This article is the blog Mysql Series II: CentOS 7.4 install Mysql 5.7.28 source code
There are many ways to install mysql. Take Centos7 as an example, you can download the compiled binary code on the official website for installation, and you can download the rpm package on the official website for installation. In this paper, we introduce the self compilation and installation of the download source code on the official website.
According to the source code downloaded from MySQL series I, we started to install MySQL source code. We hope that you can read more about the installation method from the document on the official website and learn the essence. The installation method and order are not unique. The following content is for reference.
Basic environment:
yum install -y ntp wget curl lrzsz vim sysstat iftop pcre pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel
Compile installation environment:
yum -y install wget gcc gcc-c++ cmake openssl-devel ncurses-devel zlib-devel
Download and decompress on the official website:
mysql-5.7.28.tar.gz and mysql-boost-5.7.28.tar.gz cd /data/app_install/package tar zxvf mysql-5.7.28.tar.gz mkdir mysql-boost tar zxvf mysql-boost-5.7.28.tar.gz -C mysql-boost
Create mysql user:
groupadd mysql useradd -g mysql -s /sbin/nologin -d /data/app_install/mysql_3306 mysql
Create mysql related directory:
MKDIR - P / data / logs / MySQL MKDIR - P / data / app? Install / MySQL? Install directory MKDIR - P / data / app? Install / MySQL? 3306 / conf my.cnf configuration file directory MKDIR - P / data / APP ﹐ install / MySQL ﹐ 3306 / tmp mysql.sock directory MKDIR - P / data / data / data? MySQL database file directory
Compile configuration:
cmake . -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/data/app_install/mysql_3306 -DMYSQL_DATADIR=/data/data/data_mysql -DWITH_BOOST=/data/app_install/package/mysql-boost/mysql-5.7.28/boost/boost_1_59_0 -DSYSCONFDIR=/data/app_install/mysql_3306/conf -DWITH_INNOBASE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 -DWITH_PARTITION_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 -DWITH_FEDERATED_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 -DWITH_BLACKHOLE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 -DWITH_MYISAM_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 -DENABLED_LOCAL_INFILE=1 -DENABLE_DTRACE=0 -DDEFAULT_CHARSET=utf8mb4 -DDEFAULT_COLLATION=utf8mb4_general_ci -DWITH_EMBEDDED_SERVER=1
Compile:
make
Installation:
make install
Profile:
cd /data/app_install/mysql_3306/conf vim my.cnf [client] port = 3306 socket = /data/app_install/mysql_3306/tmp/mysql.sock [mysqld] port = 3306 socket = /data/app_install/mysql_3306/tmp/mysql.sock basedir = /data/app_install/mysql_3306 datadir = /data/data/data_mysql pid-file = /data/app_install/mysql_3306/mysql.pid user = mysql bind-address = 0.0.0.0 server-id = 1 init-connect = 'SET NAMES utf8mb4' character-set-server = utf8mb4 back_log = 300 max_connect_errors = 6000 open_files_limit = 65535 table_open_cache = 128 max_allowed_packet = 4M binlog_cache_size = 1M max_heap_table_size = 8M tmp_table_size = 16M read_rnd_buffer_size = 8M join_buffer_size = 8M key_buffer_size = 4M thread_cache_size = 8 query_cache_type = 1 query_cache_size = 8M query_cache_limit = 2M ft_min_word_len = 4 log_bin = mysql-bin binlog_format = mixed expire_logs_days = 30 log_error = /data/logs/mysql_3306/mysqld-error.log slow_query_log = 1 long_query_time = 1 slow_query_log_file = /data/logs/mysql_3306/mysql-slow.log performance_schema = 0 explicit_defaults_for_timestamp skip-external-locking default_storage_engine = InnoDB innodb_file_per_table = 1 innodb_open_files = 500 innodb_buffer_pool_size = 2048M innodb_write_io_threads = 4 innodb_read_io_threads = 4 innodb_thread_concurrency = 0 innodb_purge_threads = 1 innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 2 innodb_log_buffer_size = 2M innodb_log_file_size = 32M innodb_log_files_in_group = 3 innodb_max_dirty_pages_pct = 90 innodb_lock_wait_timeout = 120 default-time-zone = '+08:00' interactive_timeout = 28800 wait_timeout = 86400 sql-mode= NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION [mysqld_safe] log-error = /data/logs/mysql_3306/mysqld_safe-error.log pid-file = /data/app_install/mysql_3306/mysql.pid
Startup file:
cp /data/app_install/mysql_3306/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
Jurisdiction:
chown -R mysql:mysql /data/app_install/mysql_3306/ chown -R mysql:mysql /data/data/data_mysql/ chown -R mysql:mysql /data/logs/mysql_3306/
Environment variable:
mkdir /data/env cd /data/env vim mysql.env export PATH=$PATH:/data/app_install/mysql_3306/bin vim /etc/profile source /data/env/mysql.env
Initialize database:
– initialize means that a random security password is generated by default, – initialize execute means that no password is generated, and you do not want to find and use random password in the log. You can initialize it in the following way, and then set the password in the security initialization boot
mysqld --defaults-file=/data/app_install/mysql_3306/conf/my.cnf --user=mysql --initialize-insecure
Start mysql:
/etc/init.d/mysqld start
When starting, if there is no log path or permission problem, re create and assign mysql:mysql permission. At the same time, if there is a Starting MySQL. ERROR! The server quit without updating PID file (/data/app_install/mysql_3306/mysql.pid), it is also a permission problem. All involved directory files need mysql:mysql permission except the startup file
Try to log in: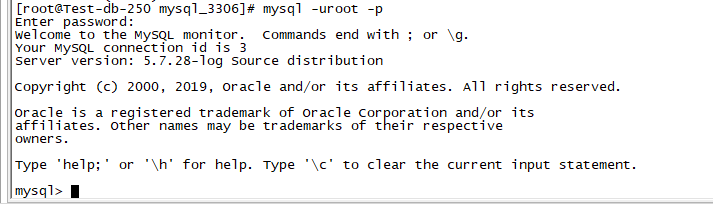
Login without password
Security initialization boot:
When using this function, the mysql process needs to be online, and use the mysql ﹣ secure ﹣ installation command for security initialization and boot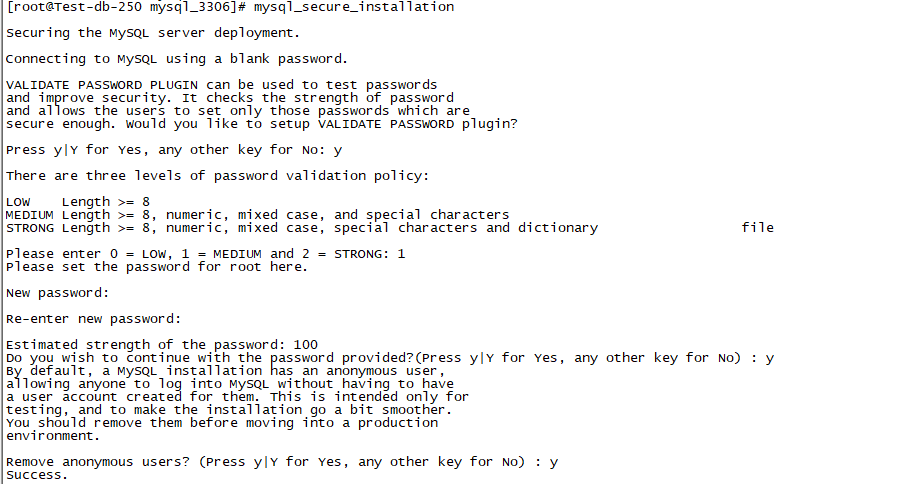
After setting, use the new password to log in again.
Setup self start:
chkconfig --add mysqld chkconfig mysqld on service mysqld start service mysqld stop service mysqld restart
In fact, Centos7 can already use system D to manage services and support self startup. mysql can also be used. For example, to install using the source version, you need to add the compile item - dwith UU systemd = 1. At the same time, configure a self named file under the directory / etc/systemd/system/mysqld.service.d, and then describe the following contents according to the actual situation:
[Service] LimitNOFILE=*`max_open_files`* PIDFile=*`/path/to/pid/file`* Nice=*`nice_level`* LimitCore=*`core_file_limit`* Environment="LD_PRELOAD=*`/path/to/malloc/library`*" Environment="TZ=*`time_zone_setting`*"
Systemctl daemon reload
It can be seen that the download source installation on the official website supports the service configuration and management of chkconfig+service and systemd+systemctl, which need manual step-by-step practice, which is very helpful to understand the whole principle and process.
If the compiled binary downloaded from the official website is used for installation, only chkconfig+service and systemd+systemctl can be used for service configuration and management. If the rpm package downloaded from the official website is used for yum installation, systemd+systemctl can be directly used for service configuration and management.
After that, you can package the installation process and compiled files into an automatic installation script, install mysql database with one click, and manually configure and compile from scratch every time.
We will talk about some simple and practical commands of mysql in the next section, which are often used in actual combat.