1.mongodb official website
MongoDB: the application data platform | MongoDB
2. Go to the official website of MongoDB and download MongoDB, MongoDB compass and Mongodb--database--tools
3. The operation of the MongoDB database by nodejs needs to rely on the third-party package mongoose of nodejs
Terminal instruction: npm install mongoose
4.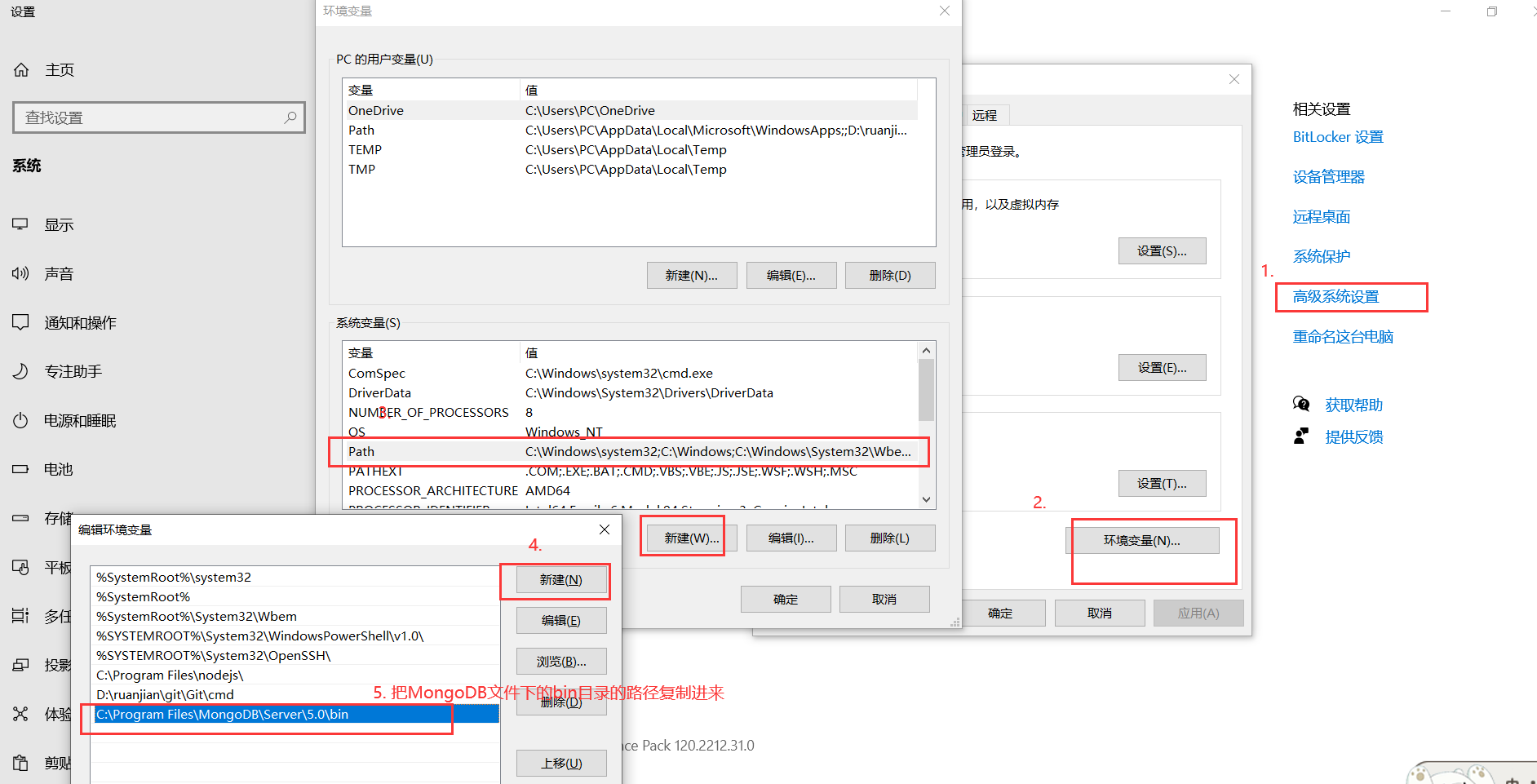
5.
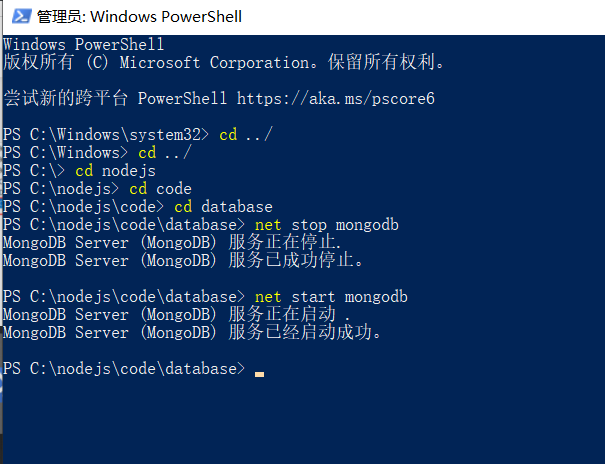
Run PowerShell cd as an administrator to the directory where the file is located. If MongoDB is not enabled
Start using the net start mongodb command
6.
//Introduce mongoose module
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// console.log(mongoose);
//todo connection database
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/test001')
.then(() => console.log('Database link succeeded'))
.catch(erro => console.log('connection failed'))7. In the vscode integration terminal, cd to the directory where the file is located, and use the nodemon 'node 02.js' command to open the file
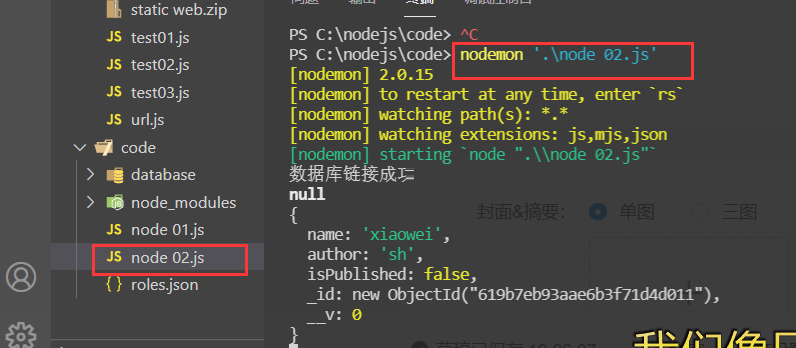
8. Set set set rules, create sets and apply rules
//todo set collection rules
const courseSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
author: String,
isPublished: Boolean
});
// todo creates collections and applies rules
// todo 1. Collection name '' 2. Collection rule
const Course = mongoose.model('Course', courseSchema);9. Two ways to create a collection instance document
// todo is the first way to create a collection instance document
const course = new Course({
name:'xiaoguo',
author:'aaa',
tags:['node','backend'],
isPublished:false
})
// Save data in database
course.save();
//The second method of todo creates a document without using course.save(), which will be automatically saved into the database
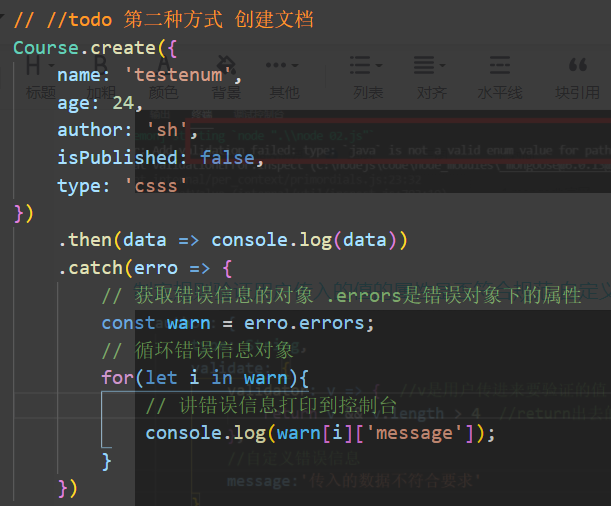
Course.create({
name:'xiaowei',
author:'sh',
isPublished:true
},(erro,data)=>{
console.log(erro);
console.log(data)
});
//promise objects are also supported
Course.create({
name:'xiaoli',
author:'zz',
isPublished:true
}).then(data=> console.log(data))
.catch(erro=>console.log(erro))10. Query all documents in the user collection and return an array
// todo queries all documents in the user collection and returns an array
Course.find()
.then(result =>{console.log(result)})11. Query a document in the user collection through the ID field and return an array
// todo returns an array by querying a document in the user collection through the ID field
Course.find({
_id:"619b0f75dc5e07d1b9924ee9"
})
.then(result =>{console.log(result)})12. Find the document according to the condition. If the condition is not written, return the first document in the database and return an object
// todo finds documents according to conditions. If no conditions are written, the first document in the database returns an object
Course.findOne({
name:'xiaowei'
})
.then(result=>console.log(result))13. Find document based on range criteria $gt min $lt Max
// todo finds documents based on range criteria
Course.find({
age: { $gt: 20, $lt: 50 }
})
.then(result => console.log(result))14. Query contains
// todo finds documents based on range criteria
Course.find({
name: { $in: ['xiao'] }
})
.then(result => console.log(result))15. Select the fields to query and sort them. The default ascending and descending order is plus one-
// todo select the fields to query (in ascending order)
Course.find().select('name age')
//The reverse order is. sort('-age') (descending)
.then(result => console.log(result))sixteen Skip skip the first two data limits limit the number of queries
// todo skip skip the first two data limits limit the number of queries Course.find().skip(2).limit(2) .then(result => console.log(result))
seventeen Find a document and delete it. The return value is the deleted document. If multiple documents are matched, only the first one will be deleted
// todo finds a document and deletes it. The return value is the deleted document. If multiple documents are matched, only the first one will be deleted
Course.findOneAndDelete({
_id:"619b0f75dc5e07d1b9924ee9"
})
.then(result=>console.log(result))
eighteen Delete multiple documents Return an object {n: number of deleted documents ok: 1 (deleted successfully)}
// todo deletes multiple documents and returns an object {n: number of deleted documents ok: 1 (deletion succeeded)}
Course.deleteMany({
_id:"619b0f75dc5e07d1b9924ee9"
})
.then(result=>console.log(result))nineteen When updating a single document, two objects are passed. The first object is the second value of the query condition
// todo updates two objects in a single document. The first object is the second value to be changed in the query condition
Course.updateOne(
{name:'xiaoguo'},
{name:'xiaoguoguo'}
)
.then(result=>console.log(result))twenty Update multiple documents and transfer two objects. The first object is the second value of the query condition to be changed
// todo updates multiple documents and passes two objects. The first object is the second value to be changed in the query condition
Course.updateMany(
{},
{age:18}
)
.then(result=>console.log(result))twenty-one Set mongoose authentication
For String type fields required: [true, 'error description'] Required fields 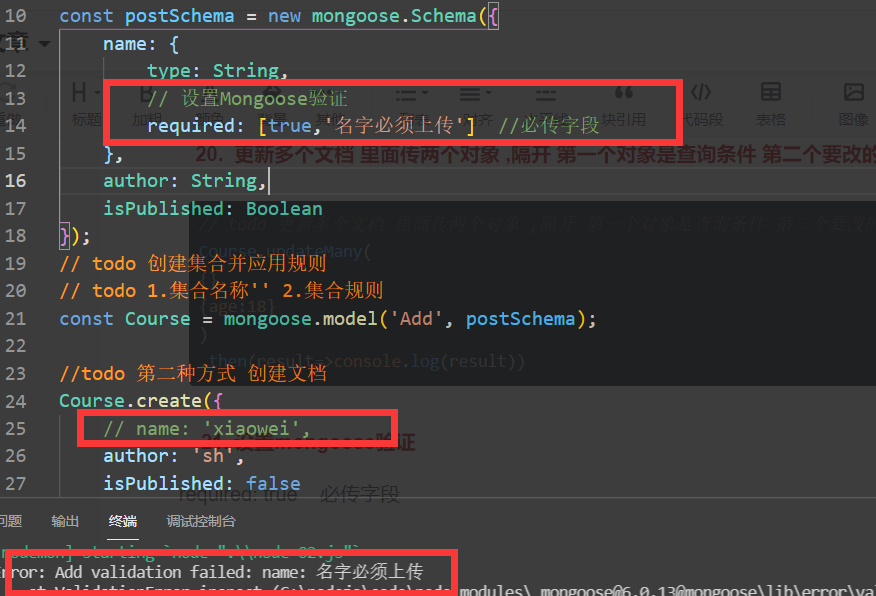
For String type fields minlength: [n, 'error description'] Minimum field length
For String type fields maxlength: [n, 'error description'] Maximum field length
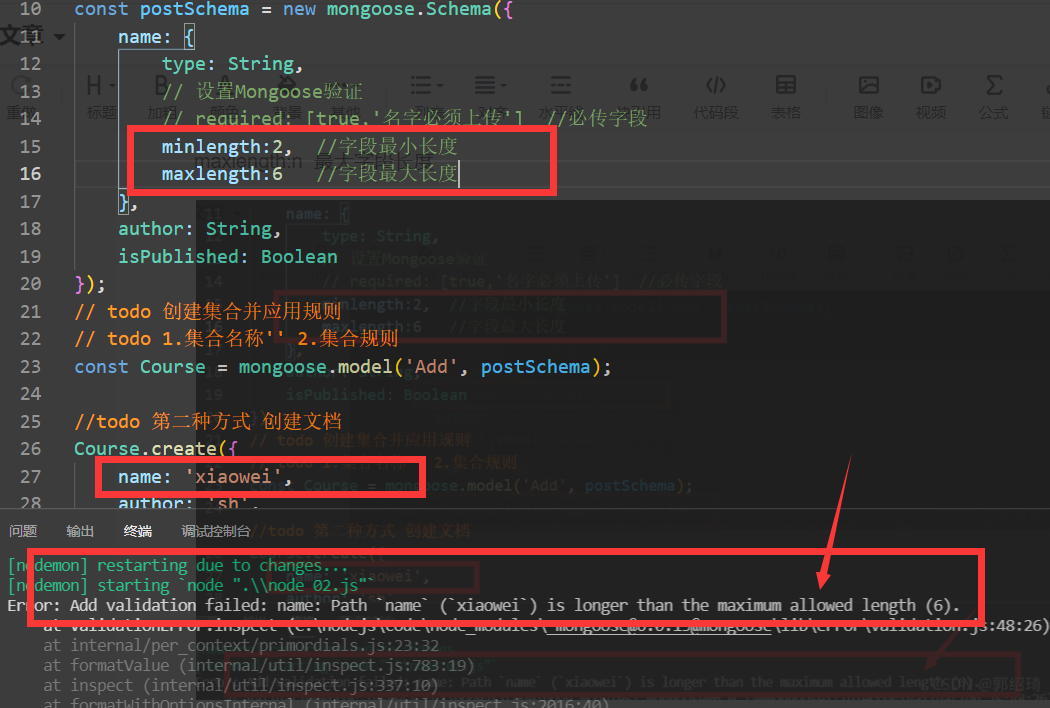
For String type fields trim:true // Remove spaces at both ends of the String
For Number type field min: [n, 'error description'] Minimum value
For Number type field max: [n, 'error description'] Maximum value
Set the default value of time. When the user does not transfer the data of this field, enable the current time as the default value 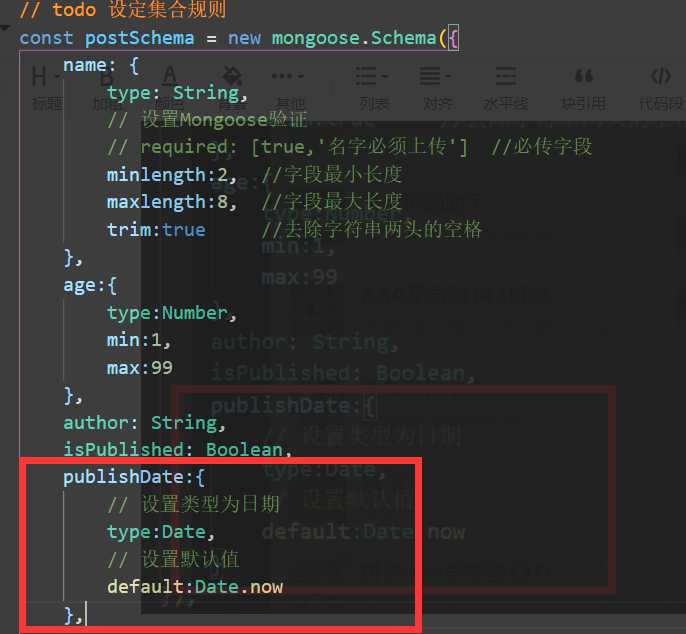
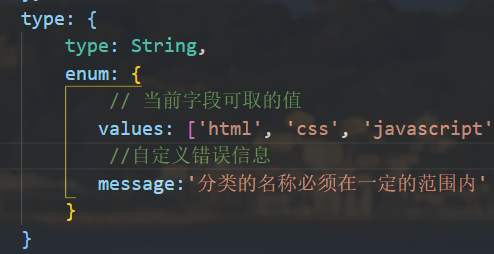
List the available values of the current field, which must be uploaded within the range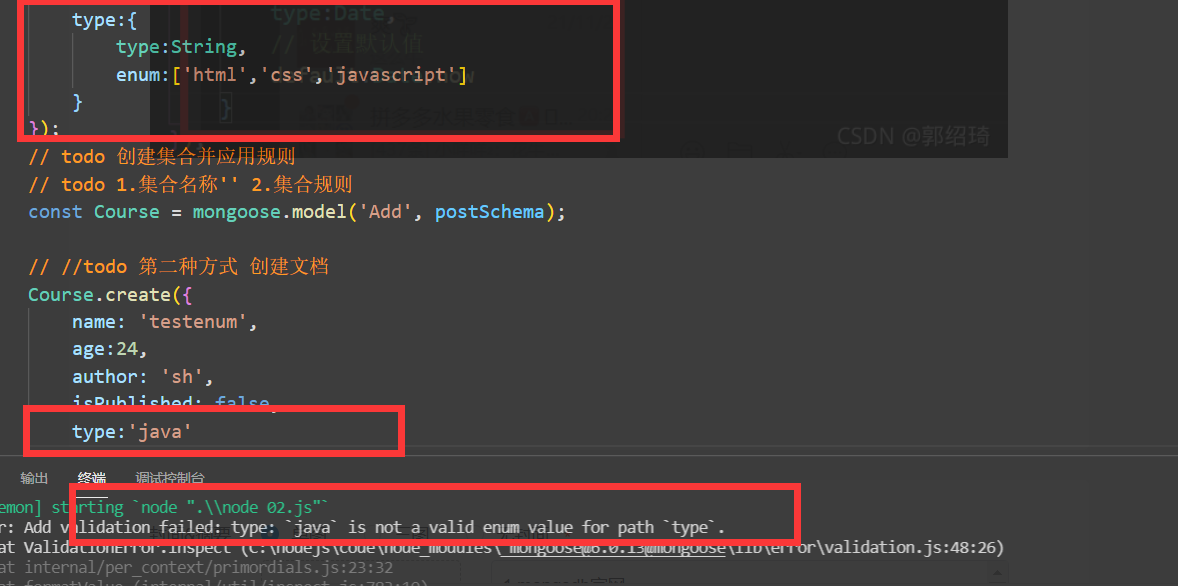
Format when customizing error messages
Make rules to verify whether the attribute of the value passed in by the user conforms to the specification. Customize the error message message 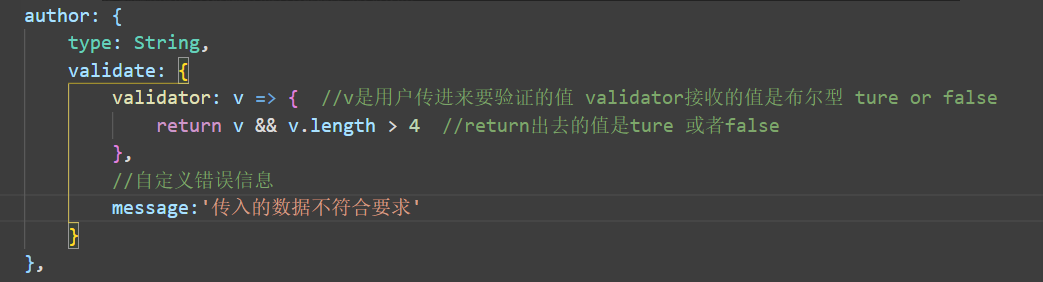
Get error information from console