1, maven basics review
1. Introduction to maven
- Maven is a project management tool, which is mainly used for dependency management and project construction of Java projects in the project development stage.
- Dependency management: it is the management of jar packages. Importing maven coordinates is equivalent to importing jar packages in the warehouse into the current project.
- Project construction: the whole process of project cleaning, compiling, testing, reporting, packaging and deployment can be completed through a command of maven.

2. Warehouse type of maven
① Local warehouse
② Remote warehouse
- ① maven central warehouse (address: http://repo2.maven.org/maven2/)
- ② maven private server (the warehouse in the company's LAN needs to be built by yourself)
- ③ Other public remote warehouses (such as those provided by apache, address:
http://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/)
Local warehouse - > Maven private server - > Maven central warehouse
3.maven common commands
Clean: clean
Compile: compile
test: test
Package: package
Install: install
4.maven coordinate writing specification
<dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.32</version> </dependency>
2, Maven's dependency passing
1. What is dependency delivery
In maven, dependency is transitive. It is assumed that there are three projects, namely project A, project B and project C. assuming that C depends on B and B depends on A, it is not difficult to deduce that project C also depends on A according to the characteristics of Maven project dependency.
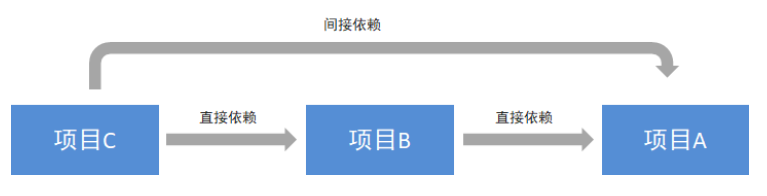

As can be seen from the above figure, the web project directly relies on spring webmvc, and spring webmvc relies on spring AOP, spring beans, etc. the final result is that our web project indirectly relies on spring AOP, spring beans, etc.
Dependency conflict
Due to the existence of dependency transfer, spring webmvc relies on sping-beans-5.1.5 and spring AOP relies on spring-beans-5.1.6. However, it is found that sping-beans-5.1.5 is added to the project, and we hope spring-beans-5.1.6 is added to the project. This leads to dependency conflict.

2. How to resolve dependency conflicts
- 1. Use the principle of relying on mediation provided by maven
Principle of first declaration priority
The principle of "the nearest path first" - 2. Exclude dependencies
- 3. Locked version
3. The principle of relying on Regulation - the first declaration takes precedence
The dependencies defined in the pom file shall be subject to the dependencies declared first. In fact, it is to determine which passed dependencies are finally used according to the order of coordinate import.
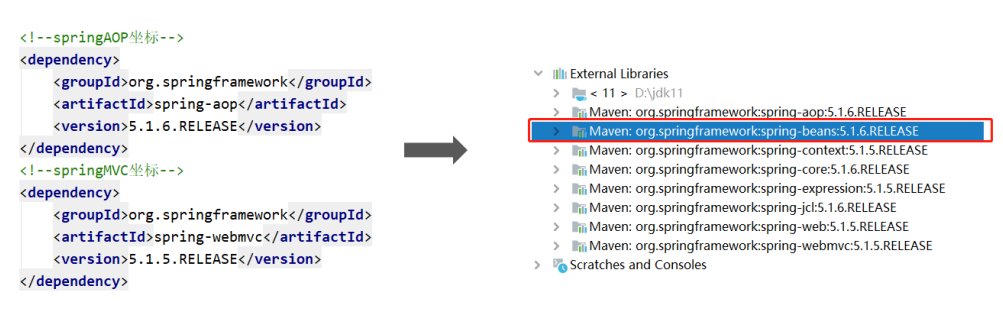 Conclusion: as can be seen from the above figure, spring beans are passed from both spring AOP and spring webmvc, but because spring AOP is in front, the final spring beans are passed from spring AOP, while the spring beans passed from spring webmvc are ignored.
Conclusion: as can be seen from the above figure, spring beans are passed from both spring AOP and spring webmvc, but because spring AOP is in front, the final spring beans are passed from spring AOP, while the spring beans passed from spring webmvc are ignored.
4. The principle of dependence and regulation -- the principle of "the nearest path first"
 Summary: direct dependency is greater than dependency passing
Summary: direct dependency is greater than dependency passing
5. Exclude dependencies
You can use the exclusions tag to exclude the passed dependencies.

6. Version locking
The method of directly locking the version is adopted to determine the version that depends on the jar package. After the version is locked, the dependent declaration order or dependent path will not be considered, and the locked version will prevail. This method is often used in enterprise development.
How to use version locking:
Step 1: lock the dependent version in the dependency management tab
Step 2: declare the maven coordinates to be imported in the dependencies tab
① Lock the dependent version in the dependency management tab
 ② Declare the maven coordinates to be imported in the dependencies tab
② Declare the maven coordinates to be imported in the dependencies tab
 Particular attention
Particular attention
The dependency management tag is only used to lock the jar package version, and does not introduce the function of jar package
7. Use of properties tag
<properties>
<spring.version>5.1.5.RELEASE</spring.version>
<springmvc.version>5.1.5.RELEASE</springmvc.version>
<mybatis.version>3.5.1</mybatis.version>
</properties>
<!--locking jar edition-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- Mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- springMVC -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${springmvc.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
3, Maven polymerization project (sub module)
Concept:
In real life, when automobile manufacturers produce automobiles, because the whole production process is very complex and cumbersome and the workload is very large, manufacturers will produce the parts of the whole automobile separately, and finally assemble the produced parts to form a complete automobile.
1. Module construction maven engineering analysis
In enterprise project development, due to the large scale of the project, complex business and large number of participants, a large project is generally divided into N small modules for development through reasonable module splitting, and the split modules can be easily reused by other modules
There are two common splitting methods:
The first method is to split according to business modules. Each module is divided into a maven project. For example, a project is divided into user module, order module, shopping cart module, etc. each module corresponds to a maven project
The second is to split according to layers, such as persistence layer, business layer and presentation layer. Each layer corresponds to a maven project
Regardless of the above splitting method, a parent project is usually provided to extract some public code and configuration into the parent project for unified management and configuration.
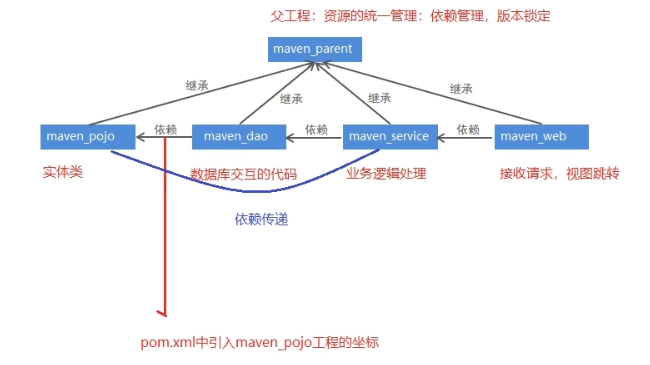
2. Inheritance of Maven project
In the Java language, classes can inherit. Through inheritance, subclasses can reference non private properties and methods in the parent class. Similarly, maven projects can inherit. After the child project inherits the parent project, it can use the dependencies introduced in the parent project. The purpose of inheritance is to eliminate duplicate code.
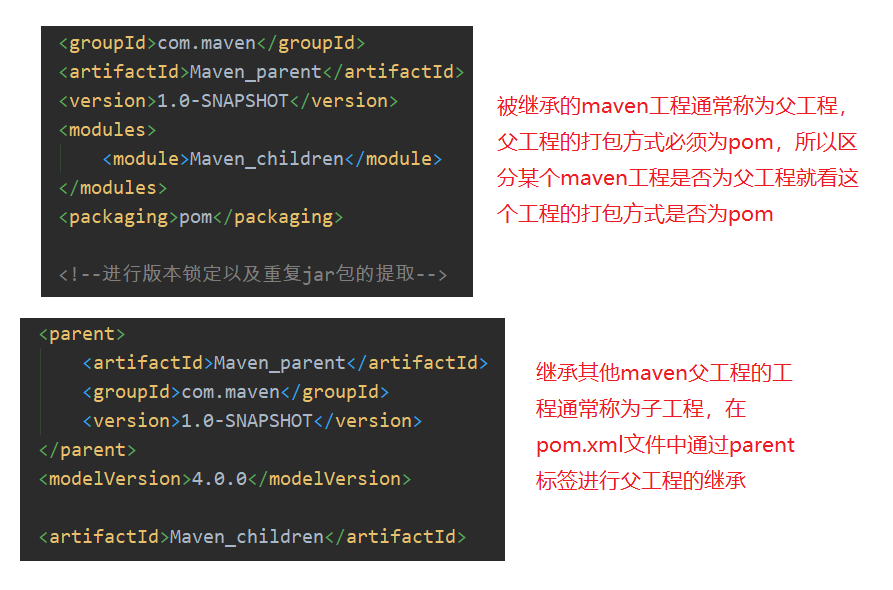
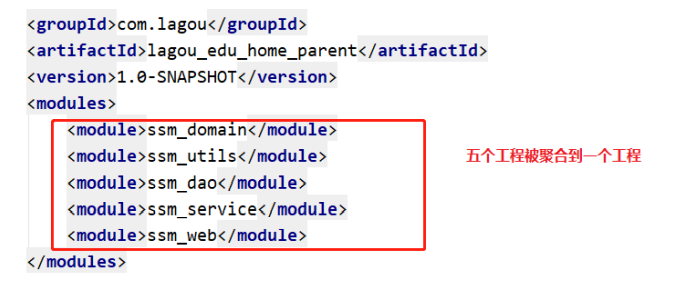
3. Aggregation of Maven project
In the pom.xml file of maven project, you can use the < modules > tag to aggregate other maven projects. The purpose of aggregation is to carry out unified operation.
For example, there are multiple maven projects after splitting. If you want to package, you need to execute the packaging command for each project, which is very cumbersome. At this time, you can use tags to aggregate these projects into maven parent projects. When you need to package, you only need to execute the packaging command in this project once, and the aggregated projects under it will be packaged.