subject
Topic Description
Input two monotonically increasing linked lists, output two combined linked lists, of course, we need to synthesize the linked list to meet the monotonic rule.
Corresponding to LeetCode21.
Thoughts on Problem Solving
Violent Solution:
- Create a new linked list;
- Determine the size of the two linked lists in turn, and choose a small build until the end.
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# Returns the merged list
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code here
if pHead1 is None and pHead2 is None:
return None
if pHead1 is None:
return pHead2
if pHead2 is None:
return pHead1
root = ListNode(0)
first=root
while pHead1 and pHead2:
val1=pHead1.val
val2=pHead2.val
if val1<=val2:
root.next=ListNode(val1)
pHead1=pHead1.next
else:
root.next=ListNode(val2)
pHead2=pHead2.next
root=root.next
if pHead1:
root.next=pHead1
if pHead2:
root.next=pHead2
return first.next
Recursive approach
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# Returns the merged list
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code here
if pHead1 is None and pHead2 is None:
return None
if pHead1 is None:
return pHead2
if pHead2 is None:
return pHead1
if pHead1.val<=pHead2.val:
pHead1.next = self.Merge(pHead1.next, pHead2)
return pHead1
else:
pHead2.next = self.Merge(pHead1, pHead2.next)
return pHead2
LeetCode 23 also has an upgraded version that combines K sorted linked lists.
Violent Solution:
- Take out all values;
- Sorting;
- Create a new list.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
arr=[]
for i in lists:
while i:
arr.append(i.val)
i=i.next
root=ListNode(0)
first=root
for i in sorted(arr):
root.next=ListNode(i)
root = root.next
return first.next
Time complexity: O (N log N), where N is the total number of nodes.
- It takes O(N) time to traverse all values.
- A stable sorting algorithm takes O(NlogN) time.
- It takes O(N) time to traverse and create a new ordered list at the same time.
Spatial complexity: O(N).
- Sorting costs O(N)O(N) space (depending on the algorithm you choose).
- Creating a new list costs O(N)O(N) space.
Merge two linked lists one by one
- Determine if there is more than one linked list; if not, return.
- Merge two linked lists one by one.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code her
root = ListNode(0)
first=root
while pHead1 and pHead2:
val1=pHead1.val
val2=pHead2.val
if val1<=val2:
root.next=ListNode(val1)
pHead1=pHead1.next
else:
root.next=ListNode(val2)
pHead2=pHead2.next
root=root.next
if pHead1:
root.next=pHead1
if pHead2:
root.next=pHead2
return first.next
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
if len(lists)==0:
return None
if len(lists)==1:
return lists[0]
res = self.Merge(lists[0],lists[1])
for i in range(2,len(lists)):
res = self.Merge(res,lists[i])
return res
Complexity analysis
Time complexity: O(kN), where k is the number of linked lists.
- We can merge two ordered lists in O(n) time, where n is the total length of the two lists.
- Add up all the time required for the merging process and we can get: O(kN)
Spatial complexity: O(1)
- We can merge two ordered lists in O(1) space.
But the python implementation timed out
Divided approach
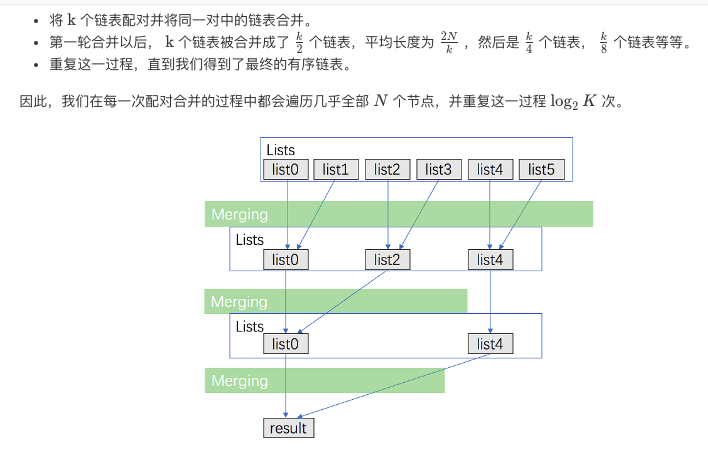
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
# write code here
if pHead1 is None and pHead2 is None:
return None
elif pHead1 is None:
return pHead2
elif pHead2 is None:
return pHead1
elif pHead1.val<=pHead2.val:
pHead1.next = self.Merge(pHead1.next, pHead2)
return pHead1
else:
pHead2.next = self.Merge(pHead1, pHead2.next)
return pHead2
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
if len(lists)==0:
return None
if len(lists)==1:
return lists[0]
amount = len(lists)
interval = 1
while interval < amount:
for i in range(0, amount - interval, interval * 2):
lists[i] = self.Merge(lists[i], lists[i + interval])
interval *= 2
return lists[0] if amount > 0 else lists