Initial architecture design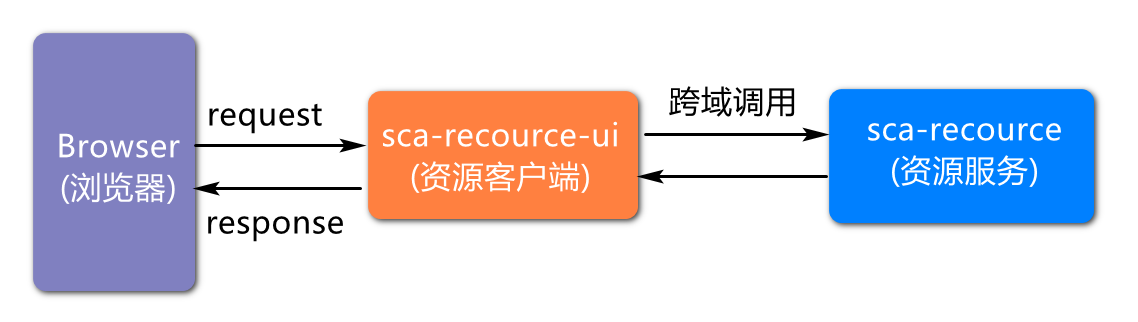
Note: in order to reduce the learning difficulty, only the initial architecture design is made here, and the subsequent evolution will be based on this architecture. For example, we will add Gateway project, authentication project, etc
Project creation and initialization
Refer to the following engineering structure for project creation, such as

Create parent project
Create a project parent project to manage project dependencies
Create file service project
Create a project to handle file upload business, for example:


Create client service project
Create a client project in which some static pages are defined, such as file upload page


Parent project initialization
Open the pom.xml file of the parent project and add the following dependencies:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Hoxton.SR9</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
File resource service implementation
Add project dependency
Add the following dependencies to the SCA resource project:
<!--Spring Boot Web (service-built-in tomcat)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Nacos Discovery (Service registration discovery)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Nacos Config (Configuration center)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Sentinel (Traffic guard-Current limiting and fusing)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Spring Boot monitor-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
Service initialization configuration
Create a bootstrap.yml configuration file in the resources directory of the project (if subsequent configuration information is to be written to the configuration center, the configuration file name must be bootstrap.yml), and add the following contents:
server:
port: 8881
spring:
application:
name: sca-resource
servlet:
multipart:
max-file-size: 100MB #Controls the size of uploaded files
max-request-size: 110MB #Request data size
resources: #Define the path to the uploaded resource
static-locations: file:d:/uploads #Static resource path (resources originally stored in the resources/static directory can be stored in this directory)
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
config:
server-addr: localhost:8848
jt: #The configuration here will be read later in some related classes through the @ Value annotation
resource:
path: d:/uploads #The root directory where the design upload file is stored (to be written to the configuration file later)
host: http://localhost:8881 / # define the access server corresponding to the uploaded file
Build project startup class
In the current project, create a project startup class, for example:
package com.jt;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class FileApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FileApplication.class, args);
}
}
After the class is created, start the current project to check whether it can be started successfully and whether there are configuration errors
Controller logic implementation
Define the Controller object that handles the upload request, for example:
package com.jt.resource.controller;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.UUID;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/resource/")
public class ResourceController {
//When @ Slf4J is added to the class, you don't have to create the following log objects yourself
// private static final Logger log=
// LoggerFactory.getLogger(ResourceController.class);
@Value("${jt.resource.path}")
private String resourcePath;//="d:/uploads/";
@Value("${jt.resource.host}")
private String resourceHost;//="http://localhost:8881/";
@PostMapping("/upload/")
public String uploadFile(MultipartFile uploadFile) throws IOException {
//1. Create file storage directory (create by time - yyyy/MM/dd)
//1.1 get a directory of the current time
String dateDir = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd")
.format(LocalDate.now());
//1.2 build directory file object
File uploadFileDir=new File(resourcePath,dateDir);
if(!uploadFileDir.exists())uploadFileDir.mkdirs();
//2. Name the document (try not to repeat it)
//2.1 obtain the suffix of the original document
String originalFilename=uploadFile.getOriginalFilename();
String ext = originalFilename.substring(
originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));
//2.2 build a new file name
String newFilePrefix=UUID.randomUUID().toString();
String newFileName=newFilePrefix+ext;
//3. Start file upload
//3.1 build a new file object and point to the final address of the actually uploaded file
File file=new File(uploadFileDir,newFileName);
//3.2 upload files (write file data to the designated service location)
uploadFile.transferTo(file);
String fileRealPath=resourceHost+dateDir+"/"+newFileName;
log.debug("fileRealPath {}",fileRealPath);
//Can I write the uploaded file information to the database later?
return fileRealPath;
}
}
Cross domain configuration implementation
When accessing the file upload service through the client project, we need to carry out cross domain configuration. There are many schemes in the cross domain configuration of the server. The most common is to carry out cross domain design at the filter level, such as:
package com.jt.files.config;
/**
* Cross domain configuration (configure based on filter mode, and set the filter priority higher)
*/
@Configuration
public class CorsFilterConfig {
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean<CorsFilter> filterFilterRegistrationBean(){
//1. Configure this filter (cross domain settings - url,method)
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource configSource=new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
CorsConfiguration config=new CorsConfiguration();
//Which request headers are allowed to cross domains
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
//Which method types are allowed to cross domain get post delete put
config.addAllowedMethod("*");
// Which request sources (IP: ports) are allowed to cross domains
config.addAllowedOrigin("*");
//Whether to allow carrying cookie s across domains
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
//2. Register the filter and set its priority
configSource.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
FilterRegistrationBean<CorsFilter> fBean= new FilterRegistrationBean(new CorsFilter(configSource));
fBean.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return fBean;
}
}
Client engineering logic implementation
In this project, our client project is designed based on springboot project. When the project goes online, its static resources can be directly put into a static resource directory
Add dependency
Add web dependency in pom file of SCA resource UI project, for example:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
Build project startup class
package com.jt;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ClientApplication .class, args);
}
}
Create file upload page
Create a static directory under the resources directory of the project (if this directory already exists, it does not need to be created), and then create a fileupload.html static page in this directory, for example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>File upload demo</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<form id="fileForm" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" onsubmit="return doUpload()">
<div>
<label>Upload file
<input id="uploadFile" type="file" name="uploadFile">
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit">Upload file</button>
</form>
</body>
<script>
//Form submission event for jquery code
function doUpload(){
//Get all pictures selected by the user (get array)
let files=document.getElementById("uploadFile").files;
if(files.length>0){
//Get the unique picture selected by the user (take it out of the array)
let file=files[0];
//Start uploading this picture
//Since there are many uploaded codes, you do not want to interfere with other codes here, so define a method call
upload(file);
}
//Block form submission effect
return false;
};
// Method of uploading file to server
function upload(file){
//Define a form
let form=new FormData();
//Add file to form
form.append("uploadFile",file);
//Asynchronous commit
let url="http://localhost:8881/resource/upload/";
axios.post(url,form)
.then(function (response){
alert("upload ok")
console.log(response.data);
})
.catch(function (e){//Execute catch code block on failure
console.log(e);
})
}
</script>
</html>
Start service access test
Step 1: start the nacos service (do service registration and configuration management here)
Step 2: start the SCA resource service, which provides file upload function
Step 3: start the SCA resource UI service, which is a client project and provides access to static resources. All pages are placed in this project
Step 4: open the browser and access the file upload page under SCA resource UI project, for example: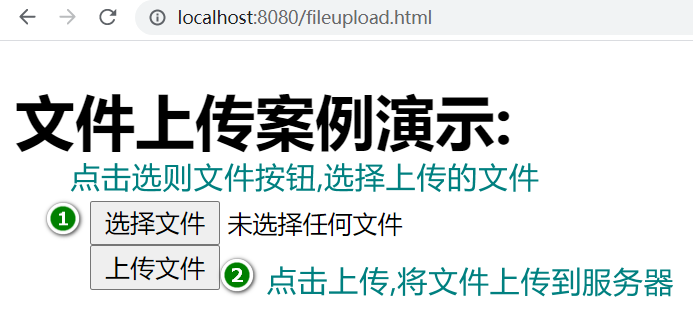
Engineering practice of API gateway
summary
API gateway is the entrance for external resources to access the internal resources of the service, so the file upload request should first request the gateway service, and then be forwarded by the gateway service to the specific resource service.
Service invocation architecture
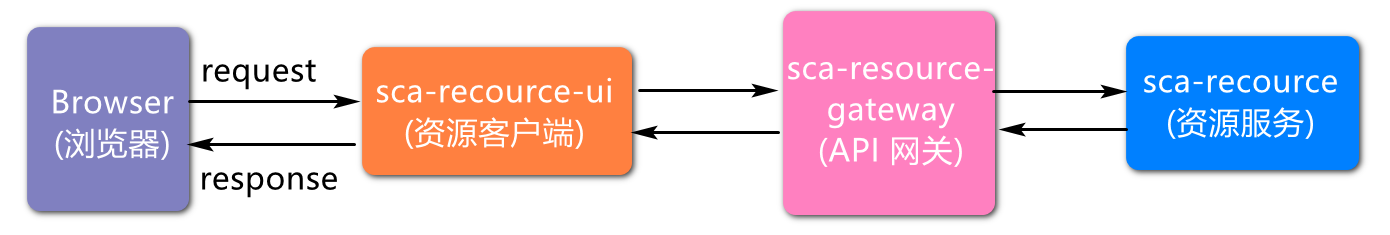
Project structure design

Create Gateway project and initialization
Step 1: create an SCA resource Gateway project, for example:

Step 2: add project dependencies, for example:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
Step 3: create the configuration file bootstrap.xml, and then perform the initial configuration, for example:
server:
port: 9000
spring:
application:
name: sca-resource-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
config:
server-addr: localhost:8848
file-extension: yml
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true
routes:
- id: router01
uri: lb://sca-resource
predicates:
- Path=/sca/resource/upload/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
Step 4: build the project startup class and start the service to check whether it is correct, for example:
package com.jt;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ResourceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ResourceApplication.class,args);
}
}
Gateway cross domain configuration
When we access the gateway based on Ajax technology, we need to conduct cross domain design at the gateway level, for example:
package com.jt.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.reactive.CorsWebFilter;
import org.springframework.web.cors.reactive.UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource;
//@Configuration
public class CorsFilterConfig {
@Bean
public CorsWebFilter corsWebFilter(){
//1. Build a cross domain configuration based on url
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source= new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
//2. Cross domain configuration
CorsConfiguration config=new CorsConfiguration();
//2.1 allow all IP: ports to cross domain
config.addAllowedOrigin("*");
//2.2 allow all request headers to cross domains
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
//2.3 allow all request methods to cross domains: get,post
config.addAllowedMethod("*");
//2.4 it is allowed to carry valid cookie s across domains
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**",config);
return new CorsWebFilter(source);
}
}
For cross domain design in Spring Gateway project, in addition to cross domain filter configuration in java code in the gateway project, cross domain configuration can also be directly carried out in the configuration file, for example:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
globalcors: #Cross domain configuration
corsConfigurations:
'[/**]':
allowedOrigins: "*"
allowedHeaders: "*"
allowedMethods: "*"
allowCredentials: true
Start the project for service access
First open the gateway, the resource server, and the client engineering service (UI), and then modify the url to access the resource server in the fileupload.html file, such as
let url="http://localhost:9000/sca/resource/upload/";
Limit file upload flow on the gateway
Step 1: add dependency in gateway pom file
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
Step 2: add sentinel configuration in gateway configuration file
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8180
eager: true
Step 3: configure jvm startup parameters when the gateway project is started, for example:
-Dcsp.sentinel.app.type=1
Step 4: first perform an upload, and then design the current limiting rules for the upload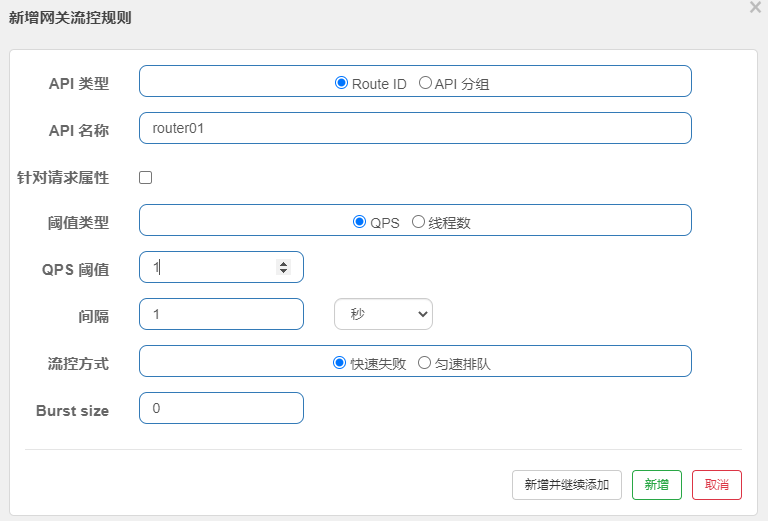
Step 5: modify the file upload page js to process the current limit results, for example:
function upload(file){
//Define a form (form object provided in axios)
let form=new FormData();
//Add file to form
form.append("uploadFile",file);
//Asynchronous commit (now commit to gateway)
//let url="http://localhost:8881/resource/upload/"
let url="http://localhost:9000/sca/resource/upload/";
axios.post(url,form)
.then(function (response){
alert("upload ok")
console.log(response.data);
})
.catch(function (e){//Execute catch code block on failure
//After the current is limited, the status code returned by the server is 429
if(e.response.status==429){
alert("Upload too often");
}
console.log("error",e);
})
}
Step 6: start the service for file upload test to detect the current limiting effect
AOP mode operation logging
Page description
When the file upload business is implemented, add the operation of logging
Add project dependency
Add AOP dependency in SCA resource project, for example:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
Create pointcut annotations
Our project aims to enhance the function of the target business, but the system should specify who is the target business. Here we define an annotation, which will be used to describe the target business later.
package com.jt.resource.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface RequiredLog {
String value() default "";
}
Define pointcut methods
Describe the resource controller file upload method in the SCA resources project through the annotation RequiredLog defined above, for example:
@RequiredLog("upload file")
@PostMapping("/upload/")
public String uploadFile(MultipartFile uploadFile) throws IOException {...}
Define log operation facet
In AOP programming, we will encapsulate the definitions of Pointcut and extended business logic (Around,...) through aspects, such as:
package com.jt.resource.aspect;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
//Define pointcuts
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.jt.resource.annotation.RequiredLog)")
public void doLog(){}//Icing on the cake (annotation description method)
//Define extended business logic
@Around("doLog()")
//@Around("@annotation(com.jt.resource.annotation.RequiredLog)")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.debug("Before {}",System.currentTimeMillis());
Object result=joinPoint.proceed();//Execution chain (other aspects, target method - Jin)
log.debug("After {}",System.currentTimeMillis());
return result;//Execution result of target method (pointcut method)
}
}
Analysis of AOP logging principle
When we record user operation logs based on AOP, the underlying workflow is as follows:

Note: after defining the AOP Aspect in the project, when the system starts, it will load and analyze the classes described by the @ Aspect annotation, create a proxy object based on the description of the pointcut as the target type object, and create an execution chain inside the proxy object, which contains interceptors (encapsulating the pointcut information), notifications (Around,...), When we request the target object resources, we will directly call the resources in the order of the execution chain.