt = -1;
for(int j = 0; j < t[y].size(); ++j)
if(t[y][j] == q) {tt = j; break;}
for(int j = 0; j < f[x].size(); ++j){
if(t[x][j] > p) continue;
int len = p - t[x][j];
if(tt == -1){
f[y].push_back(f[x][j] + calc(len));
t[y].push_back(q);
tt = f[y].size() - 1;
}
else if(f[x][j] + calc(len) < f[y][tt]){
f[y][tt] = f[x][j] + calc(len);
}
}
}
LL ans = INF;
for(int i = 0; i < f[n].size(); ++i)
ans = min(ans, f[n][i] + t[n][i]);
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}