Module expansion and cognition· Process oriented programming · Module introduction · import sentence pattern · from...import... Sentence pattern · Circular import problem · Absolute import and relative Import · Software development catalog specification 1, Process oriented programming
Process oriented programming is like designing a product pipeline, and the results are visible. The drawback of process oriented is that once the function is to be modified, it needs to be transformed as a whole (pulling one hair and moving the whole body) def get_info(): username = input('username>>>:').strip() password = input('password>>>:').strip() if len(username) == 0 or len(password) == 0: print('User name or password cannot be empty') return user_idf = { '1':'admin', '2':'user', } print(user_idf) choice = input('Please select your identity>>>:').strip() if choice in user_idf: id = user_idf.get(choice) return deal_data(username, password,id) else: print('Illegal input') return def deal_data(username,password,id): data = '%s|%s|%s\n'%(username,password,id) return save_data(data) def save_data(data): with open(r'userinfo','a',encoding='utf8') as f: f.write(data) print('login was successful') get_info() Two. Module introduction
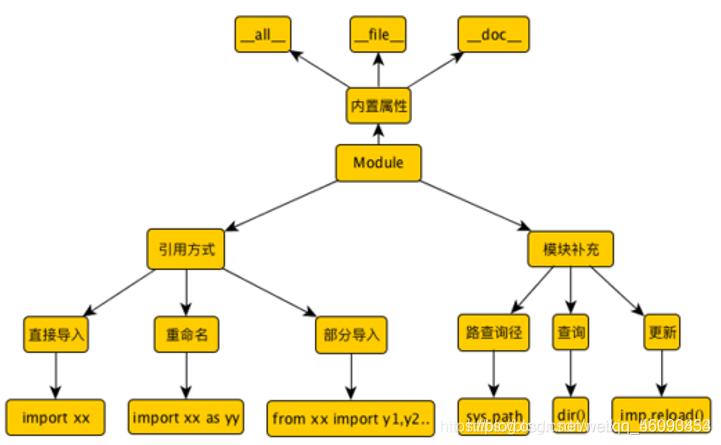
1. What is a module? Module: a combination of a series of functions 2. Why use modules? In order to improve development efficiency 3. Three sources of modules 1. Built in 2. Of third parties 3. Customized 4. Four forms of modules 1. Code written in python 2. C or C + + extensions that have been compiled as shared libraries or DLL s 3. Pack a group of modules 4. Use C to write and link to the built-in module of python interpreter 3, import sentence pattern
When learning the module Be sure to distinguish who is the import file and who is the module file Import file module The file suffix must not be added Import the same module multiple times It will only be executed once What happened when the module was imported for the first time 1. Run the imported file to generate the global namespace of the store waiter of the file 2. Operation documents 3. Generate file global namespace Run the code in the file Archive all the generated names and namespaces 4. When importing, the file namespace generates a file name that points to the file global namespace import sentence after importing the module You can use all the names in the module by clicking the module name And there will certainly be no conflict 4, from...inportfrom...inport... Multiple imports will only import once 1. First generate the global namespace of the execution file 2. Execute module file Generate the global namespace of the module 3. Archive all the names generated after execution in the module in the module namespace 4. In the execution file, there is a value pointed to by money in the namespace of the money execution module from...inport... Import a name by name Just write your name when you use it But when the current namespace has the same name There will be conflict The used name becomes the current namespace # money = 999 # print(money) money = 999 # def read1(): # print('Miss Dong') # read1() change() print(money) 5, Import module extension usage1. Alias You can alias either the module name or a name in the module 2. Continuous import import Module name 1, module name 2 Multiple modules can be imported continuously However, only when multiple modules have similar functions or belong to the same series If the functions are different and do not belong to a series It is recommended to import by branch import Module name 1 import Module name 2 from Module name 1 import Name 1,Name 2,Name 3 3. General import from md import * # Import all the names in the module(*Represents all) print(money) print(read1) print(read2) print(change) __all__ = ['money','read1'] # It can be used in the imported module file__all__Specifies the name that can be imported 6, Determine file typeDetermine whether the py file is a module file or an execution file _ name_ Returns when the file is an executable file_ main_ If the file is imported as a module, the file name is returned if __name__ == '__main__': read1() """stay pycharm You can knock directly in main Press tab Key to complete automatically if judge""" 7, Circular importIn the future, when we import modules, if circular import occurs It means that your program design is unreasonable Remember that circular import is not allowed in the future programming career Make mistakes again and again: 1. Change position Put the sentences imported from each other at the end of the code 2. Function form Put the imported sentence into the function body code Wait until all names are loaded before calling 8, Order of module import1. Search from memory first 2. Search in the built-in module 3. Finally, go to sys.path to find the system path If none, an error is reported # I'll give it later py Try not to conflict with the built-in module name when naming the file import sys print(sys.path) # The first element in the result is always the path of the current execution file Solution when a custom module cannot be found 1.Manually add the path of the module to the sys.path in import sys sys.path.append(r'D:\py20\day18\aaa') 2.from...import...Sentence pattern from Folder name.Folder name import Module name from Folder name.Module name import name -------- That's all for today. I'll see you next time----------
|
Module expansion and cognition
Posted by 22Pixels on Tue, 23 Nov 2021 03:14:08 -0800