Batch recognition of Baidu AI Cloud voice with WeChat
If you don't see this article in the cnblog author carr0t2, it is recommended to visit the original webpage for better typesetting and picture experience
I'm not sure if I want to continue to develop graphical interface, more support, if you really need, please leave a message below.
Prepare tools and environment
- Python3.7
- silk-v3-decoder https://github.com/kn007/silk-v3-decoder
- Baidu AI Cloud account (with Baidu account), apply for API Key and Secret Key.
- Baidu short speech recognition API Demo modified based on official Demo code https://github.com/Baidu-AIP/speech-demo/tree/master/rest-api-asr/python
- The environment of this article is windows Python 3.7
General idea
-
Mobile wechat finds the location where voice files are saved and exports them
-
Using silk-v3-decoder to convert recording to wav format
-
ffmpeg transforms wav into pcm with sampling frequency of 16000
-
Identifying with python
-
Personal handling only, please point out if there is any problem
Specific operation
Export wechat voice file
-
Wechat voice files of mobile phones are generally saved in internal storage \ Tencent \ micromsg \ ****************************** \ voice2
Inside the asterisk is a long string of alphanumeric characters
It includes many of these folders
-
Copy, paste, and extract all audio files
Search under Windows.amr
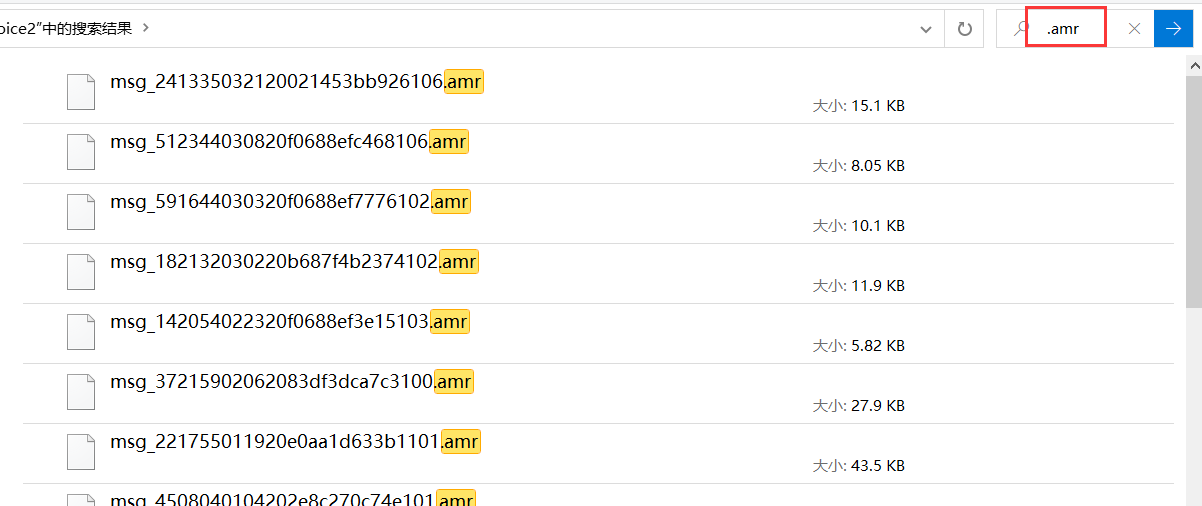
Copy and paste all to a new folder
-
These are the recording files, but the format is strange and needs to be processed into the normal format
Processing exported voice files
rename file
- Because it is necessary to keep the relative order, and the direct conversion will lead to the change of file modification time, so the normal voice order cannot be restored
- With python, extract the file modification time and rename it
import os
import time
path='.\\lecture'
dirs = os.listdir(path)
for file in dirs:
finfo = os.stat(path+'\\'+file)
timeArray = time.localtime(finfo.st_mtime)
nametime = time.strftime("%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S", timeArray)
os.rename(path+'\\'+file,path+'\\'+nametime+'.amr')
print(nametime)
Convert to pcm format
- python calls silk · V3 · decoder.exe from the command line to decode. The specific command is written as follows
- It seems that pcm files cannot be played directly. Audacity is OK
Modify Demo code
-
copy code first
https://github.com/Baidu-AIP/speech-demo/tree/master/rest-api-asr/python
I don't think json is different from raw in small scale
-
Fill in API Key and Secret Key
-
Write python, I only changed a little bit, and pasted all the code in github
Previous changes
- The format of silk ﹣ V3 ﹣ decoder.exe is converted to 16k pcm
FORMAT = 'pcm'
pathamr=r'.\amr'
pathpcm=r'.\pcm'
dirs = os.listdir(pathamr)
#dirs.remove('desktop.ini')### Windows may have this file
for file in dirs:
time.sleep(0.3)
name=file[:-3]
commandstring= ' silk_v3_decoder.exe ' + str(pathamr) + '\\' + name + 'amr ' + str(pathpcm) +'\\'+ str(name) + 'pcm' +' -Fs_API 16000 '
os.system(commandstring)
AUDIO_FILE =str(pathpcm)+'\\'+ str(name) + 'pcm'
Later changes
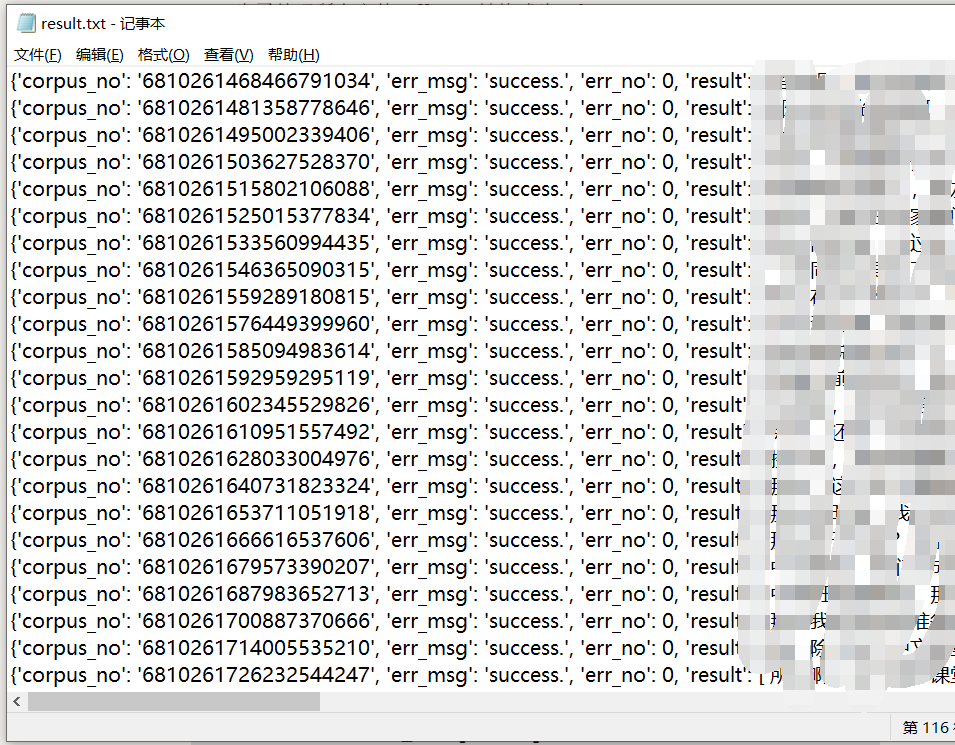
- Make the output append, and add the time field. Subsequent processing has not been done, so the exported file is still json
with open("result.txt","a") as of:
result_dict=eval(result_str)
result_dict["time"]=name
of.write(str(result_dict)+'\n')
Epilogue
- Just learned python, write casually, welcome to point out the mistakes
- The follow-up processing of the file has not been done well. The output is the time in the front line and the identification content in the back line. If there is a large identification deviation, it is convenient to find the location and listen again
- Without full automation, we still need to handle the content manually.
- Baidu's voice self training platform is not used
Code (for reference only)
import sys
import json
import base64
import time
import os
import subprocess
IS_PY3 = sys.version_info.major == 3
if IS_PY3:
from urllib.request import urlopen
from urllib.request import Request
from urllib.error import URLError
from urllib.parse import urlencode
timer = time.perf_counter
else:
from urllib2 import urlopen
from urllib2 import Request
from urllib2 import URLError
from urllib import urlencode
if sys.platform == "win32":
timer = time.clock
else:
# On most other platforms the best timer is time.time()
timer = time.time
API_KEY = '****************'### Fill in your own
SECRET_KEY = '*****************'
# Documents to be identified
# file format
FORMAT = 'pcm' # The file suffix only supports pcm/wav/amr format, and the speed version additionally supports m4a format
###In order to facilitate the direct restriction of death
CUID = '****************'
# sampling rate
RATE = 16000 # Fixed value
DEV_PID = 1537 # 1537 means to recognize Putonghua, using input method model. Fill in PID according to documents, select language and recognition model
ASR_URL = 'http://vop.baidu.com/server_api'
SCOPE = 'audio_voice_assistant_get' # If you have this scope, it means that you have asr capability. If not, please check it in the web page. Very old applications may not have
class DemoError(Exception):
pass
""" TOKEN start """
TOKEN_URL = 'http://openapi.baidu.com/oauth/2.0/token'
def fetch_token():
params = {'grant_type': 'client_credentials',
'client_id': API_KEY,
'client_secret': SECRET_KEY}
post_data = urlencode(params)
if (IS_PY3):
post_data = post_data.encode( 'utf-8')
req = Request(TOKEN_URL, post_data)
try:
f = urlopen(req)
result_str = f.read()
except URLError as err:
print('token http response http code : ' + str(err.code))
result_str = err.read()
if (IS_PY3):
result_str = result_str.decode()
print(result_str)
result = json.loads(result_str)
print(result)
if ('access_token' in result.keys() and 'scope' in result.keys()):
print(SCOPE)
if SCOPE and (not SCOPE in result['scope'].split(' ')): # SCOPE = False ignore check
raise DemoError('scope is not correct')
print('SUCCESS WITH TOKEN: %s EXPIRES IN SECONDS: %s' % (result['access_token'], result['expires_in']))
return result['access_token']
else:
raise DemoError('MAYBE API_KEY or SECRET_KEY not correct: access_token or scope not found in token response')
""" TOKEN end """
if __name__ == '__main__':
token = fetch_token()
pathamr=r'.\amr'
pathpcm=r'.\pcm'
dirs = os.listdir(pathamr)
#dirs.remove('desktop.ini')### Windows may have this file
for file in dirs:
time.sleep(0.2)
name=file[:-3]
commandstring= ' silk_v3_decoder.exe ' + str(pathamr) + '\\' + name + 'amr ' + str(pathpcm) +'\\'+ str(name) + 'pcm' +' -Fs_API 16000 '
os.system(commandstring)
######There's not much movement down here
AUDIO_FILE =str(pathpcm)+'\\'+ str(name) + 'pcm'
speech_data = []
with open(AUDIO_FILE, 'rb') as speech_file:
speech_data = speech_file.read()
length = len(speech_data)
if length == 0:
raise DemoError('file %s length read 0 bytes' % AUDIO_FILE)
speech = base64.b64encode(speech_data)
if (IS_PY3):
speech = str(speech, 'utf-8')
params = {'dev_pid': DEV_PID,
#"lm_id" : LM_ID, #Test this item from the training platform
'format': FORMAT,
'rate': RATE,
'token': token,
'cuid': CUID,
'channel': 1,
'speech': speech,
'len': length
}
post_data = json.dumps(params, sort_keys=False)
# print post_data
req = Request(ASR_URL, post_data.encode('utf-8'))
req.add_header('Content-Type', 'application/json')
try:
begin = timer()
f = urlopen(req)
result_str = f.read()
print ("Request time cost %f" % (timer() - begin))
except URLError as err:
print('asr http response http code : ' + str(err.code))
result_str = err.read()
if (IS_PY3):
result_str = str(result_str, 'utf-8')
print(result_str)
with open("result.txt","a") as of:
result_dict=eval(result_str)
#result_dict["time"]=name
#of.write(str(result_dict)+'\n')
of.write('{'+name+'}'+'\n')
try:
of.write(str(result_dict["result"])[2:-2]+'\n\n')
except:
of.write('Error'+'\n')