catalogue
(1) The first way is to query through linked list.
(2) The second way is through nested query. ---- two queries.
(2) [choose when otherwise] and where
(3)set tag --- modify some fields
1. Multi table query
1.1 many to one
example: Query student information and class information according to student id
(1) The first way is to query through linked list.
one Create two data tables with logical or physical foreign keys
Class table: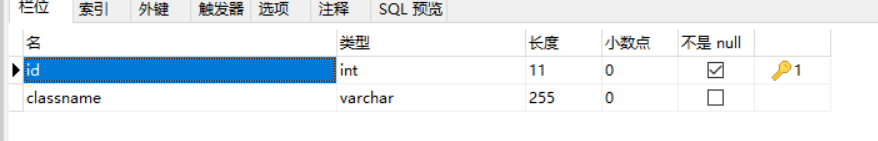
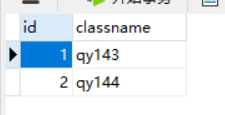
Student form: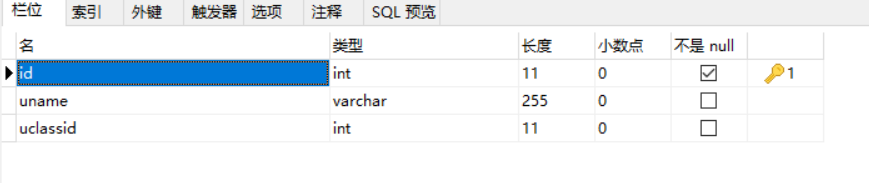
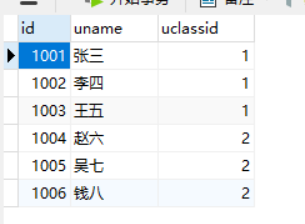
two Entity classes corresponding to common data tables
Class entity class:
public class Cls {
private Integer id;
private String cname;
public Cls() {
}
public Cls(Integer id, String cname) {
this.id = id;
this.cname = cname;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cls{" +
"id=" + id +
", cname='" + cname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Student entity class:
public class Stu {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String classid;
//In the student class, you need to create an entity class of class class!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
private Cls cls;
public Stu() {
}
public Stu(Integer id, String name, String classid, Cls cls) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.classid = classid;
this.cls = cls;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClassid() {
return classid;
}
public void setClassid(String classid) {
this.classid = classid;
}
public Cls getCls() {
return cls;
}
public void setCls(Cls cls) {
this.cls = cls;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Stu{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", classid='" + classid + '\'' +
", cls=" + cls +
'}';
}
}
3. Create student dao layer interface and define method
public interface StuDao {
Stu selectstuandclassbystuid(int id);
}4. Write the sql statement in the corresponding dao interface method in the mapping file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.dao.StuDao">
<select id="selectstuandclassbystuid" resultMap="getstu">
select * from stu s join class c on s.uclassid=c.id where s.id = #{id}
</select>
<!--
<id>Label: the label used by the attribute in the entity class corresponding to the database primary key
<result>Label: the label used by other attributes of the entity class corresponding to the column name of the database
The above applies only to the eight basic types and String Simple properties of type
For entity class attributes, use<association>Complex label
<association>label: property:The variable name corresponding to the entity class in the student class( cls)
javaType: Corresponds to the entity class corresponding to the variable name(Cls)Path of
Written in this label javaType Corresponding entity class(Cls)The relationship between the attribute name of the and the data table name
If entity class(Cls)The property name is the same as the data table name. It can not be written, but it must be in the
<association>Writing in label autoMapping="true"
-->
<resultMap id="getstu" type="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.entity.Stu">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="uname"/>
<result property="classid" column="uclassid"/>
<association property="cls" javaType="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.entity.Cls" autoMapping="true">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="cname" column="classname"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
</mapper>5. Register the mapping file in the configuration file and test it
Registration:
<mappers>
<mapper resource="Mapper/StuMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>Test:
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StuDao stuDao = session.getMapper(StuDao.class);
Stu stu = stuDao.selectstuandclassbystuid(1001);
System.out.println(stu);
}result:
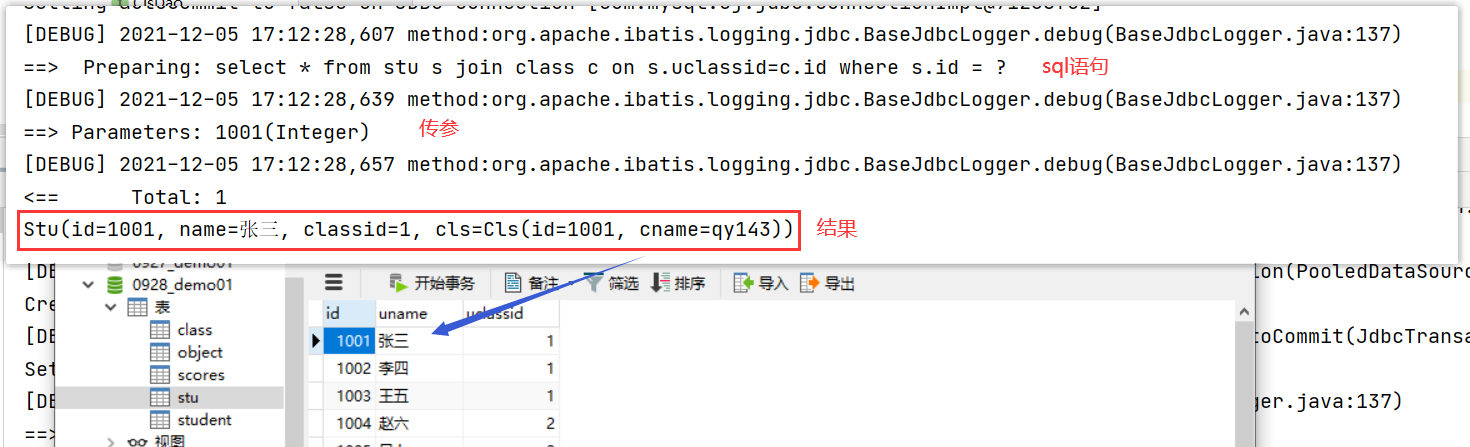
(2) The second way is through nested query. ---- two queries.
one Write the sql statement in the corresponding dao interface method in the student mapping file
<!--
Should sql Statements are based on students only id Find all data in the student data table
-->
<select id="selectstuandclassidbystuid" resultMap="getstuandclassid">
select * from stu where stu.id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap id="getstuandclassid" type="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.entity.Stu">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="uname"/>
<result property="classid" column="uclassid"/>
<!--
column: Corresponds to the foreign key column names of the student data table and the class data table
select: Corresponding to the class in the class mapping file id To find class information sql The corresponding path of the statement
-->
<association property="cls" javaType="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.entity.Cls"
column="uclassid"
select="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.dao.ClsDao.getclassbyclassid">
</association>two Write an sql statement to find class information according to the class id in the class mapping file
<mapper namespace="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.dao.ClsDao">
<!--
Because the attribute name in the class entity class is different from the column name, the second alias method is adopted: the alias of the column name is the same as the attribute name of the entity class
Can also be used resultMap Both methods are OK
-->
<select id="getclassbyclassid" resultType="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.entity.Cls">
select id id,classname cname from class where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>3. Register the mapping files of the two tables in the configuration file And test
Registration:
<mappers>
<mapper resource="Mapper/StuMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="Mapper/ClasMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>Test:
@Test
public void test01()throws IOException {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StuDao stuDao = session.getMapper(StuDao.class);
Stu stu = stuDao.selectstuandclassbystuid(1001);
System.out.println(stu);
} Test results:
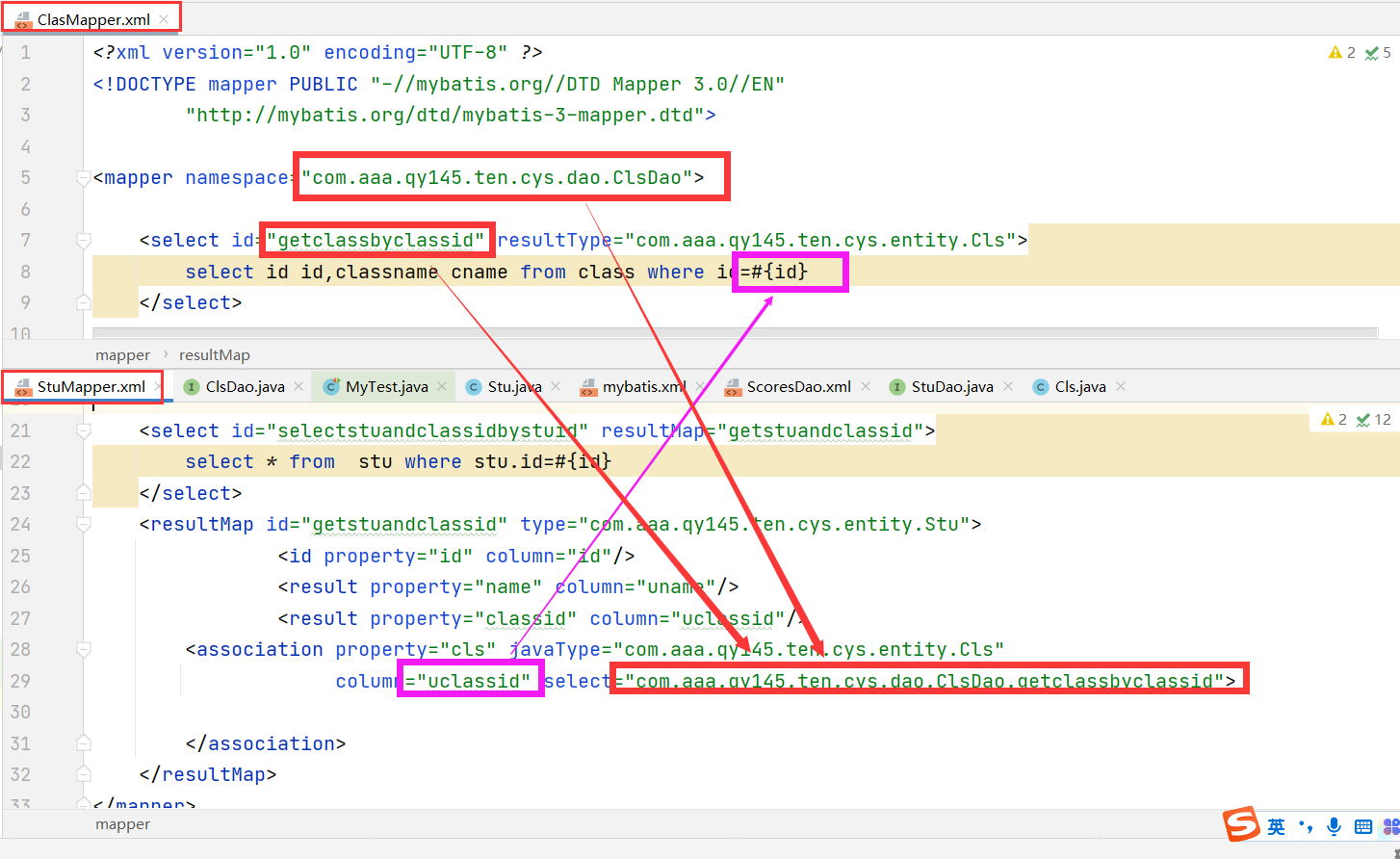
one point two One to many
Example: find class information and all students in the class according to the class id
one Use the many to one data table of the above example
2. Create the entity class corresponding to the data table
Students:
public class Stu {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String classid;
public Stu() {
}
public Stu(Integer id, String name, String classid) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.classid = classid;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClassid() {
return classid;
}
public void setClassid(String classid) {
this.classid = classid;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Stu{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", classid='" + classid + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Class:
public class Cls {
private Integer id;
private String cname;
//There are many students in the class, so you need to create a collection of student classes
private List<Stu> stus;
public Cls() {
}
public Cls(Integer id, String cname, List<Stu> stus) {
this.id = id;
this.cname = cname;
this.stus = stus;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
public List<Stu> getStus() {
return stus;
}
public void setStus(List<Stu> stus) {
this.stus = stus;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cls{" +
"id=" + id +
", cname='" + cname + '\'' +
", stus=" + stus +
'}';
}
}
3. Create class dao interface
public interface ClsDao {
Cls selectclassandstubyclassid(int id);
}
4. Write the corresponding sql of dao interface method in the mapping file of class table
<mapper namespace="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.dao.ClsDao">
<!--
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
If the two tables do not have the same column name, you can directly select * ....
But because the primary keys in the class table and the student table are id
Therefore, one of them needs to be displayed by alias, otherwise the queried data will be incomplete
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
-->
<select id="selectclassandstubyclassid" resultMap="getclass">
select c.*,s.id sid,s.uname name,s.uclassid classid from class c join stu s on c.id = s.uclassid where c.id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap id="getclass" type="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.entity.Cls">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="cname" column="classname"/>
<collection property="stus" ofType="com.aaa.qy145.ten.cys.entity.Stu" autoMapping="true">
<id property="id" column="sid"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
</mapper>5. Test
@Test
public void test02()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
ClsDao clsDao = session.getMapper(ClsDao.class);
Cls cls = clsDao.selectclassandstubyclassid(1);
System.out.println(cls);
}Test results: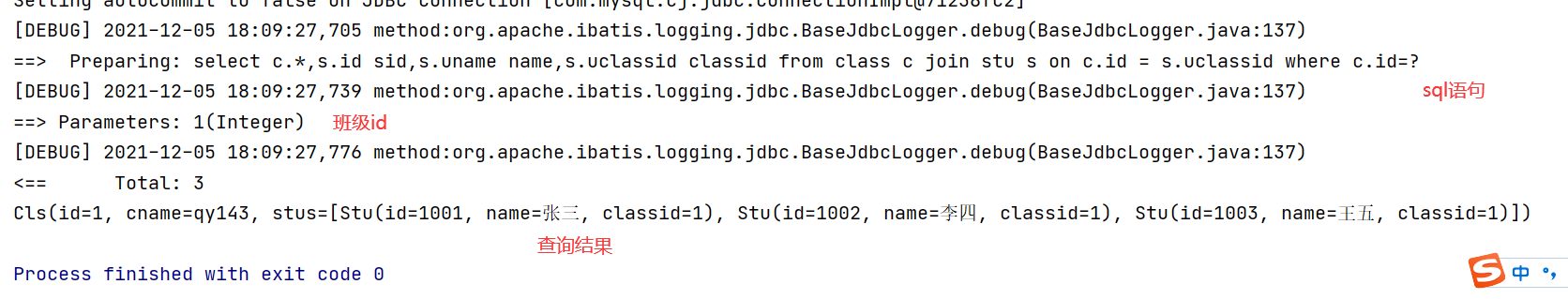
The above is the first linked list query The second nested query is the same as the many to one second slightly
2. Dynamic SQL
Dynamic sql That is, sql statements change according to conditions. The general methods used are:
| element | effect | describe |
| if | Conditional judgment | But conditional judgment |
| choos(when,otherwise) | Conditional selection, equivalent to Java when | Multi conditional branch judgment |
| where,set | auxiliary | Dealing with sql statement splicing |
| foreache | loop | loop |
First create a data table And store the data
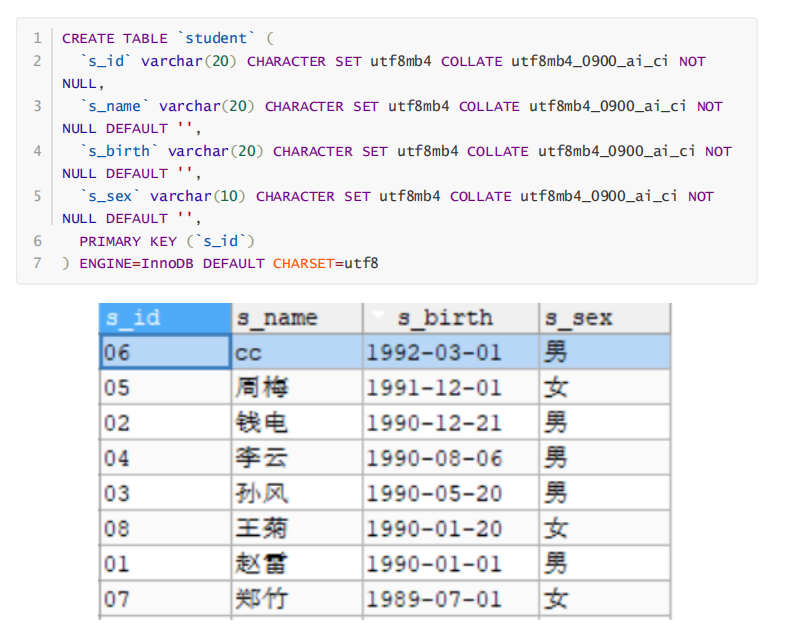
Create corresponding entity class and dao interface And create sql methods
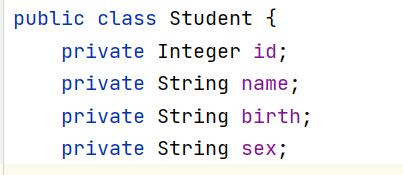
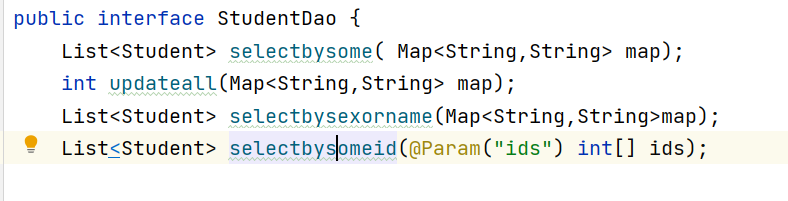
(1) if with where
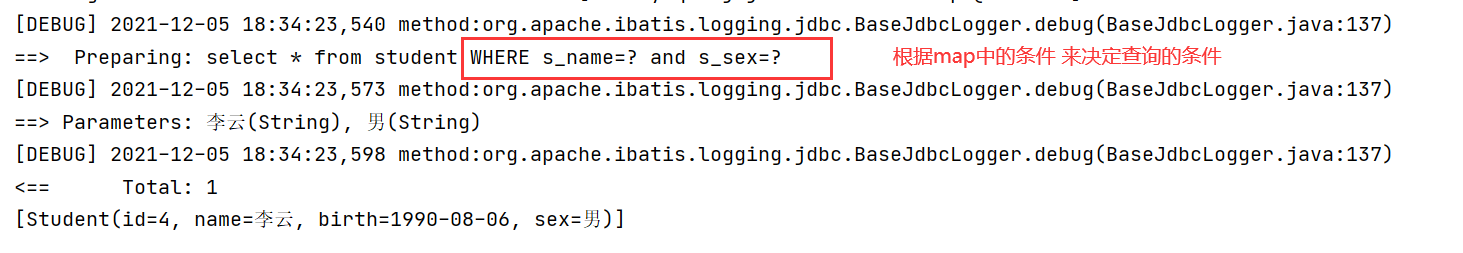
<!-- #{parameter name} parameter name: the parameter passed can only be obtained by corresponding to the key in the map set
If name If it is empty, it will only be based on sex To query; if sex If it is also blank, all items will be queried
where:Can help you add where Key and put the first and | or remove
-->
<select id="selectbysome" resultMap="my01">
select * from student
<where>
<if test="sname!=null and sname!=''">
and s_name=#{sname}
</if>
<if test="ssex!=null and ssex!=''">
and s_sex=#{ssex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
Test:
@Test
public void test03()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//The parameter values are obtained from the web page and encapsulated in the map object.
map.put("sname","Li Yun");
map.put("ssex","male");
List<Student> list = studentDao.selectbysome(map);
System.out.println(list);
}
(2) [choose when otherwise] and where
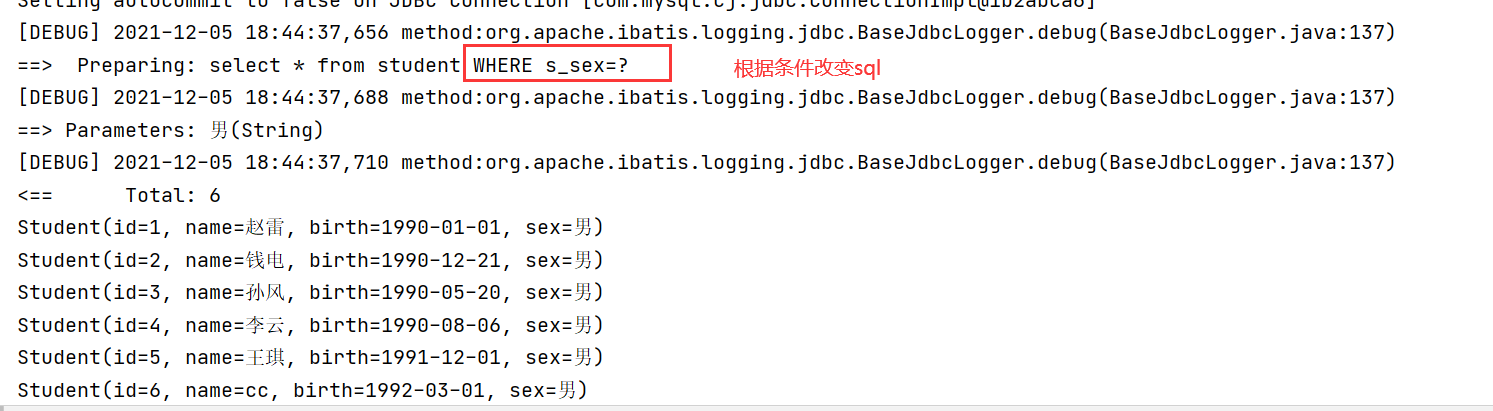
Query data by name and sex If name has data, query by name If name has no data Query by sex If sex has no data, query the student with id 1
<!--
choose +where
when:When the conditions are met, the following will not be performed when and other If not, execute otherwise
-->
<select id="selectbysexorname" resultMap="my01">
select * from student
<where>
<choose>
<when test="name!=null and name!=''">
and s_name=#{name}
</when>
<when test="sex!=null and sex!=''">
and s_sex=#{sex}
</when>
<otherwise>
s_id=1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>Test:
@Test
public void test05()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//The parameter values are obtained from the web page and encapsulated in the map object.
map.put("sex","male");
List<Student> list = studentDao.selectbysexorname(map);
System.out.println(list);
}
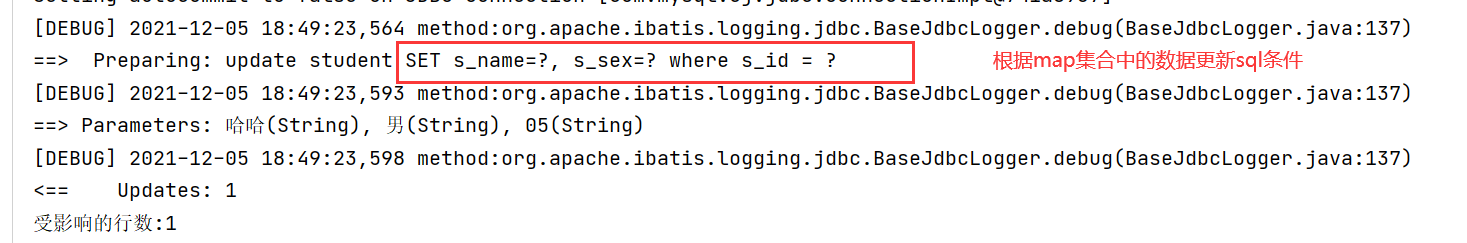
(3)set tag --- modify some fields
<!--
Modify the values of some columns.
set Can help you add set Keyword and remove the last comma.
-->
<update id="updateall">
update student
<set>
<if test="name!=null and name!=''">
s_name=#{name},
</if>
<if test="birth!=null and birth!=''">
s_birth=#{birth}
</if>
<if test="sex!=null and sex!=''">
s_sex=#{sex}
</if>
</set>
where s_id = #{id}
</update>Test:
@Test
public void test04()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//The parameter values are obtained from the web page and encapsulated in the map object.
map.put("id","05");
map.put("name","ha-ha");
map.put("sex","male");
int i = studentDao.updateall(map);
System.out.println("Number of rows affected:"+i);
session.commit();
}
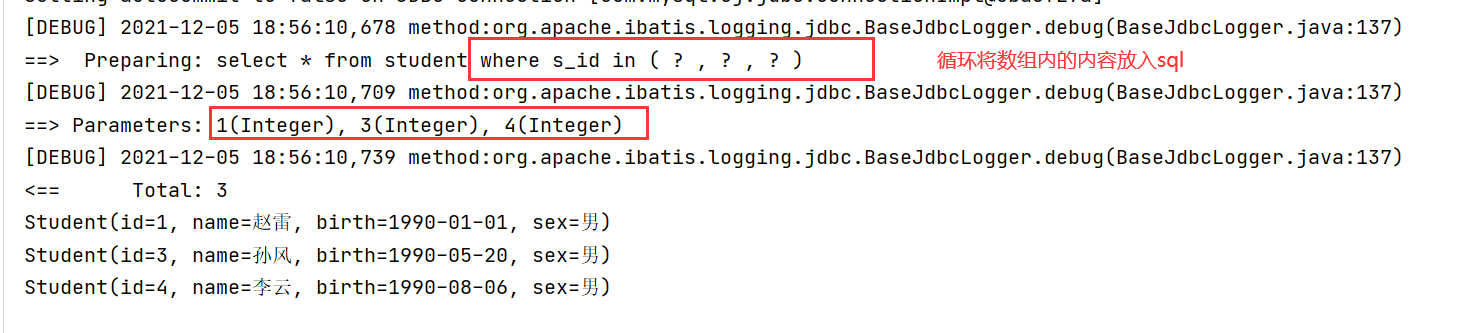
(4) foreach batch processing
Query students with id=01, 02, 03, 04.
<!--
foreach:
collection:The name of the collection and array to traverse
item: The name of the element variable assigned during each traversal
open: Start with what
close:End with what
separator: Separator
List<Student> selectbysomeid(@Param("ids") int[] ids);
#{parameter name}: corresponding to @ Param("parameter name") of the corresponding method
-->
<select id="selectbysomeid" resultMap="my01">
select * from student where s_id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="tid" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{tid}
</foreach>
</select>Test:
@Test
public void test06()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
int[] ids = {1,3,4};
List<Student> list = studentDao.selectbysomeid(ids);
for(Student s:list){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Finally, this concludes the basic use of the mybatis framework. Thank you for browsing^_^