The basic operation of SQL is nothing more than adding, deleting and modifying (CRUD). According to the classification of operation objects, it can be divided into three categories: library operation, table operation and data operation.
Library operation
New database
CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] db_name [library options]
The library option is used to constrain the database and is divided into two options.
Character Set Setting: CHARACTER SET Specific Character Set (Data Storage Encoding Format): Common Character Sets: GBK and UTF8
Proofreading Set Setting: COLLATE Specific Proofreading Set (Data Comparing Rules)
-- Create a name of db The database, and set the character set to _____________ utf8 CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS db CHARACTER SET utf8;
Note that the names of the databases created here cannot be keywords (characters already used) or reserved words (which may be used in the future)

If you want to use keywords or reserve words, you need to use back quotation marks (usually under Esc on the keyboard, output in English).
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `database` CHARACTER SET utf8;
Of course, you can also create a database of Chinese names (not recommended)
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `database `CHARACTER SET utf8;
view the database
SHOW DATABASES [LIKE 'pattern']
Patterns are matching pattern s
% Represents matching multiple characters
_ Represents matching a character
-- View all databases SHOW DATABASES;
-- View to information_Starting databases need to be aligned_Transference SHOW DATABASES LIKE 'information\_%';
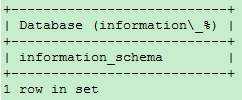
-- View to information Beginning database, equivalent to information% SHOW DATABASES LIKE 'information_%';
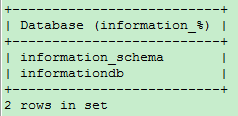
View database creation statements
SHOW CREATE DATABASE db_name
-- view the database db Creative Sentences SHOW CREATE DATABASE db;
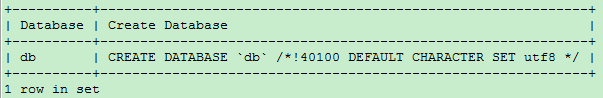
Update database
ALTER DATABASE db_name [Library Options]
-- modify the database db Character set ALTER DATABASE db CHARACTER SET gbk;
Delete the database
DROP DATABASE [IF EXISTS] db_name
-- delete db data base DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS db;
Table operation
New Data Table
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] tbl_name(
col_name type,
col_name type
)
Any table design must specify a database
Display designation
-- Establish student surface CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS db.student ( id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, name VARCHAR(10), age TINYINT )
Implicit designation
-- Specify a database USE db; -- Establish student surface CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS student ( id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, name VARCHAR(10), age TINYINT )
View data tables
View all tables
SHOW [FULL] TABLES [FROM db_name] [LIKE 'pattern']
The FULL modifier displays the second output column, which is BASE TABLE for a table and VIEW for a view.
SHOW TABLES;
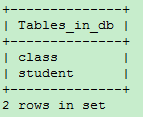
SHOW FULL TABLES;
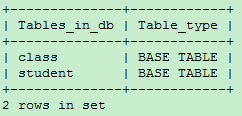
View partial tables based on matching patterns
-- View to s The beginning of the table SHOW TABLES LIKE 's%';
View table creation statement
SHOW CREATE TABLE student;
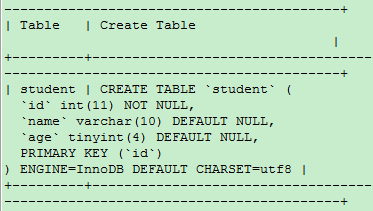
View table structure
DESC student;

Update data table
Modify table name
RENAME TABLE tbl_name TO new_tbl_name
[, tbl_name2 TO new_tbl_name2] ...
One or more tables can be renamed
-- take student Rename to teacher RENAME TABLE student to teacher;
New field
There are many operations for fields, including adding, modifying, renaming and deleting fields.
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD [COLUMN] col_name type [FIRST | AFTER col_name ]
FIRST: Represents the first place in the insert table
AFTER: Indicates insertion after a field by default after the last field
-- stay name Insert after field grade field ALTER TABLE class ADD COLUMN grade VARCHAR(10) AFTER name;
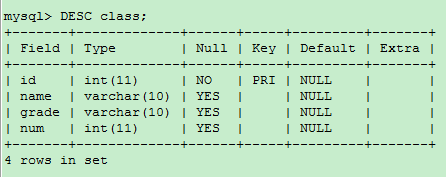
Modify fields
ALTER TABLE tbl_name MODIFY [COLUMN] col_name type [FIRST | AFTER col_name ]
-- modify grade Length of field ALTER TABLE class MODIFY COLUMN grade VARCHAR(20);
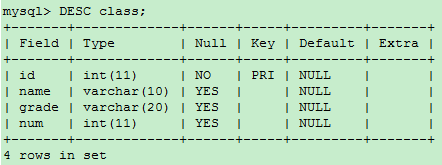
Rename fields
ALTER TABLE tbl_name CHANGE [COLUMN] old_col_name new_col_name type [FIRST | AFTER col_name ]
-- Modify table class Of num The field name is total ALTER TABLE class CHANGE COLUMN num total int(11);
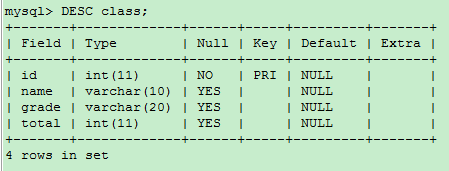
Delete field
ALTER TABLE tbl_name DROP [COLUMN] col_name
-- delete class Table total field ALTER TABLE class DROP COLUMN total;
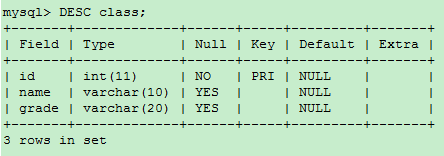
Delete data tables
DROP TABLE [IF EXISTS] tbl_name [, tbl_name] ...
You can delete one or more tables
-- delete class surface DROP TABLE IF EXISTS class;
Data manipulation
New data
INSERT [INTO] tbl_name [(col_name,...)] VALUES ({expr | DEFAULT},...)
The column name is not specified explicitly. It needs to be in the same order as the fields in the data table.
-- student Table inserts a piece of data INSERT INTO student VALUES(1, 's1', 20);
Specified column name
-- According to the ranking and order, go to _____________ student Table inserts a piece of data
INSERT INTO student(name, age) VALUES('s2', 20);
View data
Update data
Update sheet
UPDATE [LOW_PRIORITY] [IGNORE] tbl_name
SET col_name1=expr1 [, col_name2=expr2 ...]
[WHERE where_definition]
-- To update student surface name by s2 Of age field value UPDATE student SET age = 22 WHERE `name` = 's2';
Update multiple tables
UPDATE [LOW_PRIORITY] [IGNORE] table_references
SET col_name1=expr1 [, col_name2=expr2 ...]
[WHERE where_definition]
UPDATE class, student SET student.age = 23 WHERE student.classId = class.id;
Delete data
DELETE FROM tbl_nam [WHERE where_definition]
-- Delete name s1 Data DELETE FROM student WHERE student.`name` = 's1'