1. memcached Distributed Introduction
Although memcached is called a "distributed" cache server, there is no "distributed" function on the server side. Memcache cluster hosts can not communicate with each other to transmit data, and its "distributed" is further realized based on client-side program logic algorithm.
See the following sketch:
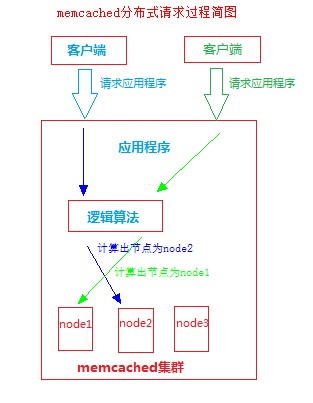
Based on the above figure, we briefly describe the process of analyzing set and get of distributed memcached
set process:
1. First, through the application set('key','value')
2. Enter the program and use key to get the location of the node that the key needs to store by logical algorithm.
3. Connect the corresponding memcached server according to the node location and send the set command
get process:
1. First, get('key') through the application.
2. Then use the key to get the storage node of the key by logical algorithm.
3. Connect the corresponding memcached server according to the node and send get command
There are many ways to implement memcached, among which the most common one is the distribution of consistent hashing (hereinafter referred to as uniform hashing). Good things of course need inferior products to foil its advantages, so besides uniform hash distribution, we will also talk about modular distribution here. So we can further analyze their advantages and disadvantages.
The examples here will be implemented in PHP code, of course, the most important thing is the ideas and methods. After all, these two things are common in any language.
2. Modeling Algorithms
What is the distributed mode of modular algorithm? The key is converted to a 32-bit number and divided by the total number of memcached servers to get the remainder. The remainder is the node of the memcached server. With this node, we can determine the memcached server and send commands to memcached to execute.
Graphic analysis:
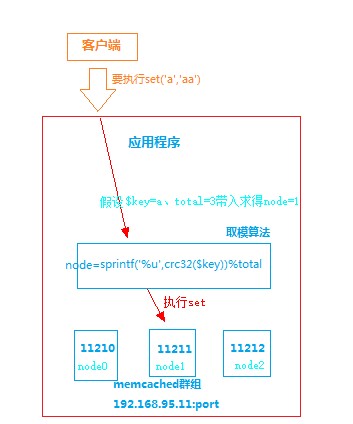
The whole process is shown in the figure above.
1) PHP Code Implementation
GetModMemcache.class.php
1 <?php 2 #Distributed memcache(Modeling calculation) 3 class GetModMemcache 4 { 5 private $total=''; #storage memcache Total number of servers 6 private $servers=array(); #storage memcache Server Specific Information 7 /** 8 * @desc Constructor 9 * 10 * @param $serversArr array | memcache Server Specific Information 11 */ 12 public function __construct($serversArr) 13 { 14 $this->total=count($serversArr); 15 $this->servers=$serversArr; 16 } 17 18 /** 19 * @desc Calculate the storage location of $key (that is, which server) 20 * 21 * @param string | key Character string 22 * 23 * @return int Return to the number of servers 24 */ 25 protected function position($key) 26 { 27 #Use crc32(),Converting strings to 32 digits 28 return sprintf('%u',crc32($key))%$this->total; #Remainder 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * @desc Getting memcached objects 33 * 34 * @param $position int | key Location information 35 * 36 * @return object Returns the instantiated memcached object 37 */ 38 protected function getMemcached($position) 39 { 40 $host=$this->servers[$position]['host']; #A server in the server pool host 41 $port=$this->servers[$position]['port']; #A server in the server pool port 42 $m= new memcached(); 43 $m->addserver($host, $port); 44 return $m; 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * @desc Set the key-value value value 49 * 50 * @param string | key Character string 51 * @param mixed | Values can be any valid non-resource php type 52 * 53 * @return Return results 54 */ 55 public function setKey($key, $value) 56 { 57 $num=$this->position($key); 58 echo $num; #Debugging 59 $m=$this->getMemcached($num); #Obtain memcached object 60 return $m->set($key, $value); 61 } 62 63 public function getKey($key) 64 { 65 $num=$this->position($key); 66 $m=$this->getMemcached($num); 67 return $m->get($key); 68 } 69 70 71 } 72 73 74 $arr=array( 75 array('host'=>'192.168.95.11', 'port'=>'11210'), 76 array('host'=>'192.168.95.11', 'port'=>'11211'), 77 array('host'=>'192.168.95.11', 'port'=>'11212'), 78 ); 79 $mod=new GetModMemcache($arr); 80 81 /* 82 #Storage of data 83 $a=$mod->setKey('key3', 'key33333'); 84 echo "<pre>"; 85 print_r($a); 86 echo "</pre>";die; 87 */ 88 /* 89 #get data 90 $b=$mod->getKey('key1'); 91 echo "<pre>"; 92 print_r($b); 93 echo "</pre>";die; 94 */ 95 ?>
2) Conduct corresponding tests
1. Continuous insertion of three data
#set('key1','value11111'); #node=1
#set('key2','value22222'); #node=1
#set('key3','value33333';) #node=0
2. telnet connection 192.168.95.11: (11210, 11211, 11212)
11210 contains key3 data
11211 contains key1 and key2 data
11212 does not contain data
3. Use program get data
The result is that the data can be retrieved.
3) Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
1. Simple, practical and easy to understand
2. Uniform distribution of data
Disadvantages:
1. When a memcached server is down, it can not automatically adjust the group to process data, so that some data can not be cached, and it has been continuously retrieving data from the database.
2. When need to expand, add more memcached servers, then most of the cached data can not be hit, that is, the data is useless.
3. Uniform Hash Algorithms
What is uniform hash algorithm distributed?
Imagine distributing all 32-bit numbers clockwise from small to large on a circle.
Secondly, each storage node is given a name and converted to a 32-bit number through the crc32 function, which is the storage node of the memcached server.
Next, the key is converted to a 32-bit number through the crc32 function, and its location is clockwise. The memcached server corresponding to the first encounter storage node is the final storage server of the key.
1) Image analysis
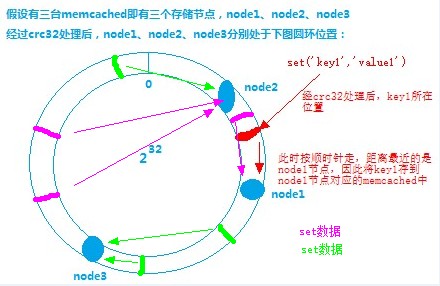
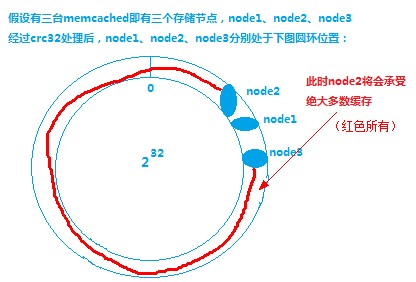
Assuming that the node1 node server hangs up, according to the clockwise nearest principle, the data originally stored in the node1 node can also be stored in the node3 node at this time.
Assuming there is a need for expansion, what about two additional memcached servers? See the chart below for analysis.
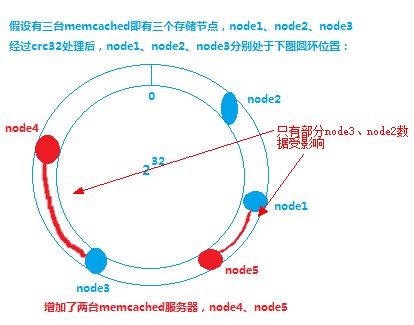
The results show that only a small amount of data will be affected, and these effects are acceptable relative to the overall data.
From the above illustration, we can easily find that we can not control the location of memcached storage nodes by using the crc32 function, and the total number of nodes is very small relative to the 32 power of 2. If it happens that even these storage nodes are very close, then there must be a memcached server to withstand the vast majority of data caching.
See the following chart for analysis:
Solution:
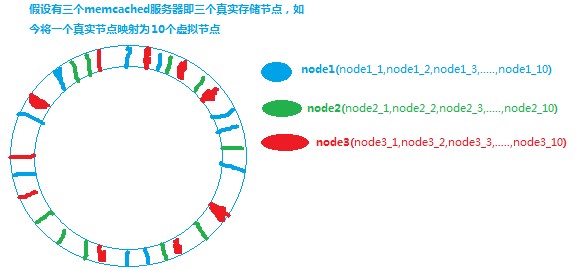
Mapping a real storage node to multiple virtual storage nodes, that is, the real node + suffix is processed by crc32 (e.g. node1_1, node1_2, node1_3,... ., node1_n)
Look at the node distribution in the following figure:
Three real nodes become thirty storage nodes on the ring, which can avoid the problem of uneven distribution of data cache caused by too close storage nodes, and the storage mechanism has no change.
2) PHP Code Implementation
ConsistentHashMemcache.class.php
1 <?php 2 #Distributed memcache Consistency hashing algorithm (using ring data structure) 3 class ConsistentHashMemcache 4 { 5 private $virtualNode=''; #Number of virtual nodes to store 6 private $realNode=array(); #Used to store real nodes 7 private $servers=array(); #Used for storage memcache server information 8 #private $totalNode=array(); #Number of nodes 9 /** 10 * @desc Constructor 11 * 12 * @param $servers array | memcache Server information 13 * @param $virtualNode int | Number of virtual nodes, default 64 14 */ 15 public function __construct($servers, $virtualNode=64) 16 { 17 $this->servers=$servers; 18 $this->realNode=array_keys($servers); 19 $this->virtualNode=$virtualNode; 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * @return int Returns a 32-bit number 24 */ 25 private function hash($str) 26 { 27 return sprintf('%u',crc32($str)); #Converting strings to 32-bit numbers 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * @desc Processing Node 32 * 33 * @param $realNode array | Real Node 34 * @param $virturalNode int | Number of virtual nodes 35 * 36 * @return array Returns all node information 37 */ 38 private function dealNode($realNode, $virtualNode) 39 { 40 $totalNode=array(); 41 foreach ($realNode as $v) 42 { 43 for($i=0; $i<$virtualNode; $i++) 44 { 45 $hashNode=$this->hash($v.'-'.$i); 46 $totalNode[$hashNode]=$v; 47 } 48 } 49 ksort($totalNode); #Sort by index, ascend 50 return $totalNode; 51 } 52 53 /** 54 * @desc Get the key's real storage node 55 * 56 * @param $key string | key Character string 57 * 58 * @return string Returns the real node 59 */ 60 private function getNode($key) 61 { 62 $totalNode=$this->dealNode($this->realNode, $this->virtualNode); #Get all virtual nodes 63 /* #View the total number of virtual nodes 64 echo "<pre>"; 65 print_r($totalNode); 66 echo "</pre>";die; 67 */ 68 $hashNode=$this->hash($key); #key Hash node of 69 foreach ($totalNode as $k => $v) #Loop Summary Point Loop Search 70 { 71 if($k >= $hashNode) #Find the first greater than key The value of hash node 72 { 73 return $v; #Returns the real node 74 } 75 } 76 return reset($totalNode); #If the value of the total node ring is equal to the value of the total node ring key If the hash node is small, the first total hash ring is returned. value value 77 } 78 79 /** 80 * @desc Return memcached object 81 * 82 * @param $key string | key value 83 * 84 * @return object 85 */ 86 private function getMemcached($key) 87 { 88 $node=$this->getNode($key); #Getting Real Nodes 89 echo $key.'Real node:'.$node.'<br/>'; #Test usage, view key True Node 90 $host=$this->servers[$node]['host']; #A server in the server pool host 91 $port=$this->servers[$node]['port']; #A server in the server pool port 92 $m= new memcached(); #instantiation 93 $m->addserver($host, $port); #Add to memcache The server 94 return $m; #Return memcached object 95 } 96 97 /** 98 * @desc Set the key-value value value 99 */ 100 public function setKey($key, $value) 101 { 102 $m=$this->getMemcached($key); 103 return $m->set($key, $value); 104 } 105 106 /** 107 * @desc Get the value in the key 108 */ 109 public function getKey($key) 110 { 111 $m=$this->getMemcached($key); 112 return $m->get($key); 113 } 114 115 116 } 117 118 ?>
3) Testing
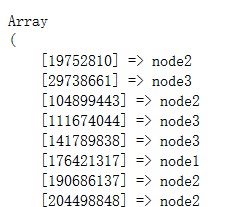
1. View all virtual nodes
A total of 64*3 = 132 virtual nodes (virtual node settings are still relatively small, usually between 100 and 200)
2. set test
1 include './ConsistentHashMemcache.class.php'; 2 header("content-type: text/html;charset=utf8;"); 3 $arr=array( 4 'node1'=>array('host'=>'192.168.95.11', 'port'=>'11210'), 5 'node2'=>array('host'=>'192.168.95.11', 'port'=>'11211'), 6 'node3'=>array('host'=>'192.168.95.11', 'port'=>'11212'), 7 ); 8 9 $c=new ConsistentHashMemcache($arr); 10 11 #test set 12 $c->setKey('aaa', '11111'); 13 $c->setKey('bbb', '22222'); 14 $c->setKey('ccc', '33333');

telnet connection 192.168.95.11: (11210, 11211, 11212)
In node 1, get('aaa') and get('bbb') can get values.
get('ccc') can get the value in node 3
3. get test
1 include './ConsistentHashMemcache.class.php'; 2 header("content-type: text/html;charset=utf8;"); 3 $arr=array( 4 'node1'=>array('host'=>'192.168.95.11', 'port'=>'11210'), 5 'node2'=>array('host'=>'192.168.95.11', 'port'=>'11211'), 6 'node3'=>array('host'=>'192.168.95.11', 'port'=>'11212'), 7 ); 8 9 $c=new ConsistentHashMemcache($arr); 10 #test get 11 echo $c->getKey('aaa').'<br/>'; 12 echo $c->getKey('bbb').'<br/>'; 13 echo $c->getKey('ccc').'<br/>';

4. Advantages and disadvantages
Comparing with the distributed mode, the code complexity of the consistent hash mode is higher, but it is acceptable and does not pose any obstacles. On the contrary, its advantages are very significant. By means of virtual nodes, uncontrollable storage nodes can be distributed as evenly as possible in the ring, so that data can be evenly cached in each host. Secondly, adding and deleting virtual nodes has little impact on the overall data cached before.
(These are my own opinions and summaries. If there are any shortcomings or mistakes, please point them out.)
Authors: That leaf follows the wind
Statement: The above only represent my own views or conclusions summarized during a certain period of work and study. When reprinting, please give a link to the original text in a clear place on the article page.