1, mysql database common operations
Account login
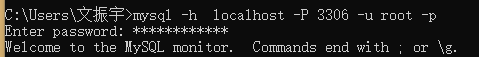
-h specifies the host address of the server, - p specifies the port number, - u specifies the current shell user, - p is the password, which can not be entered on the command line
Create database
The database is a collection of tables. The database server can contain multiple databases. The logical relationship is as follows:
Database server - > Database - > Table - > row.
Create a database named company
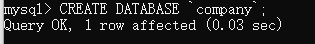
1. About sql statements: case insensitive under windows, case sensitive under linux, default to\ G. \ g end.
2. When the database name contains special characters such as period (.), the anti marking character ` ` needs to be used.
View current data directory
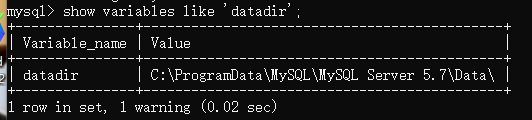
mysql> show variables like 'datadir';
View databases that you have access to

mysql> show databases;
mysql data type
| integer | Range | Byte size |
|---|---|---|
| BIT | Unsigned [0255], signed [- 128127] | 1 |
| TINYINT | Integer [0255] | 1 |
| SMALLINT | Unsigned [065535], signed [- 3276832767] | 2 |
| MEDIUMINT | Unsigned [0224-1], signed [- 223,2 ^ 23-1]] | 3 |
| INT | Unsigned [0232-1], signed [- 231,2 ^ 31-1] | 4 |
| BIGINT | Unsigned [0264-1], signed [- 263, 2 ^ 63 - 1] | 8 |
Note: one byte is 8-bit binary
| floating-point | Range | Byte size |
|---|---|---|
| DECIMAL(M,D) | — | It is determined by M (the length of the whole number, including the decimal point, the number of digits to the left of the decimal point, the number of digits to the right of the decimal point, but excluding the minus sign) and D (the number of digits to the right of the decimal point). M defaults to 10 and D defaults to 0 |
| FLOAT | (-3.402823466E+38 ,-1.175494351E-38),0,(1.175494351E-38 - 3.402823466E+38) | 4 |
| DOUBLE | (-1.7976931348623157E+308 - -2.2250738585072014E-308),0,(2.2250738585072014E-308 - 1.7976931348623157E+308) | 8 |
Note: one byte is 8-bit binary
| character string | definition | Byte size |
|---|---|---|
| CHAR | Fixed length string | 0-255 bytes |
| VARCHAR | Variable length string | 0-65535 bytes |
| TEXT | Long text data | 0-65 535 bytes |
BINARY and VARBINARY are similar to CHAR and VARCHAR, except that they contain BINARY strings instead of non BINARY strings. That is, they contain byte strings instead of character strings. This means that they have no character set, and they sort and compare numeric values based on column value bytes.
In addition, it also includes JSON, time and other data types.
2, Table operation
Create table

mysql> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `CUSTOMERS` (`id` int unsigned
AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
-> `first_name` varchar(20),
-> `last_name` varchar(20),
-> `country` varchar(20)
-> ) ENGINE=InnoDB;
The content is explained as follows:
- ``The meaning is shown above.
- IF NOT EXISTS, do not create if it exists, and warn if it exists.
- AUTO_INCREMENT means that the key increases automatically; PRIMARY KEY stands for PRIMARY KEY.
- InnoDB is the storage engine and the default engine. In addition, MYISAM is commonly used.
- There is no punctuation in the last place of the table definition. country varchar(20)
View table structure
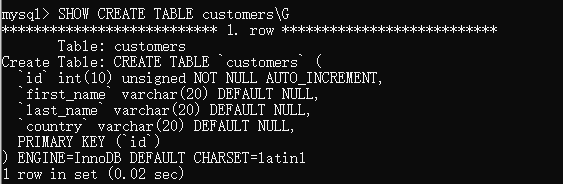
mysql> SHOW CREATE TABLE customers\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: customers
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `customers` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`first_name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`country` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Explanation: \ the function of G is to turn the detected structure 90 degrees into vertical
perhaps

mysql> DESC customers;
Clone a new table

mysql> CREATE TABLE new_customers LIKE customers;
3, Add, delete, modify and query
insert data
INSERT IGNORE INTO Table name (field) VALUES(value)
Note: if the declared unique field is repeated, the IGNORE statement will be executed and the new data will be ignored, but the id will still increase by 1.
INSERT INTO Table name (field) VALUES(value) ON DUPLICATE KEY (operation)
Note: if you want to trigger some operations when a unique field is encountered, use ON DUPLICATE KEY
update fields
UPDATE Table name SET (field)=(value) WHERE (condition)
Delete field
DELETE FROM Table name WHERE (condition)
Delete table
TRUNCATE TABLE (Table name)
query
IN operation: check whether a value is IN a group of values.
mysql> select * from Table name where field IN (Candidate value 1,Candidate value 2,......,Candidate value n);
BETWEEN... AND: select according to the range
mysql>select * from customer where field between Left interval and Right interval;
Note: both the left section and the right section can be obtained.
NOT: negate the condition and select the item that does NOT meet the condition.
Field matching
Simple matching
The underscore () matches exactly one character, the percent sign (%) matches greedily, and matches as many characters as possible.
#Match all names with M mysql> select * from customer where first_name like '%M%'; #Match all names with the first three letters of MAR and the name length of 4 mysql> select * from customer where first_name like 'MAR_';
Regular matching
# Writing method 1 mysql> select * from Table name where field rlike 'regular expression '; # Writing method 2 mysql> select * from Table name where field regexp 'regular expression ';
For common usage, see regular expression syntax
Note. * represents greedy matching. *? Represents the minimum match