Basic operations on MongoDB in SpringBoot
Creation of Database Library
Firstly, the database is created in the MongoDB operation client Robo 3T:
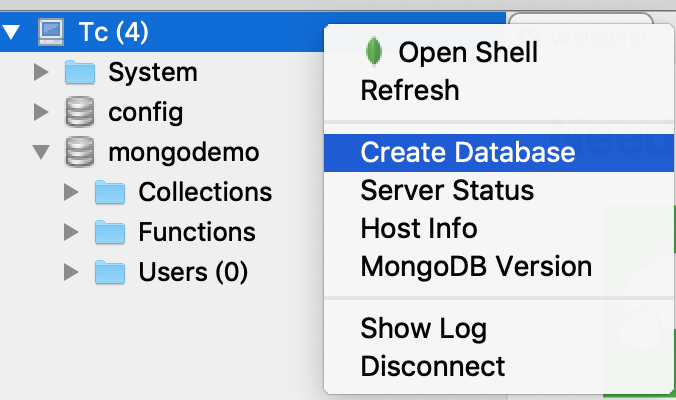
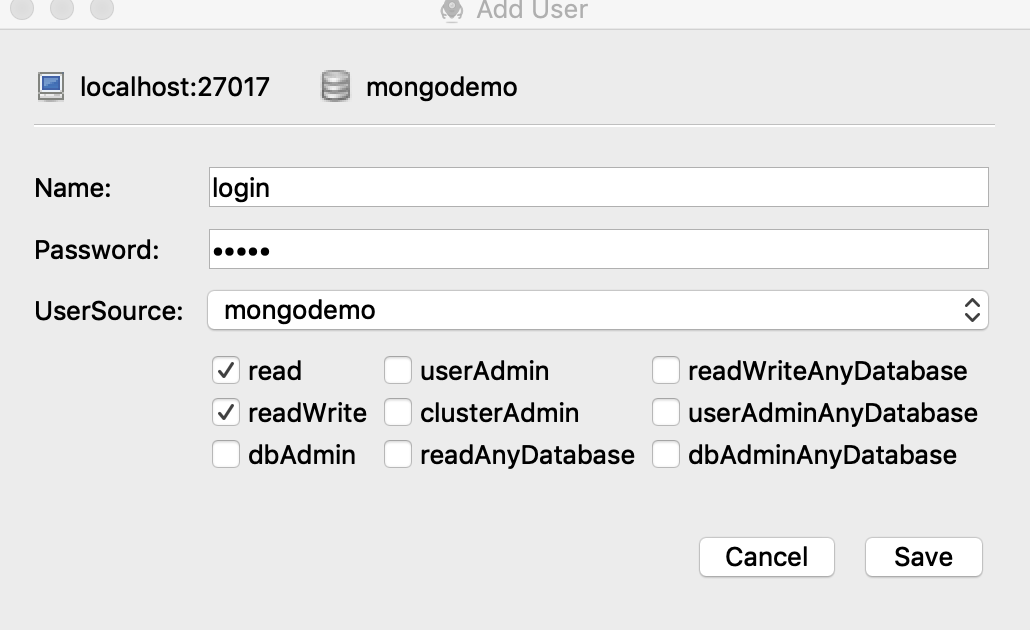
Add User:
Create Collections collections (similar to tables in mysql):
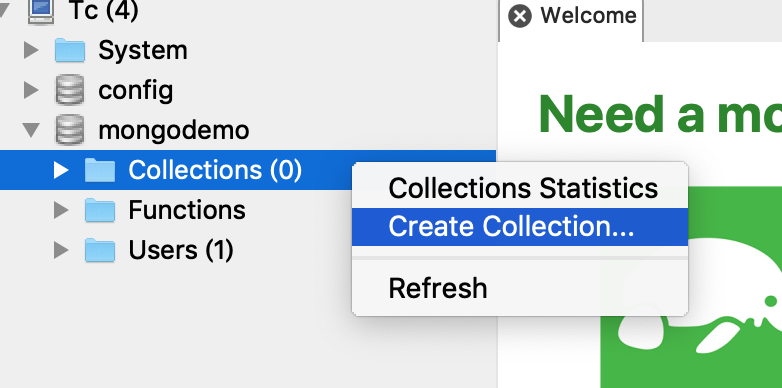
Most of the rest of us are based on the Collection "collection emo" operation created.
Dependency package
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId> <version> 2.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <version> 2.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <version> 2.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
application.properties file configuration in SpringBoot
spring.data.mongodb.host=localhost spring.data.mongodb.port=27017 spring.data.mongodb.database=mongodemo spring.data.mongodb.username=login spring.data.mongodb.password=login
Addition, deletion and alteration checking operations in MongoDB
Define MongoTemplate
@Autowired private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate; private static String COLLECTION_DEMO = "collectiondemo";
mongoTemplate-based operation
Add data
@PostMapping("/insertDocument") public void insertDocument(String document) { //Get set MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO); Document parse = Document.parse(document); //Insert document collection.insertOne(parse); }
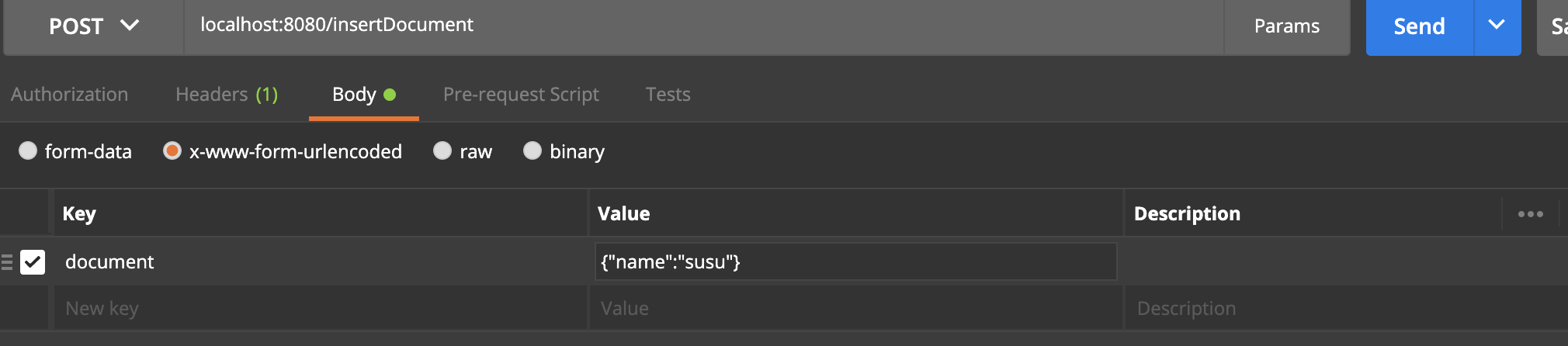
Posman test parameters:
In Robo, you can find:
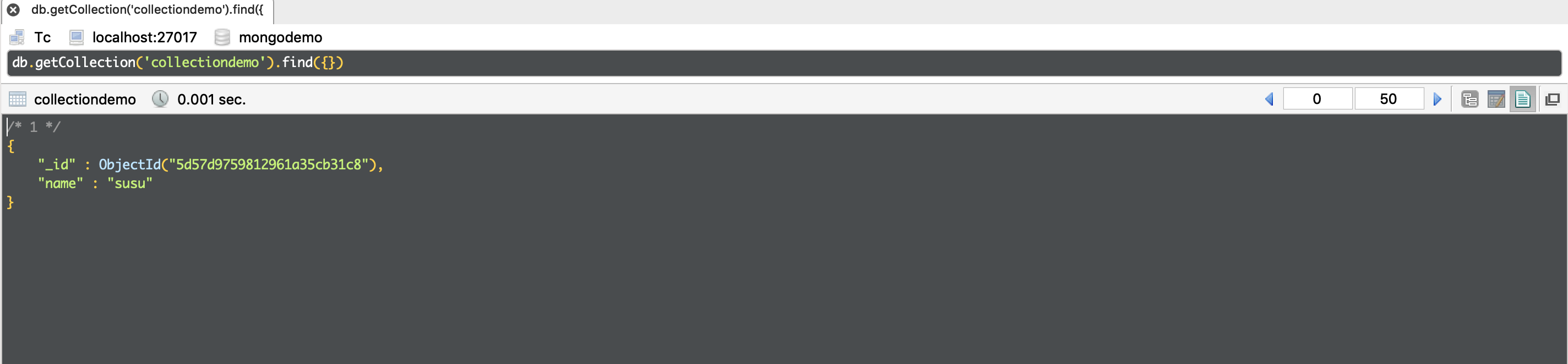
Successful addition of data, where ObjectId is a 12-byte BSON type string, by
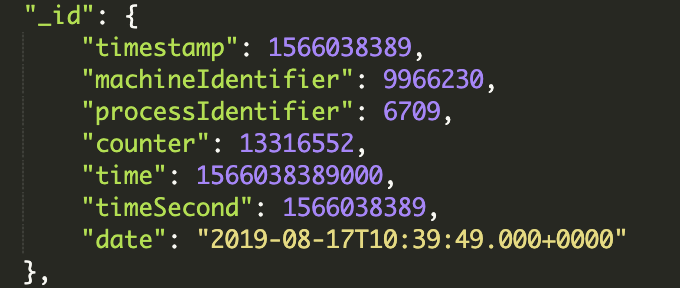
Form
insert data
@PutMapping("/updateDocument") public Long updateDocument(String queryDocument, String ducument) { MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO); BasicDBObject queryParse = BasicDBObject.parse(queryDocument); BasicDBObject parse = BasicDBObject.parse(ducument); UpdateResult result = collection.updateOne(queryParse, new BasicDBObject("$set",parse)); return result.getModifiedCount(); }
Input parameters:
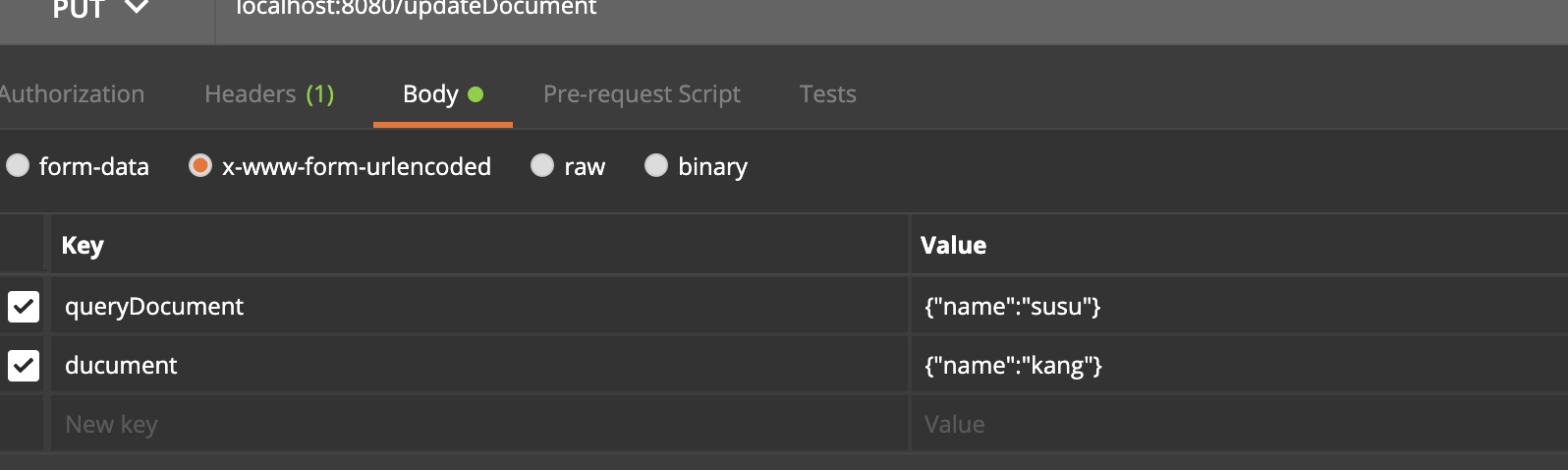
As you can see:

But there is a problem, when the key in the parameter does not exist in mongodb, it creates itself:
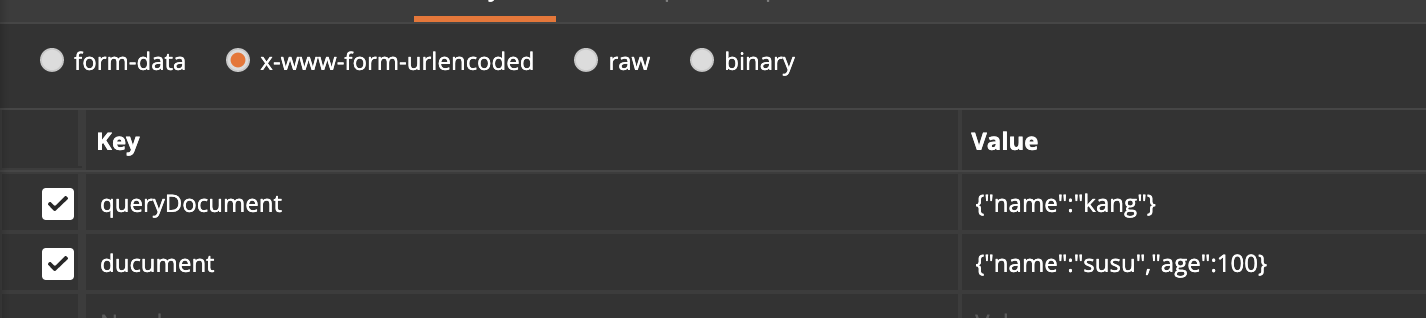
mongodb did not have an age field before, and now you can see that:

For some business scenarios, a strict key requirement can't be met. In this case, mongodb can be solved with $exists:
@PutMapping("/updateDocumentOnlyHave") public Long updateDocumentOnlyHave(String id, String ducument) { MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO); BasicDBObject parse = BasicDBObject.parse(ducument); Set<String> keySet = parse.keySet(); BasicDBObject dbObject = new BasicDBObject(); dbObject.put("id",id); for (String key : keySet) { dbObject.put(key, new BasicDBObject("$exists",true)); } UpdateResult result = collection.updateOne(dbObject, new BasicDBObject("$set",parse)); return result.getModifiedCount(); }
Query data
@GetMapping("/listDocuments") public List<Document> findDocuments() { MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO); FindIterable<Document> documents = collection.find(); List<Document> listDocuments = new ArrayList<>(); for (Document document : documents) { listDocuments.add(document); } return listDocuments; }
Delete data
@DeleteMapping("/deleteDocument") public DeleteResult deleteDocument(String name) { MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO); DeleteResult result = collection.deleteOne(new BasicDBObject("name", name)); return result; }