Pycharmlog in to MySQL
1. Create project
2. Click the Database button on the right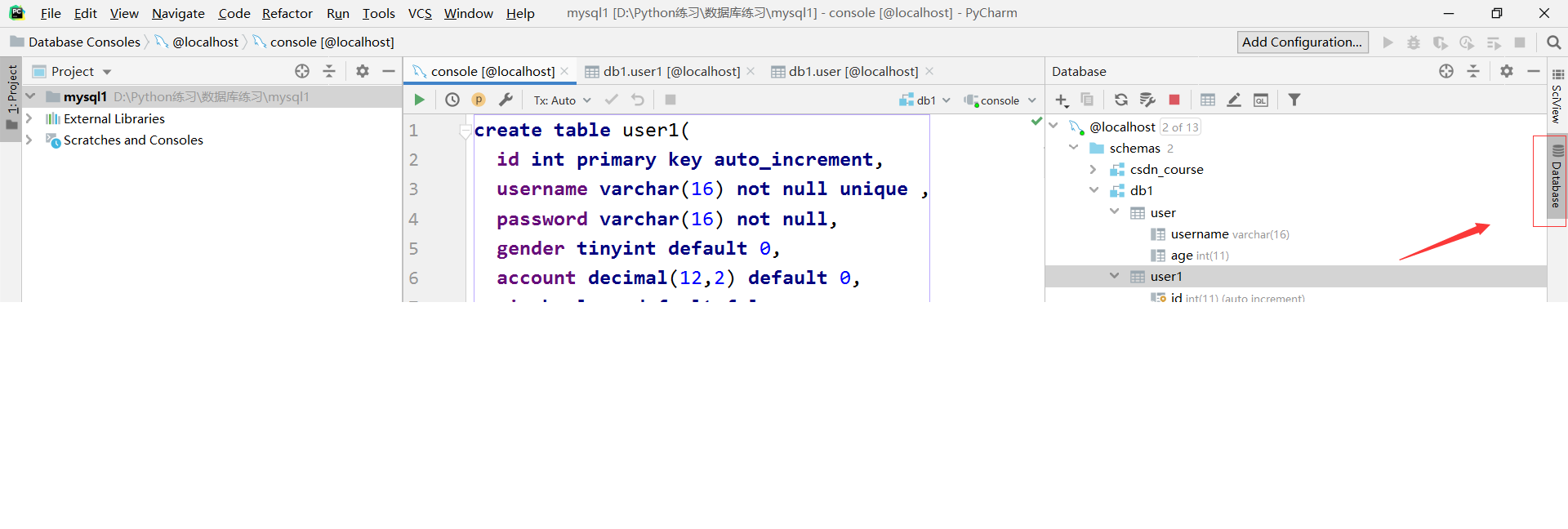 3. Enter the user name and password of mysql in the pop-up edit box
3. Enter the user name and password of mysql in the pop-up edit box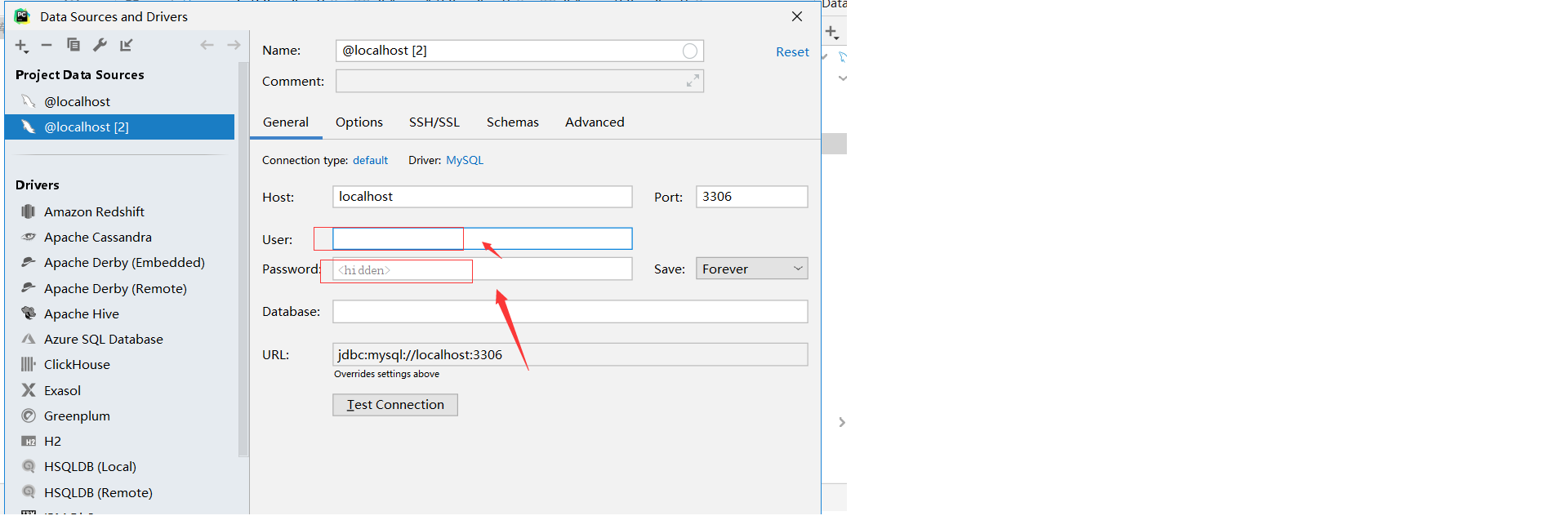 If Server returns invalid timezone. Go to 'Advanced' tab and set 'serverTimezone' profile error is prompted, please refer to: Problem solving
If Server returns invalid timezone. Go to 'Advanced' tab and set 'serverTimezone' profile error is prompted, please refer to: Problem solving
Database common field constraints
| Constraint type | Keyword |
|---|---|
| Primary key self increment | primary key auto_increment |
| Can not repeat | unqiue |
| Can not be empty | not null |
| Default value | default |
Code:
create table user1( id int primary key auto_increment, username varchar(16) not null unique , password varchar(16) not null, gender tinyint default 0, account decimal(12,2) default 0, vip boolean default false );
Database addition, deletion, modification, query and other commands
insert data
Syntax: insert into [table name] value ([data 1], [data 2] );
Code:
insert into user3 (username,password,createDatetime) values ('Zhang Wei','pass1','2019-07-11'),('Wang Wei','pass2','2019-07-11'), ('Wang Fang','pass3','2019-07-12'),('Li Wei','pass4','2019-07-11'), ('Xiu Ying Wang','pass5','2019-07-12'),('Grace','pass6','2019-07-11'), ('Li Na','pass7','2019-07-10'),('Xiu Ying Zhang','pass8','2019-07-10'), ('Liu Wei','pass9','2019-07-12'),('Aman Chang','pass10','2019-07-10');
Modifying data
Syntax: update table name set field 1 = value, field 2 = value where [conditions]
Code:
update user1 set username='name2' where id=1;
Delete data
Syntax:
delete from [table name] where [condition]
Code:
delete from user1 where id=1;
Other
Add a new field in the table. Specify the type and constraint of the new field
alter table table name add field name type constraint;
Modify the field in the table, specify the modified field and the modified name, field type and constraint
alter table table name change original field name new field name type constraint;
Delete field in table
alter table drop field name;
Modify the name of the table
rename table [original table name] to [new table name]
Code:
alter table user2 add tel tinyint unique; alter table user2 change tel tel varchar(16) unique; alter table user2 drop tel; rename table user2 to user3;
Query statement
1. View all data in the table
select * from [table name]; note: * indicates all fields
Example:
select * from user3;
2. View the specified fields
select field 1, field 2 from table name;
Example:
select username, password from user3;
3. Comparison criteria query
select * from table name where condition;
| condition | command |
|---|---|
| Equal | = |
| Unequal | != |
| Empty | is null |
| Not empty | is not null |
| Greater than (greater than or equal to) | >(>=) |
| Less than (less than or equal to) | <(<=) |
Example:
select * from user3 where username='Wang Wei'; select * from user3 where username!='Wang Wei'; select * from user3 where createDatetime is not null; select * from user3 where id >=5;
4. Fuzzy condition query
select * from table name where field like expression;
| condition | command |
|---|---|
| % | Match any number of characters |
| _ | Match a character |
Code:
select * from user where username like '%king%' select * from user where username like 'king_'
5. Scope query
select * from table name where field in ([May 1], [May 2]...) ;
Code:
select * from user where username in ('Wang Wei','Li Na');
6. Logical operators
| condition | command |
|---|---|
| and | And |
| or | or |
Code:
select * from user3 where username='Wang Wei' or username='Li Na';
7. grouping
Format:
select * from table name where condition group by field 1, field 2 ;
Explain:
- By which field, which field will not be repeated.
- group by should be written after where
Code:
select count(*),createDatetime from user3 group by createDatetime;
Format:
select * from table name where condition group by field 1, field 2 having [conditions];
Explain:
where is to filter the results of select * from
having is to filter the final result of group by
Code:
select count(*),createDatetime from user3 group by createDatetime having count(*) > 3;
8. ranking
Format:
select * from table name where condition group by field 1, field 2 having [condition] order by [field 1] asc|desc, [field 2] asc|desc;
Explain:
- Meaning of asc and desc asc: ascending (default) desc: descending
- The sorting priority is based on field 1. If field 1 is the same, the sorting priority is based on field 2
Code:
select * from user3 order by createDatetime desc,id asc;
9. Paging (limit)
Format:
select * from table name where condition group by field 1, field 2 having [condition] order by [field 1] ASC DESC, [field 2] ASC desc limit [start index], [number of data];
Code:
select * from user3 limit 3,5;

