Node.js beginner's notes
Node.js learning notes, including the basic use of native modules, Express framework and Koa framework. And the construction based on Koa project, Postman interface test and some usage skills.
Basic functions of Node.js http module
The node.js version is v14.17.3
Record common functions of http module:
1. url parsing
2. headers data acquisition
3. Get by request (get/post, etc.)
4. Response status code setting
5. Response header settings
6. Get data from a third-party server
const http = require('http');
const url = require('url');
const querystring = require('querystring');
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// request
console.log(`req.url = `, req.url);
console.log(`req.headers = `, req.headers);
console.log(`req.method = `, req.method);
// url parsing processing
const parseUrl = url.parse(req.url);
console.log( `parseUrl = `, parseUrl);
const {pathname, query} = url.parse(req.url);
console.log(`pathname = ${pathname}, quary = ${pathname}`);
if (pathname === '/login') {
if (req.method === 'GET') {
// quary analysis
// http://localhost:8989/login?name=zhangsan&age=18
const result = querystring.parse(query);
console.log(result);
console.log(result.name);
console.log(result.age);
res.end("hello world get");
return;
} else if (req.method === 'POST') {
// http://localhost:8989/login postman raw -> json
// json parsing of post request parameters
req.on('data', (data) => {
// req.setEncoding('utf-8');
const {name, age} = JSON.parse(data);
console.log(name, age);
});
res.end("hello world post");
// Response header file
// res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=utf8");
// res.writeHead(200, {
// "Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf8"
// });
// Response results
// res.end("<h2>Hello Server</h2>");
// return;
}
}
// http request, requesting data from a third-party server
if (pathname === '/getData') {
if (req.method === 'GET') {
console.log('Get data from a third-party server get');
http.get('http://apis.juhe.cn/mobile/get?phone=13429667914', (response) => {
response.on('data', (data) => {
// console.log(`getServerData =`, data);
const result = JSON.parse(data);
console.log(`result = `, result);
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/json;charset=utf8");
res.end(data);
});
});
} else {
console.log('Get data from a third-party server post');
// http://v.juhe.cn/toutiao/index?type=top&key=APPKEY
const otherReq = http.request({
method: 'POST',
hostname: 'v.juhe.cn',
path: '/toutiao/index'
}, (response) => {
response.on('data', (data) => {
// console.log(`getServerData =`, data);
const result = JSON.parse(data);
console.log(`result = `, result);
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/json;charset=utf8");
res.end(data);
});
});;
const postData = JSON.stringify({
'type': 'top'
});
otherReq.write(postData);
otherReq.end();
}
return;
}
res.end("hello world");
});
server.listen(8989, 'localhost', () => {
console.log(`Create server`);
});
Simple use of Express.js framework
- Service creation
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const port = 8989;
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening at http://localhost:${port}`)
})
- Definition and call of Middleware
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(`Middleware 1`);
// Call the next Middleware
next();
});
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(`Middleware 2`);
res.end("hello world");
});
- Parsing json parameters
app.use(express.json());
app.post('/login', (req, res, next) => {
// Parameter analysis
console.log(req.body);
res.end("hello world");
});
- Analysis of x-www-from-urlencoded parameters
app.use(express.urlencoded());
app.post('/login', (req, res, next) => {
// Parameter analysis
console.log(req.body);
res.end("hello world");
});
- From data parameter parsing
// npm install multer
const multer = require('multer');
const upload = multer();
app.use(upload.any());
app.post('/login', (req, res, next) => {
// Parameter analysis
console.log(req.body);
res.end("hello world");
});
- Query Params parsing
// url -> http://localhost:8989/login/23/zhangsan
app.get('/login/:id/:name', (req, res, next) => {
// Parameter resolution {id: '123', name: 'zhad'}
console.log(req.params);
res.end("hello world login");
});
// url -> http://localhost:8989/login?name=zhandan
app.get('/login', (req, res, next) => {
// Parameter analysis
console.log(req.query);
res.end("hello world login");
});
- File upload
const multer = require('multer');
const upload = multer({
dest: "./upload"
});
app.post('/upload', upload.single('file'), (req, res, next) => {
res.end('File uploaded successfully');
});
Modify the name and set the suffix for the uploaded file
const multer = require('multer');
const path = require('path');
const storage = multer.diskStorage({
destination: (req, file, callback) => {
callback(null, "upload/")
},
filename: (req, file, callback) => {
callback(null, Date.now() + path.extname(file.originalname));
}
});
const upload = multer({
storage
});
app.post("/upload", upload.single('file'), (req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.file.buffer);
res.end('Upload file succeeded');
});
- Logging
// npm install morgan
const fs = require('fs');
const morgan = require('morgan');
const log = fs.createWriteStream("./log/login.log", { flags: 'a+' });
// Logging
app.use(morgan('combined', {stream: log}));
app.post('/login', (req, res, next) => {
// Parameter analysis
console.log(req.body);
res.end("hello world");
});
- response returns json data
app.post('/login', (req, res, next) => {
res.json(["name", "zhangsan"]);
});
- Use of routing
const userRouter = require('./routes/users');
app.use('/user', userRouter);
// users.js file
const express = require("express");
const router = express.Router();
router.get('/:id', (req, res, next) => {
res.end("according to id obtain user info");
});
module.exports = router;
- Static server deployment
Set the directory of static resources
// http://localhost:8989/123.png
app.use(express.static('./static'));
- Error exception handling
app.get('/login', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('logon test');
// Go to the next error handling Middleware
next(new Error());
});
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.log(`err`, err);
res.status(400).json({"error": "request was aborted"});
});
Simple use of koa.js framework
- Service creation
const Koa = require("koa");
const app = new Koa();
app.listen(8989, () => {
console.log("Server created successfully");
});
- Use of Middleware
app.use((ctx, next) => {
console.log("First Middleware");
// Call the next Middleware
next();
});
app.use((ctx, next) => {
console.log("Second Middleware");
ctx.body = "hello koa";
});
- Request method and path acquisition
app.use((ctx, next) => {
console.log(`ctx.request.path = `, ctx.request.path);
console.log(`ctx.request.method = `, ctx.request.method);
ctx.body = "hello koa";
});
- Use of routing
// npm install koa-router
const userRouter = require("./router/user");
app.use(userRouter.routes());
app.use(userRouter.allowedMethods());
// user.js
const Router = require('koa-router');
const router = new Router({prefix: '/user'});
// Request URL - > http://localhost:8989/user/info
router.post('/info', (ctx, next) => {
console.log(ctx.request.query);
ctx.body = "user post";
});
- json parameter and x-www-form-urlencoded parameter parsing
// Parameter json parsing NPM install KOA bodyparser
const bodyParser = require('koa-bodyparser');
app.use(bodyParser());
app.use((ctx, next) => {
console.log(ctx.request.body);
ctx.body = "user post";
});
- Form data parameter parsing
const multer = require('koa-multer');
const upload = multer();
app.use(upload.any());
app.use((ctx, next) => {
console.log(ctx.req.body);
ctx.body = "user post";
});
- File upload
const multer = require('koa-multer');
const upload = multer({
dest: './upload'
});
router.post('/upload', upload.single('file'), (ctx, next) => {
console.log(ctx.req.file);
ctx.body = "Upload succeeded";
});
Upload the file and modify the name to add a suffix
const multer = require('koa-multer');
const path = require('path');
const storage = multer.diskStorage({
destination: (req, file, callback) => {
callback(null, "upload/")
},
filename: (req, file, callback) => {
callback(null, Date.now() + path.extname(file.originalname));
}
});
const upload = multer({
storage
});
router.post('/upload', upload.single('file'), (ctx, next) => {
console.log(ctx.req.file);
ctx.body = "Upload succeeded";
});
- Static server
// npm install koa-static
const staticRes = require('koa-static');
app.use(staticRes('./static'));
- error handling
app.use((ctx, next) => {
ctx.app.emit('error', new Error('error message', ctx));
});
app.on('error', (err, ctx) => {
console.log(`err.message = `, err.message);
});
- Combined with the use of Koa-log4.js log
// configuration file
const path = require('path');
const log4js = require('koa-log4');
log4js.configure({
appenders: {
out: { type: "console" },
access: {
type: 'dateFile',
pattern: '-yyyy-MM-dd.log', //Rules for generating files
alwaysIncludePattern: true, //File names are always distinguished by date
encoding:"utf-8",
filename: path.join('logs/', 'access.log') //Generate file name
},
application: {
type: 'dateFile',
pattern: '-yyyy-MM-dd.log',
alwaysIncludePattern: true,
encoding:"utf-8",
filename: path.join('logs/', 'application.log')
},
},
categories: {
default: { appenders: ['out'], level: 'debug' },
access: { appenders: ['access'], level: 'info' },
application: { appenders: ['application'], level: 'info' }
}
});
// Log all access levels
const accessLogger = () => log4js.koaLogger(log4js.getLogger('access'));
// console output
const debugLogger = log4js.getLogger('out');
// Log all application levels
const applicationLogger = log4js.getLogger('application');
module.exports = {
accessLogger,
applicationLogger,
debugLogger
};
// use
const { accessLogger } = require('../app/logs-config');
// koa-log
app.use(accessLogger());
// Basic use
const { applicationLogger, debugLogger } = require('../app/logs-config');
// Print debug to console
debugLogger.debug('errorHandle message = ' + error.message);
// Print error log to file
applicationLogger.error('errorHandle message = ' + message);
- Build project structure directory based on Koa.js framework
Including directory structure, routing, environment variables, database configuration, error handling, logging and other functions.
Token mechanism of JWT
Component header+payload+signature
header:
1. alg: the adopted encryption algorithm, HMAC SHA256(HS256) by default, uses the same key for encryption and decryption;
2. typ:JWT, fixed value, usually written as JWT;
3. It will be encoded by base64Url algorithm;
payload:
1. For example, we can put the user's id and name into the payload;
2. iat(issued at) will also be carried by default, indicating the issuing time of the token;
3. You can also set the expiration time: exp(expiration time);
4. It will be encoded by base64Url algorithm
signature:
1. Set a secretKey and merge the results of the first two to implement the HMACSHA256 algorithm;
2,HMACSHA256(base64Url(header)+.+base64Url(payload), secretKey);
3. However, if the secret key is exposed, it is very dangerous, because the token can be issued or decrypted;
The generated content is as follows: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VySUQiOjEsInVzZXJOYW1lIjoi5byg5LiJIiwiaWF0IjoxNjMxNzU3OTQ0LCJleHAiOjE2MzE3NjE1NDR9.ORFHXXmu_q5cFVCKhIWSfPDmUiYEE_ocN1avi8gnzkGC3BZ6bq_KZniR9TK78Yk_V9j6RedwXelPE_Y7XJHup-sMhPh6Lcsk02QnrMc_uORo2jNaD3I75S9zEl18hnFtlPJGJAbyxaLzNVTAbeJvWTVMF4tjsByCzRHx991xB3A
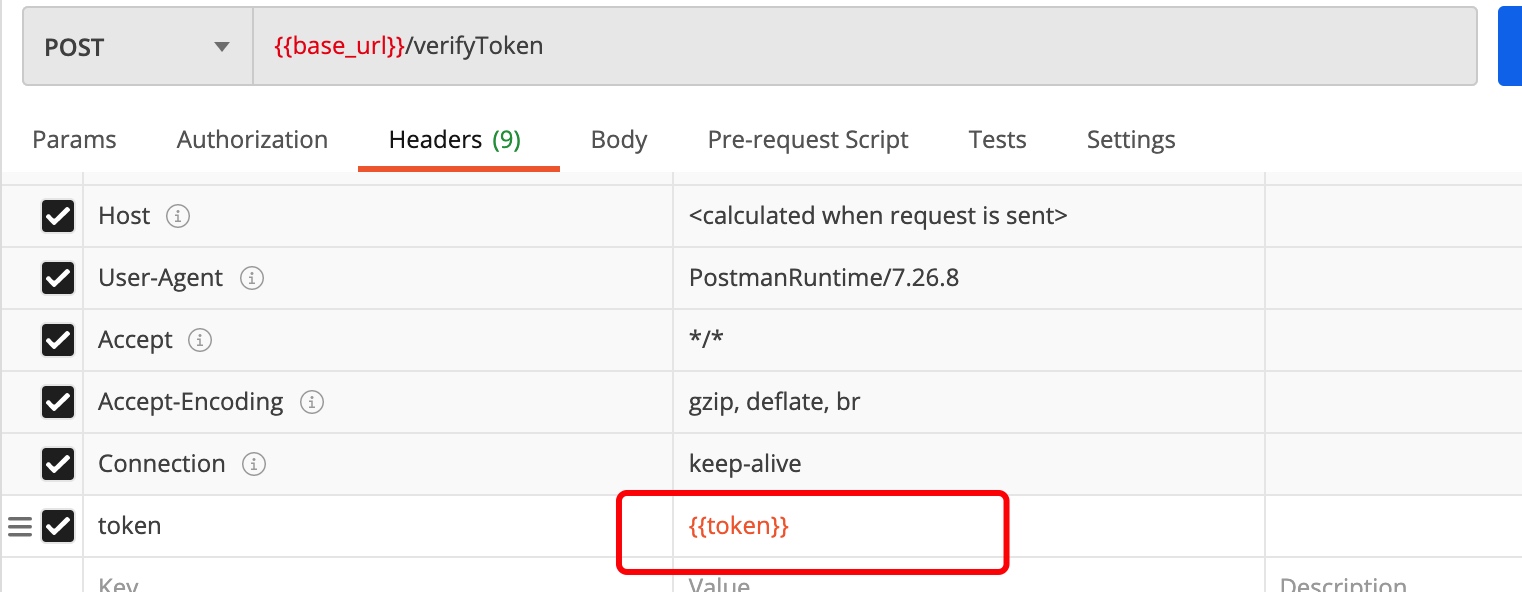
Tips for using Postman
- Setting of environment variables
Click the eye to add the environment variable
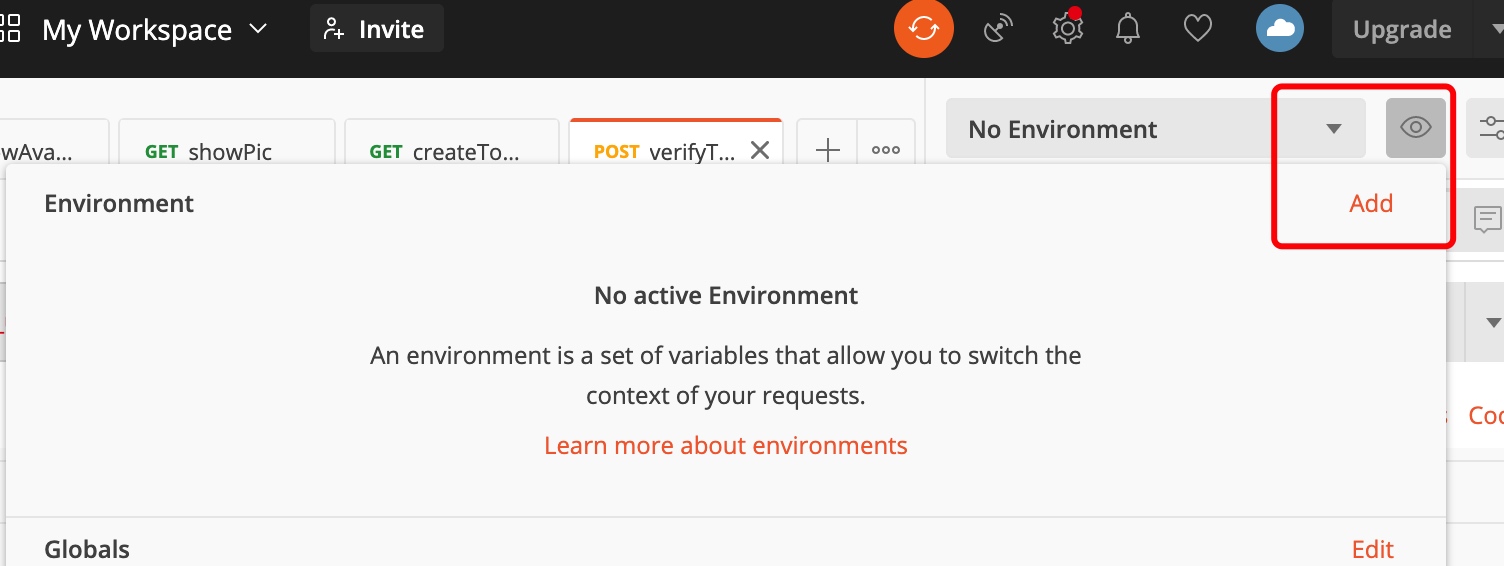
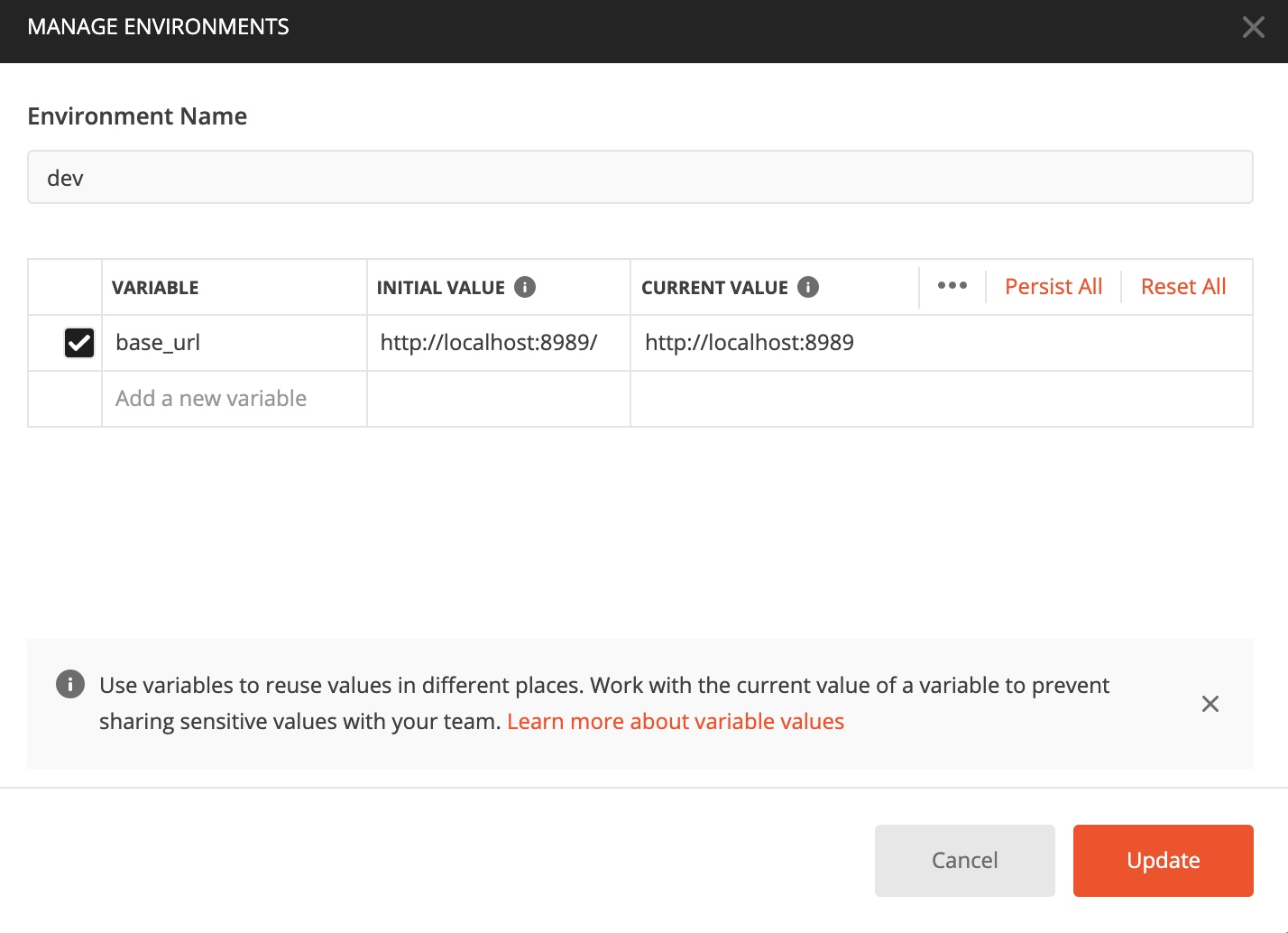
Later, it can be used in the request interface
base_url substitution http://localhost:8989
- Set global variables
Get the data of an interface and set a value as a global variable, such as token
Script in the Tests of the interface
// {{base_url}}/createToken request interface
Return value
{
"success": 0,
"data": {
"token": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VySUQiOjEsInVzZXJOYW1lIjoi5byg5LiJIiwiaWF0IjoxNjMxODQ2Nzk2LCJleHAiOjE2MzE4NTAzOTZ9.fwFUeusq0JJ_sZ7ysksH9NRlpTqanVOU10XN96kY62OzcIJSMQ3SrQVK0oBI-r2oiS-NnQUuvdwdpD14Tns6BHFuWFjNBTET_udzkOTgrgyn4xz-aDY8MjLG61XFoqEVXXnFaAi209XyKwNi-MFAEcMaieRtYJXT3dibKzi7GaU"
},
"message": null
}
// Set global variable token
const res = pm.response.json();
console.log(res.data.token);
pm.globals.set('token', res.data.token);
Use token variables at other interfaces