MongoDB pipeline definition
The aggregation pipeline of MongoDB will pass the results of MongoDB documents to the next pipeline after one pipeline is processed. Pipeline operations are repeatable.
Common Aggregate pipeline operators of Aggregate in SpringBoot
Customize the collection userCollection and initialize the data structure
Store bean user class
[@Data](https://my.oschina.net/difrik) @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Document(collection = "userCollection") public class User { [@Id](https://my.oschina.net/u/3451001) private String userId; private String userName; private List<Book> books; }
Store bean book class
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Book { private Integer bookId; private String bookName; }
Query bean uservo class
@Data public class UserVO { @Id private String userId; private String userName; private Book books; }
Initialization data

Import package
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version> 1.18.10</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
1,$project
Modify the structure of the input document, which can be used to rename, add, or delete fields, or to create calculation results and nested documents. Query fields specified in select similar to SQL query
public Object testProject() { Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation( Aggregation.project("books","userName") .and("books").as("book") .and("userName").as("name") ); AggregationResults<Map> aggregate = mongoTemplate.aggregate(aggregation, USER_COLLECTION, Map.class); List<Map> mappedResults = aggregate.getMappedResults(); return mappedResults; }
Query results
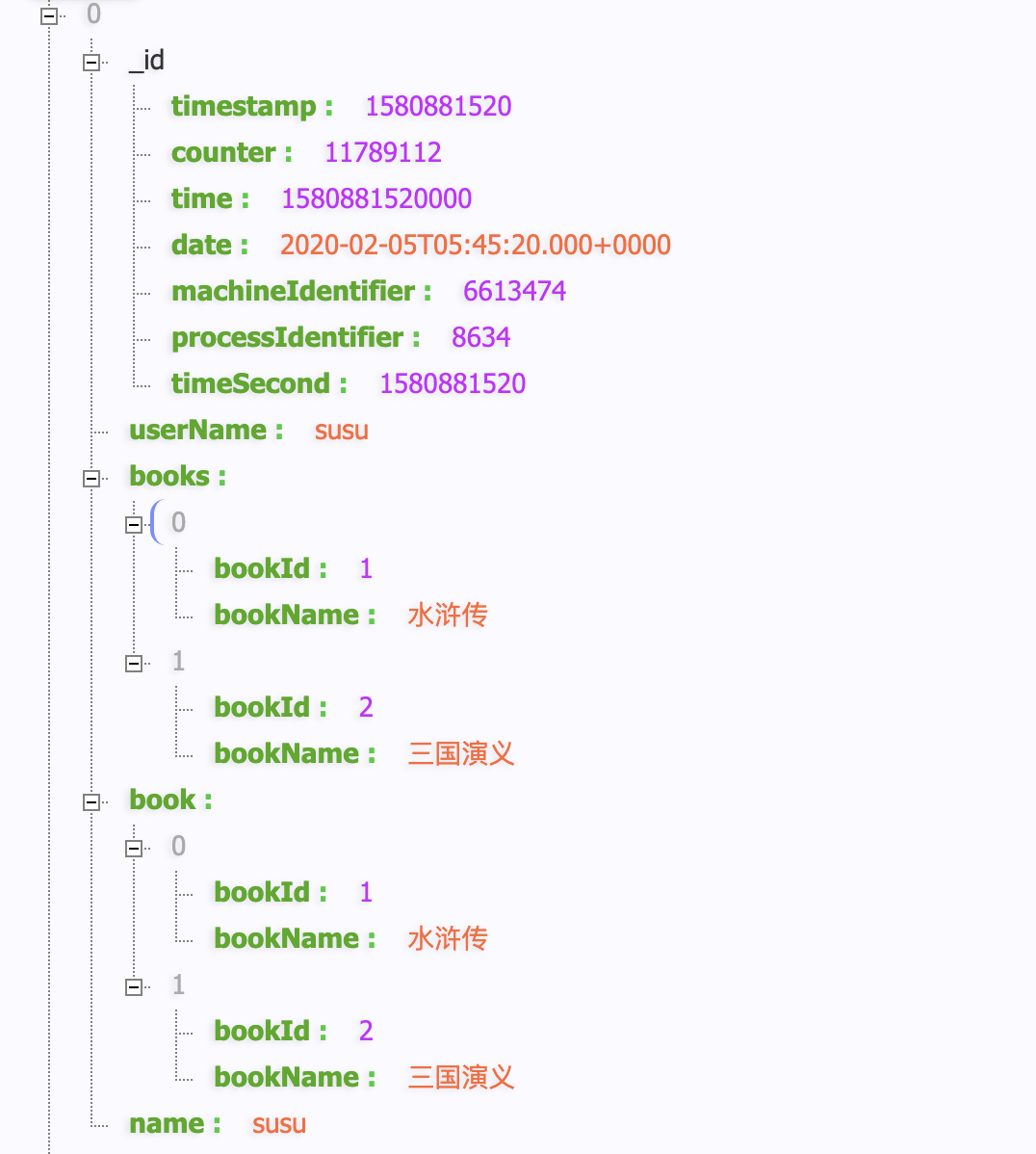
2,$match
It is used to filter data and only output qualified documents. Similar to where query criteria in SQL
public Object testMatch() { Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation( Aggregation.match(Criteria.where("userName").is("kangkang")) ); AggregationResults<User> userCollection = mongoTemplate.aggregate(aggregation, "userCollection", User.class); List<User> mappedResults = userCollection.getMappedResults(); return mappedResults; }
Query results

3,$unwind
Split an array type field in the document into multiple fields, each containing a value in the array.
public Object testUnwind() { Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation( Aggregation.unwind("books"), Aggregation.match(Criteria.where("books.bookId").is(1)) ); AggregationResults<UserVO> userCollection = mongoTemplate.aggregate(aggregation, "userCollection", UserVO.class); List<UserVO> mappedResults = userCollection.getMappedResults(); return mappedResults; }
Query results

4,$limit
Used to limit the number of documents returned by the MongoDB aggregation pipeline. Often combined with $skip for paging query
public Object testLimit() { Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation( Aggregation.limit(1) ); AggregationResults<User> aggregate = mongoTemplate.aggregate(aggregation, USER_COLLECTION, User.class); List<User> mappedResults = aggregate.getMappedResults(); return mappedResults; }
Query results

5,$skip
Skips the specified number of documents in the aggregation pipeline and returns the remaining documents. Often combined with $limit for paging queries
public Object testSkip() { Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation( Aggregation.skip((long) 1) ); AggregationResults<User> aggregate = mongoTemplate.aggregate(aggregation, USER_COLLECTION, User.class); List<User> mappedResults = aggregate.getMappedResults(); return mappedResults; }
Query results

6,$group
Groups documents in the collection, which can be used for statistics. Similar to group by in SQL
7,$sort
Sort the input documents and output them. Similar to order by in SQL