After understanding the computer foundation and the history of Linux, I believe that I can start to learn Linux through the following knowledge.
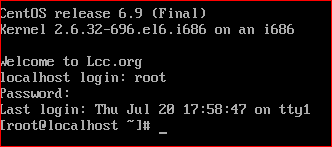
1) How to log on to Linux?
login: User name + Enter
Password: Password + Enter
2) What is a terminal?
A Computer terminal is a machine that allows users to input data and display their calculation results. Some terminals are all electronic and some are electromechanical. It is also called terminal.
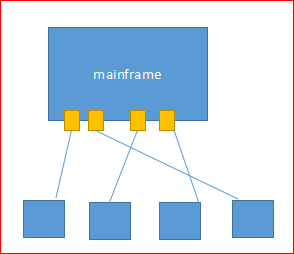
Linux is multi-user and multi-task, in the early days, a Unix host connected to multiple terminals, so that each end user can use it.
Linux also simulates and implements UNIX terminal functions:
Physical Terminal: Console
Virtual Terminal: / dev/tty# [1,7]
Graphic terminal: / dev/tty7
Analog terminal: / dev/pts/# [1,+oo)
3) User Interface: Interface to Interact with Kernel
In Windows: Desktop
Users only need to double-click the icon to complete user-kernel interaction
In Linux:
Desktop: Gnome, KDE, XFCE (for embedded environments)
Users only need to double-click the icon to complete user-kernel interaction
Command line: provided by sh,bash,csh,zsh,ksh programs
Enter the command + Enter key to complete user-kernel interaction
4) Philosophical Thought of Linux
1. Everything is a file, and almost all resources are mapped to files: e.g. devices
2. Complicated programs consist of many single-purpose small programs, such as pipelines.
3. Avoid interacting with users and implement shell programming
4. Text can be configured by text editing commands
5) document:
Failure to complete path mapping
6) Directory:
Complete path mapping
7) File name
1. Case-sensitive character
2, / Can't be a filename, / A path separator
3. Less than 255 characters in length
4. Hidden Files Beginning with.
5. See the name and meaning, abbreviation of the word; the command of copy is cp
8) path
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts
Working Directory: Current Directory
/ Refers to network-scripts
Upper Catalogue:
. / refers to sysconfig
Relative path: Start with the current directory
./ifcfg-eth0
Absolute Path: Start at the Root
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
9) Composition of procedures
Instruction + data (from files, variables, arrays, linked lists)
Algorithms + Data Structures
Binary files, library files, configuration files, help files
10) Format of commands
Order:
Command refers to a whole set of commands, options and parameters.
Command also refers to only the first word "command"
On the command line, type the command and press Enter:
The shell program parses commands, parses commands, requests the kernel to allocate CPU time slices and kernel resources to run as a process (dynamic)
The process of shell parsing commands: from the defined PATH environment variables, from left to right to find whether there is this command in the directory, find it, record it in the cache for second search, if not, BASH command error.
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# cat /etc/issue #The command is cat, \S Kernel \r on an \m [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# echo $PATH #When you enter a command, the shell program looks left-to-right from the path of the variable /usr/local/nginx/sbin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
The location of the command:
Command: in bin
Management commands: in sbin
The format of the command:
windows: EXE,MSI
linux: ELF
Type of command:
The command that comes with the shell: there is no corresponding program file under all paths of the file system
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# type cd cd is a shell builtin
External commands: There are separate executable files
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# type cat cat is /usr/bin/cat
Options: One or some of the functions used to enable or close commands
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# cat /etc/fstab # # /etc/fstab # Created by anaconda on Fri Feb 24 02:58:22 2017 [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# cat -n /etc/fstab #As you can see clearly, - n is enabled to view the number of each line. 1 2 # 3 # /etc/fstab 4 # Created by anaconda on Fri Feb 24 02:58:22 2017
Short options: - c,-l,-h, separated by spaces between multiple options
Multiple options can be merged, for example: - L - H = h l, and the merged results will remain unchanged
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ls -l -h / total 1.5M drwxr-xr-x 10 root root 4.0K Jun 28 15:19 app -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.4M Jul 3 16:04 app.tar.gz lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Feb 24 10:58 bin -> usr/bin dr-xr-xr-x. 4 root root 4.0K Mar 3 12:27 boot drwxr-xr-x 3 nginx nginx 4.0K Jun 2 21:26 cache [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ls -lh / total 1.5M drwxr-xr-x 10 root root 4.0K Jun 28 15:19 app -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.4M Jul 3 16:04 app.tar.gz lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Feb 24 10:58 bin -> usr/bin dr-xr-xr-x. 4 root root 4.0K Mar 3 12:27 boot drwxr-xr-x 3 nginx nginx 4.0K Jun 2 21:26 cache
Long option: -- character,--human-readable
Long options cannot be merged, incorrect combinations will occur, and multiple options are separated by spaces
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ls --all --human-readable . a.txt .bash_profile bin .config fstab link_test1 mariadb-5.5.56-linux-i686.tar.gz .pip .rnd .tcshrc tomcat .. .bash_history .bashrc b.sh c.sh gentoo .local .mysql_history .pki slackware test1 tomcat1 .ansible .bash_logout .bashrc_docker .cache .cshrc .lesshst manifests passwd .pydistutils.cfg .ssh tmpfile .viminfo [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ls --all--human-readable ls: unrecognized option '--all--human-readable' Try 'ls --help' for more information. [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ls --allhuman-readable ls: unrecognized option '--allhuman-readable' Try 'ls --help' for more information.
Mixed use:
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ls --all -lh total 207M drwxr-xr-x. 17 root root 4.0K Jul 28 17:33 . dr-xr-xr-x. 25 root root 4.0K Jul 28 14:54 .. drwx------ 3 root root 4.0K Jun 14 16:23 .ansible -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5 Jul 13 10:06 a.txt -rw------- 1 root root 20K Jul 28 18:14 .bash_history -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 18 Dec 29 2013 .bash_logout -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 203 Jul 10 08:45 .bash_profile
Parameter: The action object of the command
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ls a.txt bin b.sh c.sh fstab gentoo link_test1 manifests mariadb-5.5.56-linux-i686.tar.gz passwd slackware test1 tmpfile tomcat tomcat1 [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ls /tmp 123.file systemd-private-5dcdf14753784b8d848b77111bf5ef1e-systemd-machined.service-2X5usM tmp.37EDkMuqcT Aegis-<Guid(5A2C30A2-A87D-490A-9281-6765EDAD7CBA)> systemd-private-a5389471547d457d95c6184b005585f9-named.service-Bjy16G tmp.KEBXHvNPLz mykernel systemd-private-a5389471547d457d95c6184b005585f9-ntpd.service-Jqrn5o tmp.XESks7mpp9 systemd-private-5dcdf14753784b8d848b77111bf5ef1e-named.service-U672aF tmp.1GRvDKa1HN
When different parameters are given, the results are not the same.
The functions of the ls command are: list directory contents list files in directories, pass different parameters, and list files in different directories. If there are no parameters, the default is the current directory.