1, Installation of requests Library
WIN platform: run cmd with win+R and execute
pip install requests
Official documents: https://docs.python-requests.org/zh_CN/latest/
Mine is already installed
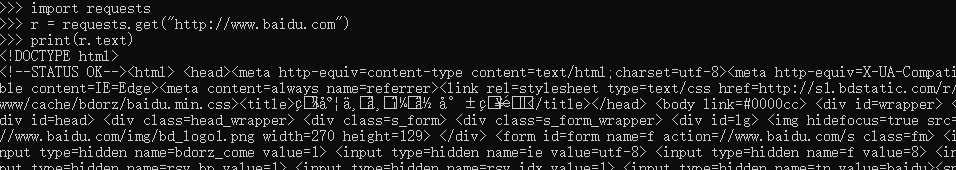
Test after successful installation
import requests
r = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
print(r.text)
2, Seven main methods and simple use of requests Library
(1) Seven methods
| method | explain |
|---|---|
| requests.request() | Construct a request to support the basic methods of the following methods |
| requests.get() | The main method to obtain HTML web pages corresponds to HTTP GET |
| requests.head() | The method for obtaining HTML web page header information corresponds to HTTP HEAD |
| requests.post() | The method of submitting POST requests to HTML web pages corresponds to HTTP POST |
| requests.put() | The method of submitting a PUT request to an HTML web page corresponds to the PUT of HTTP |
| requests.patch() | Submit a local modification request to an HTML web page, corresponding to the PATCH of HTTP |
| requests.delete() | Submit a DELETE request to the HTML page, corresponding to the DELETE of HTTP |
The most commonly used method is request(),get(),post()
(2) Simple use
1.request() method
r = requests.request(method, url, **kwargs) # Construct a request to support the basic methods of the following methods
-
Method: request method, corresponding to 7 types such as get/put/post
-
url: the url link of the page to be obtained
-
**kwargs: 13 parameters controlling access
- Method: request method
r = requests.request('GET', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('HEAD', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('POST', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('PUT', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('PATCH', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('delete', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('OPTIONS', url, **kwargs)
- Method: request method
-
params: dictionary or byte sequence, which is added to the url as a parameter
Access control parameter, that is, the third parameter kwargs example
import requests
kv1 = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
rs1 = requests.request('GET', 'http://python123.io/ws',params = kv1)
print(rs1.text)
rs2 = requests.request('POST', 'http://python123.io/ws',data = kv1)
print(rs2.text)
kv2 = {'key1': 'value1'}
rs3 = requests.request('POST', 'http://python123.io/ws', json=kv2)
print(rs3.text)
hd = {'user‐agent': 'Chrome/10'}
rs4 = requests.request('POST', 'http://python123.io/ws', headers=hd)
rs5 = requests.request('post','',cookies = 'Dictionary or cookieJar')
rs6 = requests.request('post','',auth = 'tuple')
fs = {'file':open('data.xls','rd')}
rs7= requests.request('POST','',files = fs) # transfer files
rs8 = requests.request('GET','http://www.baidu.com',timeout = 10)
pxs = { 'http': 'http://user:pass@10.10.10.1:1234','https': 'https://10.10.10.1:4321' }
rs9 = requests.request('GET','http://Www.baidu. Com ', proxies = Pxs) # proxies dictionary type, set access proxy server
| parameter | explain |
|---|---|
| files | Dictionary type, transfer file |
| timeout | Set the timeout in seconds |
| proxies | Dictionary type, set access proxy server, and add login authentication |
| allow_redirects | True/False, default to true, redirect switch |
| stream | True/False, the default is true, and the get content download now switch |
| verify | True/False, the default is true, and the SSL certificate authentication switch |
| cert | Local SSL certificate path |
2. get() method
r = requests.get(url, params = None, **kwargs)
r = requests.get(url) # The main method to obtain HTML web pages corresponds to HTTP GET r = requests.delete(url) print(r.url)
| parameter | explain |
|---|---|
| url | url link of the page to be obtained |
| params | Additional parameters in url, dictionary or byte stream format, optional |
| **kwargs | 12 control access parameters |
3.head() method
r = requests.head('http://httpbin.org/get ') # gets the header information of HTML pages, which corresponds to the HTTP HEAD
print(r.headers)
4.post() method
r = requests.post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs)
| parameter | explain |
|---|---|
| url | url link of the page to be updated |
| data | Dictionary, byte sequence or file, contents of Request |
| json | JSON format data, Request content |
Example
payload = {'key1':'value1','key2':'value2'}
r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post',data=payload) # the method of submitting POST requests to HTML web pages, corresponding to HTTP POST
r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post',data='abc')
print(r4.text)
5.put() method
r = requests.put(url, data=None, **kwargs)
r = requests.put('http://httpbin.org/put',data=payload) # the method of submitting a PUT request to an HTML web page, which corresponds to the PUT of HTTP
print(r.text)
6.patch() method
r = requests.patch(url) # Submit a local modification request to an HTML web page, corresponding to the PATCH of HTTP `
7.delete() method
r = requests.delete(url, **kwargs)
r = requests.delete(url) # Submit a DELETE request to the HTML page, corresponding to the DELETE of HTTP
url: the url link of the page to be deleted
3, Two important objects of requests Library
Response and Request
(1)Request
- r == response returns a response object containing server resources
- Request constructs a request object that requests resources from the server
- From request to response
(2) Response object
The Response object contains all the information returned by the server and the Request information of the Request
| attribute | explain |
|---|---|
| r.status_code | The return status of the HTTP request. 200 indicates successful connection and 404 indicates failure |
| r.text | The string form of HTTP response content, that is, the page content corresponding to the url |
| r.encoding | Guess the encoding of the response content from the HTTP header |
| r.apparent_encoding | Response content encoding method analyzed from the content (alternative encoding method) |
| r.content | Binary form of HTTP response content |
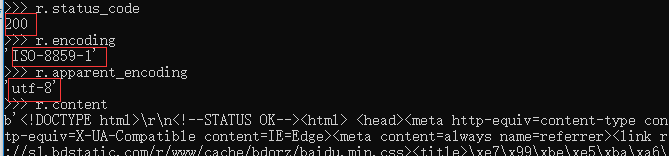
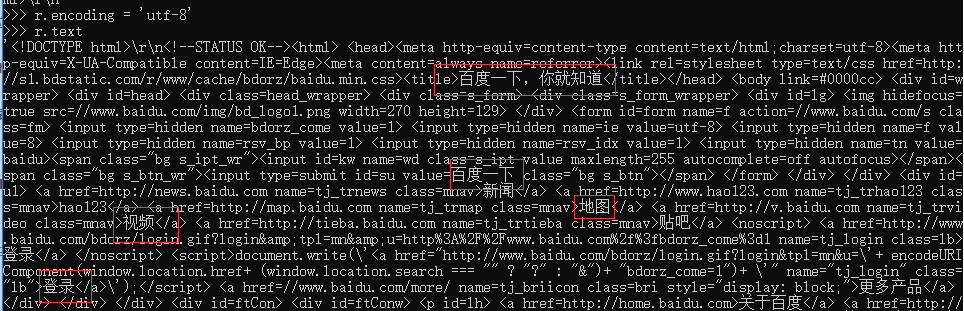
Sometimes the printed page content is garbled, as shown below
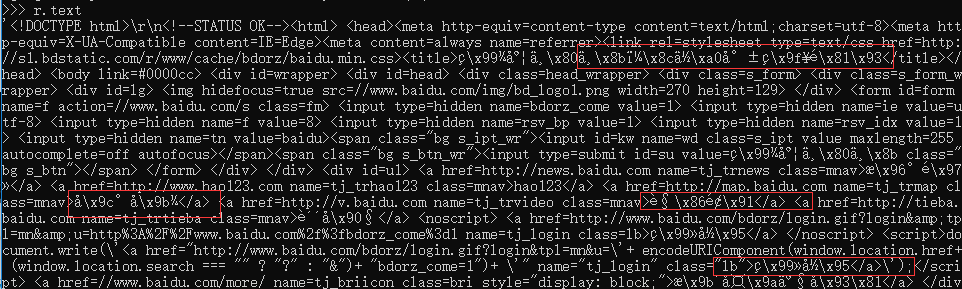
Therefore, you need to understand the encoding of Response
| r.encoding | Guess the encoding of the response content from the HTTP header |
|---|---|
| r.apparent_encoding | Response content encoding method analyzed from the content (alternative encoding method) |
1) r.encoding: if there is no charset in the header, it is considered as ISO ‐ 8859 ‐ 1
2) r.text display web page content according to r.encoding
3)r.apparent_encoding: the encoding method analyzed according to the web page content can be regarded as an alternative to r.encoding
When we change the coding method, the printed content is
There are l two ways
r.encoding = 'utf-8' #Direct change coding r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding #Use the alternative of r.encoding
4, Exception of requests Library
Network connection is risky, and exception handling is very important
(1) Requests exception
| abnormal | explain |
|---|---|
| requests.ConnectionError | Network connection errors and exceptions, such as DNS query failure, connection rejection, etc |
| requests.HTTPError | HTTP error exception |
| requests.URLRequired | URL missing exception |
| requests.TooManyRedirects | Exceeding the maximum number of redirections, a redirection exception is generated |
| requests.ConnectTimeout | Connection to remote server timeout exception |
| requests.Timeout | The request URL timed out, resulting in a timeout exception |
(2) Response exception
| r.raise_for_status() | If it is not 200, an exception requests.HTTPError is generated |
|---|
r.raise_for_status() determines r.status inside the method_ Whether code is equal to 200 is unnecessary
Add an additional if statement, which is convenient for exception handling with try ‐ exception
5, HTTP protocol
(1) HTTP is a stateless application layer protocol based on "request and response" mode
- HTTP protocol uses URL as the identification for locating network resources. The URL format is as follows:
- http://host[:port][path]
-Host: Legal Internet host domain name or IP address
-Port: port number. The default port is 80
-Path: the path of the requested resource
URL is the Internet path to access resources through HTTP protocol. A URL corresponds to a data resource
(2) HTTP operation on resources

Manage resources through URL s and commands, operate independently and stateless, and network channels and servers become black boxes
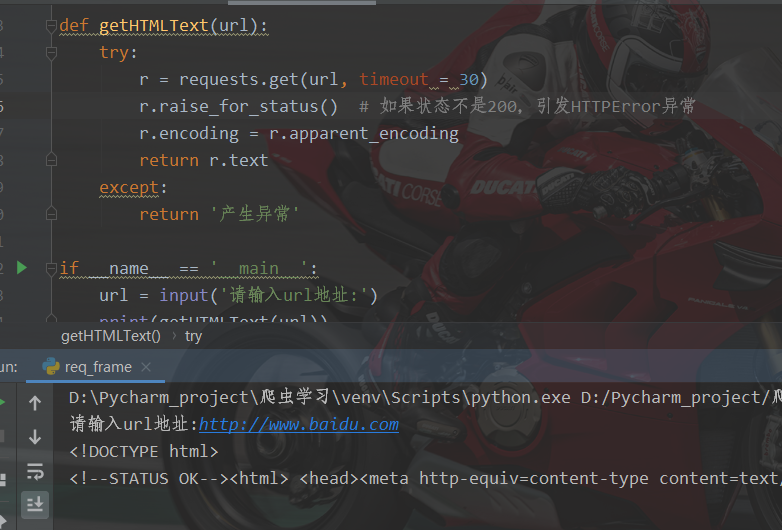
6, General code framework for crawling web pages
import requests
def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout = 30)
r.raise_for_status() # If the status is not 200, an HTTPError exception is thrown
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return 'raise an exception'
if __name__ == '__main__':
url = input('Please enter url address:')
print(getHTMLText(url))
7, Restrictions on web crawlers
Robots protocol
- Robots(Robots Exclusion Standard)
Function: the website tells web crawlers which pages can be crawled and which can't.
Form: robots.txt file in the root directory of the website
case
https://www.jd.com/robots.txt
http://www.baidu.com/robots.txt
http://www.qq.com/robots.txt
http://news.qq.com/robots.txt
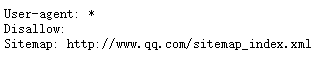
*#Comment, for all, / for root
Use of Robots protocol
Web crawler: automatically or manually identify robots.txt, and then crawl the content
Binding: Robots protocol is recommended but not binding. Web crawlers may not abide by it, but there are legal risks
Tip:
As a computer technology, crawler determines its neutrality. Crawler itself is not prohibited by law. If crawler collects public data, it is OK. Of course, improper operation may involve the risk of breaking the law or even committing a crime. Therefore, it is necessary to use reasonably and standardize crawling.