1. DDL Operation Database
Keyword should be capitalized. For easy memory, this article is in lower case.
DDL(DATA Definition Language): A data definition language used to define database objects.
1. Create a database
create database db1; #Create a database named mydb create database if not exists db2; #If db2 does not exist, create the database db2 create database db3 character set gbk; #Create a database db3 and make the character set gbk -- Comprehensive: If db4 If it does not exist, create it and set the character set to utf8(!No utf-8) create database if not exists db4 character set utf8;
2. View the database
show databases; # Query the names of all databases show create database db1; #Query character set of created database db1
3. Modify the database
alter database db2 character set utf8; #Modify database db2 character set to utf8
4. Delete database
drop database db4; #Delete database db4 drop database if exists db3; #Determine if db3 exists and delete it
5. Using databases
use db1; # Using database db1 select database(); #View the database in use
2. DDL Operational Data Table
The table structure in a library can only be manipulated if a database is used.
1. Create tables
Format Tables
create table table table name (
Column Name 1 Data Type 1, ##Field Comments can be added here
Column Name 2 Data Type 2, ##Here you can add field comments
...
Column Name n Data Type n ##Field Comments can be added here
); ##The last column does not need to be commas
For example:
create table student ( id int, -- number NAME varchar(20), -- Full name gender char(8), -- Gender birthday date -- Birthday );
MySQL data type
There are many types of data, and here are a few more fundamental ones.
Text correlation
- varchar(m): A variable-length string that takes up a few characters, m between 0 and 65535.
- char(m): A fixed-length string that will take up all characters regardless of how many they are used. The extra characters will be replaced by empty characters, m between 0 and 255.
This article is recommended for chars and varchar s: A deep analysis of the differences between char and varchar types
Number correlation
- int: Integer type.
- double: double precision floating point type.
- float: Single-precision floating-point type.
Time-dependent
-
Date: The date type, which contains only the year, month and day: yyyy-MM-dd.
-
Time: The type of time, consisting of only minutes and seconds: HH:mm:ss.
-
datetime: both date and time types, including year, month, day, time, second: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.
-
Timestamp: The timestamp format is the same as above. If this field is not assigned, the system default time is automatically assigned.
Copy Table
create table new_stu like old_stu; # Operation of copying tables
2. View Table
show tables; # Query all table names in the database
desc student; # Structure of query table student
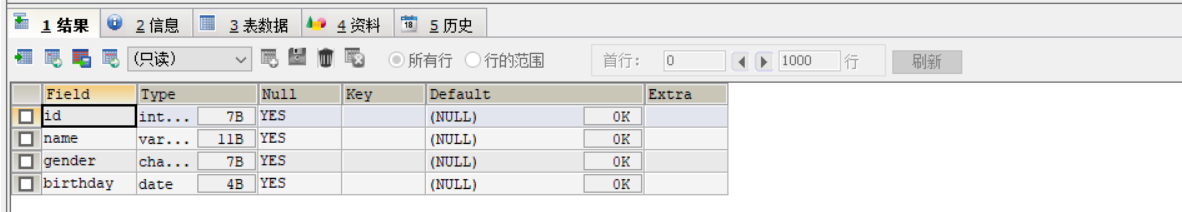
show create table student; #View student's create table SQL statement
3. Delete tables
drop table student; #Delete table student drop table if exists student; #Determine if student exists and delete
4. Modify tables
Modify Table Name
alter table student rename to stu; # Rename the student table to stu rename table student to stu;
Modify Character Set
alter table stu character set gbk; # Modify Character Set to gbk
Add Table Columns
alter table stu add address varchar(20); # Add a column named address with the data type varchar
Modify Column Type
alter table stu modify address char(10); # Modify the data type of address to char
alter table rename column
alter table stu change address addr char(10); #Change column name to addr and data type to char
Delete Columns
alter table stu drop addr; # Delete addr column

