1. MySQL installation (install using yum)
yum install mysql* –y
Linux MySQL data is stored in / var/lib/mysql by default/
[root@study ~]# cd /var/lib/mysql/ [root@study mysql]# ll //Total consumption 20488 -rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 10485760 5 23 23:55 ibdata1 -rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 5242880 5 23 23:55 ib_logfile0 -rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 5242880 5 23 / 06:26 ib_logfile1 drwx------. 2 mysql mysql 4096 5 23 / 06:26 mysql srwxrwxrwx. 1 mysql mysql 0 5 23 23:38 mysql.sock drwx------. 2 mysql mysql 4096 5 23 / 06:26 test [root@study mysql]#
2. Command classification
DDL Defining data objects CREATE ALTER DROP DML Defining language INSERT UPDATE DELETE DCL Operation language GRANT REVOKE
3. Database initialization (the database will be initialized when the database is started for the first time, and the database default user name root password is empty)
Log in to the local database mysql -u root -p Log in to the remote database mysql -u username -p password -H host
4. Database operation (create, delete)
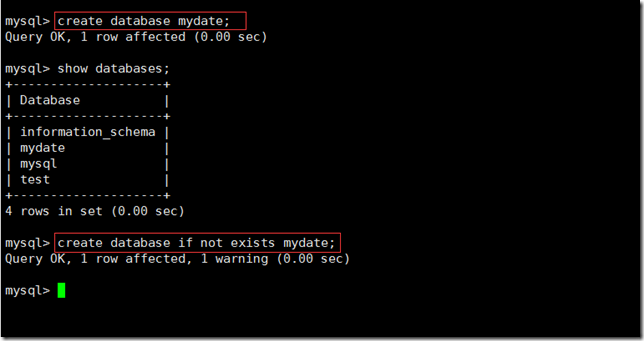
create database db_name; create database if not exists db_name;(If the database does not exist, it will be created and there will be no error)
Delete database
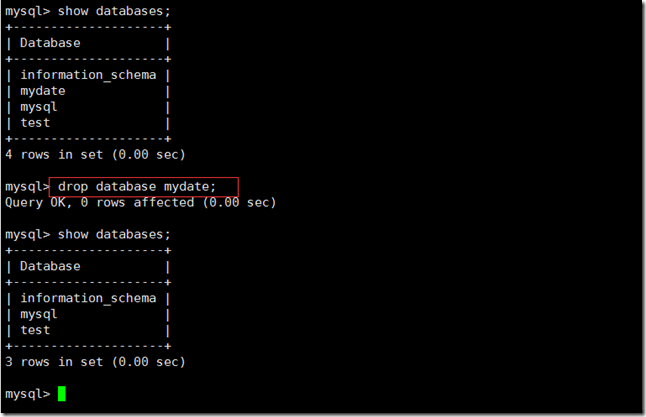
drop database db_name; drop database if exists db_name;(If the database exists, it will be deleted, and no error will be reported)
5. Table operations (create, delete, modify)
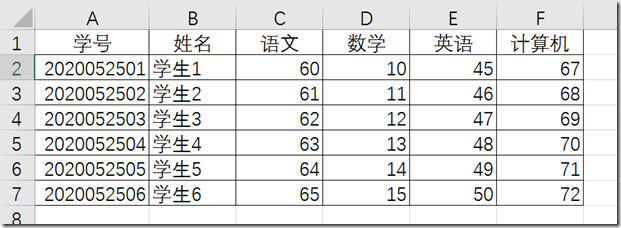
Sample data( students)
Create table
create table db_name.tb_name(col1,col2,col3);
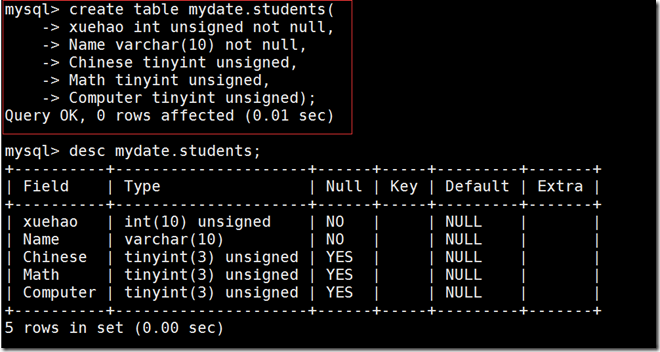
create table mydate.students( xuehao int unsigned not null, Name varchar(10) not null, Chinese tinyint unsigned, Math tinyint unsigned, Computer tinyint unsigned);
Delete table
drop db_name.tb_name;
View tables in the library
show tables from db_name;
View table structure
desc db_name.tb_name;
Modification table
alter table tb_name;
modify
change
add
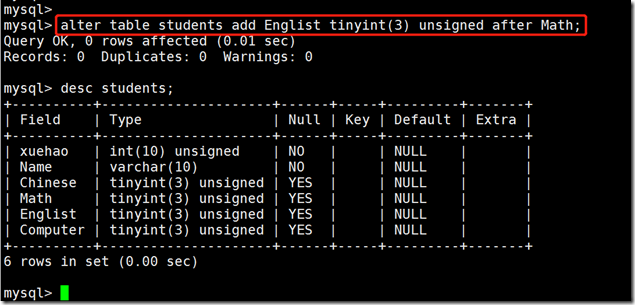
dropFor example: add a field, Englist, after Math
alter table tb_name add Englist tinyint(3) after Math;
Other self exploration
6. Operation of data in the table (insert, delete, modify, query)
insert into,delete,update,select
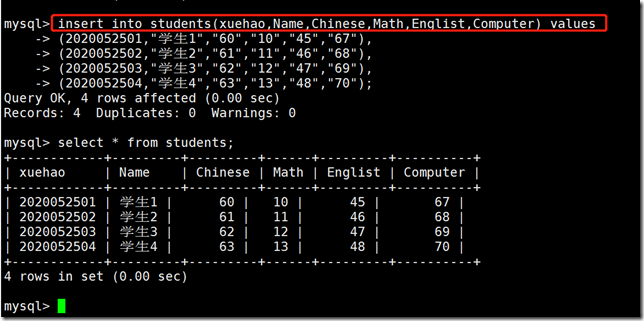
insert data
insert into tb_name (col1, col2...) values|value ("string",num,...),("string",num,...);
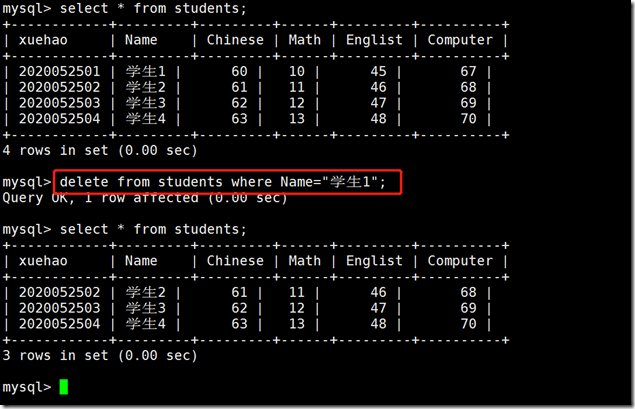
Delete data
delete from tb_name where column = "; (specify the deletion condition where)
Delete student 1
Modify data
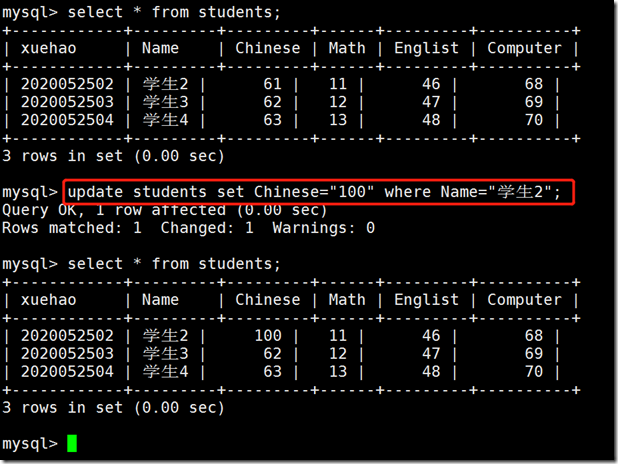
update tb_name set column = "new value" where column =; (specify condition modification)
Revise student 2's Chinese score to 100
Query data
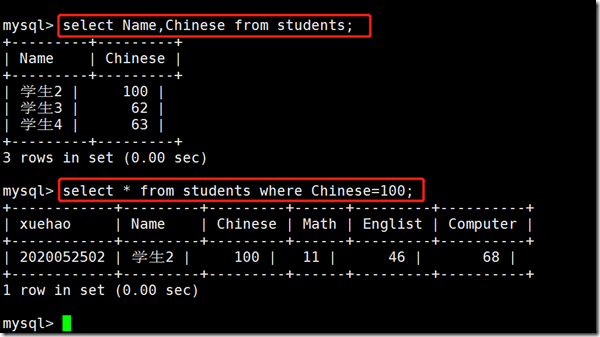
Field query select col1,col2,col3 from tb_name; Data value query select * from tb_name where col="";
The two can also be used together. Here are examples. If you do not delete the field, you can use * instead.
7. User and permission settings
Create user
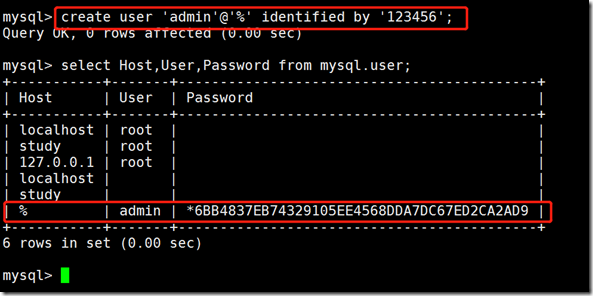
create user 'username'@'host' identified by 'password'; Host is a host that can log in It can be ip, hostname, network (wildcard)_ Any single character,% match all) If all address login flowers are allowed, set host to%
delete user
drop user 'username'@'host';
Permission settings
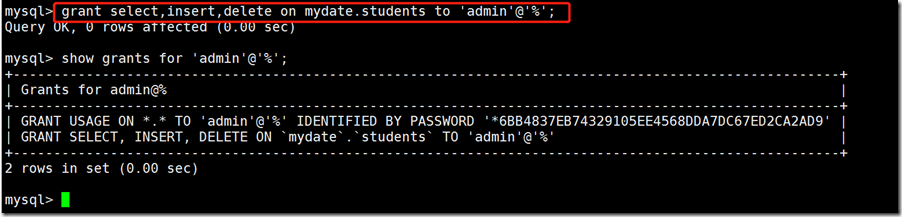
grant pri1,pri2,... on db_name.tb_name to 'username'@'host' [identified by 'password']; Set which database, which table and which user the permission is for ALL PRIVILEGES All data: **
Cancel permission
revoke pri1,pri2,... on db_name.tb_name to 'username'@'host' [identified by 'password'];
Set admin to view, insert and delete the mydate library students table.
8. Field properties
Fields of the table Field name, data type, type decoration (data constraint) character CHAR(10) VARCHAR(10) variable length characters BINARY(n) is case sensitive and stored in binary VARBINARY(n) variable length TEXT(N) long text BLOB(N) case sensitive numerical value Exact value integer TINYINT SMALLINT MEDIUMINT INT BIGINT Modifier, UNSIGNED, UNSIGNED, positive NOT NULL is not empty decimal system DECIMAL float FLOAT DOUBLE date DATE TIME DATETIME STAMP Boolean
There is always one on the way to study and keep fit