Reproduced from: https://blog.csdn.net/caoxiaohong1005/article/details/72571798
1. select into outfield function:
Export data to the specified directory of pc.
2. Syntax:
SELECT ... INTO OUTFILE 'file_name'
[CHARACTER SET charset_name]
[export_options]
export_options:
[{FIELDS | COLUMNS}
[TERMINATED BY 'string']
[[OPTIONALLY] ENCLOSED BY 'char']
[ESCAPED BY 'char']
]
[LINES
[STARTING BY 'string']
[TERMINATED BY 'string']
]
Syntax example:
SELECT customer_id, firstname, surname INTO OUTFILE '/exportdata/customers.txt'
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY '"'
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
FROM customers;
3. Practical operation example: under Mac environment
Building tables:
create table testLoadData(
id bigint(20) not null auto_increment,
username char(10) not null,
age tinyint(3) UNSIGNED not null,
description text not null,
primary key(id),
unique key(username)
)engine=myisam default charset=utf8;
Import data:
LOAD DATA local INFILE '/Users/xxx/Downloads/loaddata.txt' IGNORE INTO TABLE testLoadData
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' ENCLOSED BY '"' LINES TERMINATED BY '\n' ignore 1 lines (username, age, description);
Description: xxx is the local user name
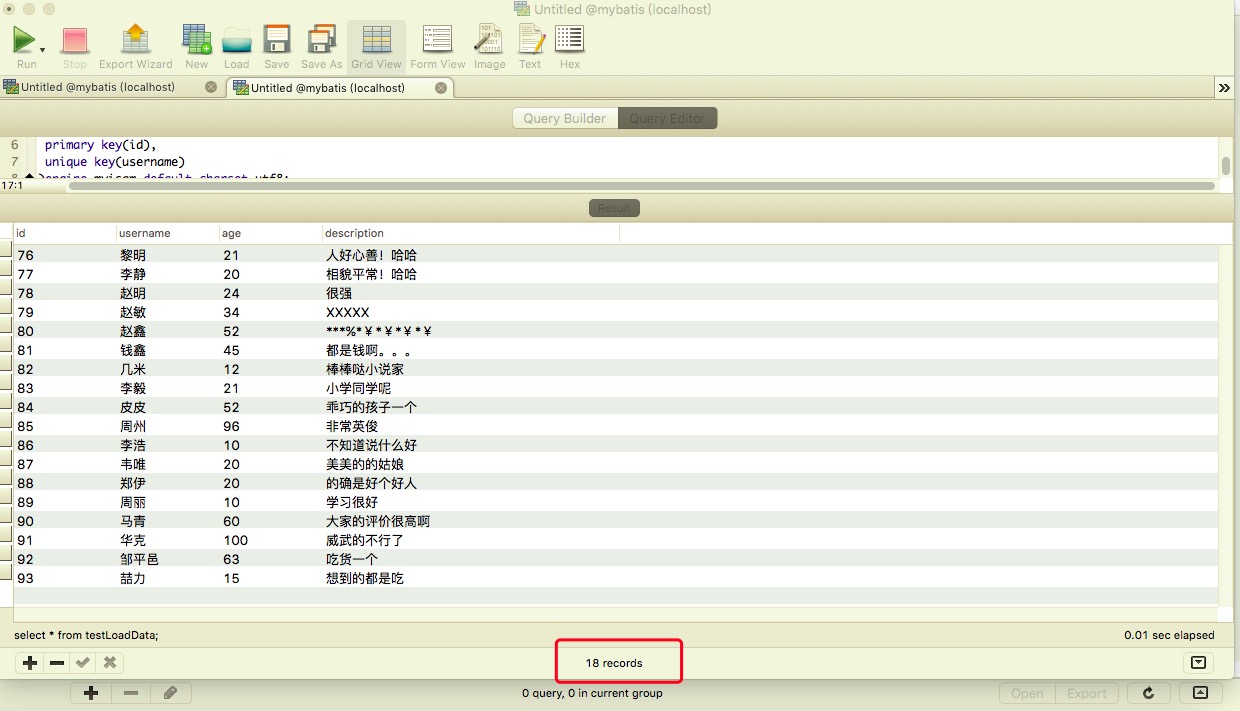
Query import data:
select * from testLoadData
Export data:
SELECT * FROM testLoadData
INTO OUTFILE '/Users/xxx/Downloads/loaddatass.txt' FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY '"' LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
View the corresponding directory: you can find that the above data has been saved in loaddata.txt.
4. Problems encountered:
(1)
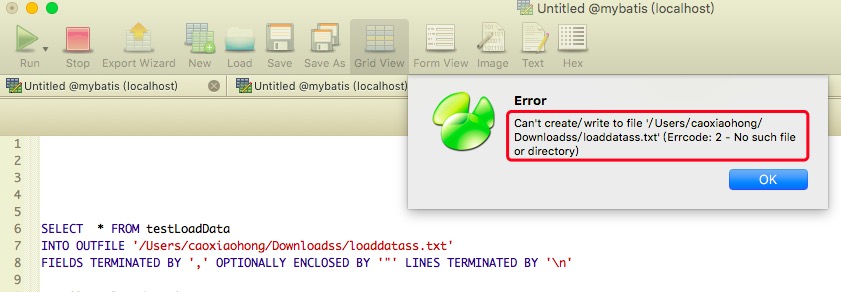
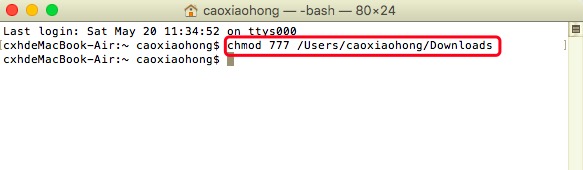
Solution: modify the write permission of the file in the corresponding directory:
Input under terminal:
(2)
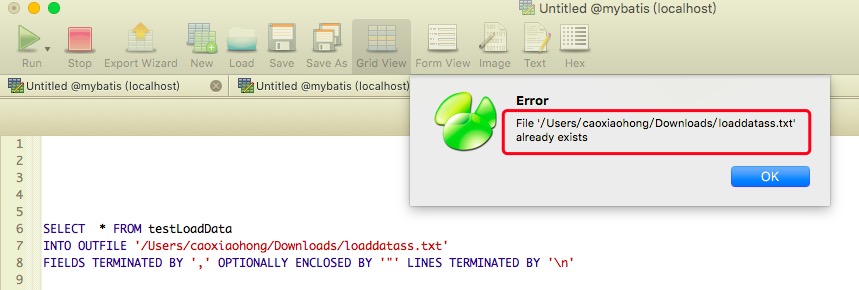
Cause of the error: the file under the path in the sql script already exists. In fact, the file under the sql script should be a file created by MySQL itself, rather than an existing file, so rewrite a file name that does not exist in the directory.