describe
The railway connection structure of a train dispatching station is shown in Figure 1
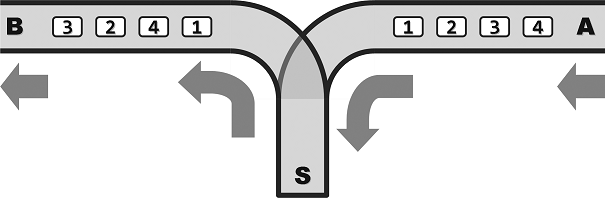
Where, A is the inlet, B is the outlet, and S is the transfer blind end. All railways are single track one-way: the train can only travel from A to s, and then from s to B; in addition, overtaking is not allowed. Because cars can reside in s, the order in which they exit from B may be different from the order in which they enter from A. However, the capacity of S is limited, and the number of cars that can stay at the same time shall not exceed m.
Suppose that the number of a train is {1, 2 , n}. The dispatcher would like to know whether these cars can be equipped with {a1, a2 The order of an} is rearranged and drives out from the B end. If so, in what order?
input
A total of two lines.
The first line is two integers n, m.
The second line is n integers separated by spaces, guaranteed to be {1, 2 A permutation of, n} that represents the exit sequence {a1, a2,... To be judged as feasible an}.
output
If the exit sequence is feasible, the operation sequence will be output, where push indicates that the car enters S from A, pop indicates that the car enters B from S, and each operation takes one line.
If not, output No.
Example
Example 1
Input
5 2
1 2 3 5 4
Output
push
pop
push
pop
push
pop
push
push
pop
pop
Example 2
Input
5 5
3 1 2 4 5
Output
No
limit
1 ≤ n ≤ 1,600,000
0 ≤ m ≤ 1,600,000
Time: 2 sec
Space: 256 MB
The code is as follows
#include<cstdio>
#include<string.h>
const int maxn = 16e5 + 5;
struct stack
{
int n = 0;
int ss[maxn];
void push(int a)
{
n++;
ss[n] = a;
}
void pop()
{
n--;
}
int top()
{
return ss[n];
}
bool empty()
{
if(n == 0)return true;
else return false;
}
int size()
{
return n;
}
};
stack a;
stack s;
stack b;
bool way[maxn];
int total[maxn];
int main()
{
int m, n;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--)
{
a.push(i);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &total[i]);
int j = 0, k = 0;
bool y = false;
while(!y)
{
if(k == n){y = true; break;}
if(s.empty())
{
s.push(a.top());
a.pop();
way[j] = true;
}
else if(total[k] == s.top())
{
b.push(s.top());
s.pop();
k++;
way[j] = false;
}
else if(!a.empty())
{
s.push(a.top());
a.pop();
way[j] = true;
}
else
{
printf("No\n");
break;
}
if(s.size() > m)
{
printf("No\n");
break;
}
j++;
}
if(y)
{
for(int i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
if(way[i]) printf("push\n");
else printf("pop\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
final result
Case No. Result Time(ms) Memory(KB)
1 Accepted 0 39000
2 Accepted 0 39000
3 Accepted 0 39000
4 Accepted 0 39000
5 Accepted 0 39000
6 Accepted 0 39000
7 Accepted 0 39000
8 Accepted 0 39000
9 Accepted 0 39000
10 Accepted 0 39000
11 Accepted 4 39000
12 Accepted 8 39000
13 Accepted 20 39000
14 Accepted 40 39000
15 Accepted 32 39000
16 Accepted 12 39000
17 Accepted 96 39000
18 Wrong Answer 292 39000
19 Wrong Answer 352 39000
20 Wrong Answer 328 39000
The simple simulation of stack operation takes a little space. Unfortunately, the last three use cases can't be passed. At present, I don't think of the reason. I hope someone can help me to have a look. Thank you.