1. Input man socket into the terminal to check the contents of socket
2. Create socket on the server side
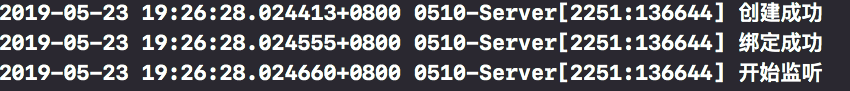
/* First parameter domain (network type): pf? INET IPv4 / PF? Inet6 IPv6 The second parameter type (socket type): sock'stream connection oriented -- TCP protocol / sock'dgram connectionless -- UDP protocol The third parameter, protocol: */ int serverSocket = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (serverSocket == -1) { NSLog(@"Create failure"); }else{ NSLog(@"Create success"); }
2. Bind port number
int bind(SOCKET sock, const struct sockaddr *addr, int addrlen);
- First parameter: created socket file descriptor,
- Second parameter: the address structure passed in. To be compatible with the old system, the function declaration type is struct sockaddr *, but we usually use sockaddr_in, which is easier to use.
//Create SOCKADDR? In structure variable struct sockaddr_in addr; addr.sin_family = AF_INET;//Use ipv4 address addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);//Binding ip address to any addr.sin_port = htons(1234);//Port number int result = bind(serverSocket, (const struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)); if (result == -1) { NSLog(@"Bind error"); }else{ NSLog(@"Binding success"); }
3. Start monitoring
int listen(SOCKET sock, int backlog);
- The socket is the socket that needs to enter the listening state, and the backlog is the maximum length of the request queue.
result = listen(serverSocket, 5); if (result == -1) { NSLog(@"Monitoring failed"); }else{ NSLog(@"Start monitoring"); }
4. accept
SOCKET accept(SOCKET sock, struct sockaddr *addr, int *addrlen);
- sock is the server socket, addr is the SOCKADDR in structure variable, addrlen is the length of parameter addr, which can be obtained by sizeof().
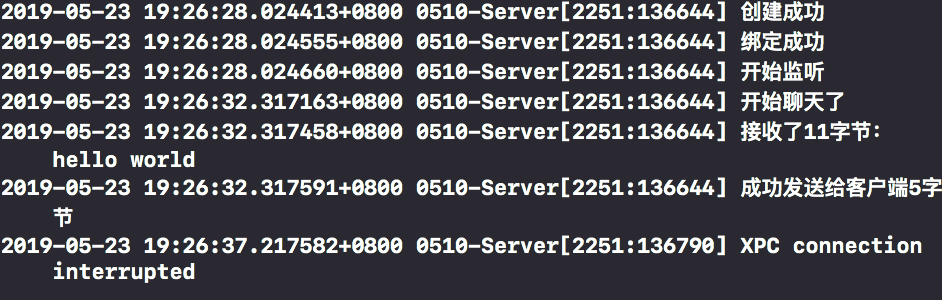
//Save client information struct sockaddr c_addr; socklen_t len; //Save received data buffer char *buff[1024]; while (1) { int newSocket = accept(serverSocket, (struct sockaddr *)&c_addr, &len); if (newSocket == -1) { NSLog(@"Failed to receive data"); }else{ NSLog(@"Start talking"); //receive data size_t length = recv(newSocket, buff, 1024, 0); NSLog(@"Received%zu Byte:%s",length ,buff); //send data char *msg = "hello"; length = send(newSocket, msg, strlen(msg), 0); NSLog(@"Successfully sent to client%zu byte",length); } }
5. Client creates socket
- Import header file
#import <sys/socket.h> #import<netinet/in.h> #import <arpa/inet.h> #import <sys/types.h>
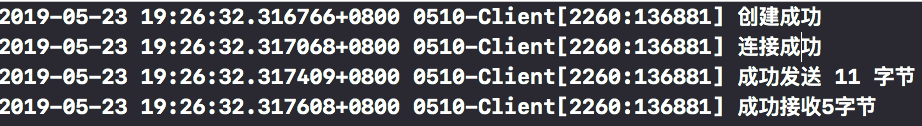
int clientSocket = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (clientSocket == -1) { NSLog(@"Create failure"); }else{ NSLog(@"Create success"); }
6. Initiate connection
int connect(SOCKET sock, const struct sockaddr *serv_addr, int addrlen);
struct sockaddr_in addr; addr.sin_family = AF_INET;//ipv4 addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");//Binding specific ip address addr.sin_port = htons(1234);//Binding port number int result = connect(clientSocket, (const struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)); if (result == -1) { NSLog(@"link error"); }else{ NSLog(@"Successful connection"); }
7. Send data
//send data char *msg = "hello world"; ssize_t len = send(clientSocket, msg, strlen(msg), 0); NSLog(@"Successful transmission %zd byte",len); char buff[1024]; len = recv(clientSocket, buff, 1024, 0); NSLog(@"Successful reception%zd byte",len,buff);
8. results