Preface:
Previously, we have been able to initially implement a model of Chinese Natural Processing Language, but the interactive interface is command-line and not very friendly.
If you want to do something similar http://xiaosi.trs.cn/demo/rs/demo The interface, then, needs to go on.
Django
Since Jiagu and others use the python language, the implementation of the Web site gives priority to python's web framework.
And here's Django, which is still popular.
Tutorial Reference:
https://www.runoob.com/django/django-tutorial.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/feixuelove1009/p/5823135.html
1. Diango Installation
pip install Diango
2. Create a Web site
Use the django-admin command to create a project called ai
Enter the deployment directory, cd under Anaconda promt
The default directory to install under Anaconda integration is: \anaconda\Lib\site-packages\django\bin\
django-admin startproject ai
Command under linux:
The default installation directory under linux is: /usr/local/python3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/django/bin/
python django-admin.py startproject ai
3. Write Web pages
1) Set up environment information, modify settings.py
django knows where our html files are and needs to modify the settings file accordingly.Do not modify by default
'DIRS': [] Modified to'DIRS': [BASE_DIR+'/templates,]
Also comment on the following lines to temporarily turn off django's csrf cross-site request protection mechanism (which is called when user input is involved and will cause errors if not handled):
MIDDLEWARE = [
# 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
Add the allowed IP ALLOWED_HOSTS = [] to ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['XX.XX.XX.XX'] -- of course, this step is not required if the default 127.0.0.1 runs
2) Presentation Layer - Create a template directory and create index.html
The content displayed in the interface (the presentation layer) is placed in the Template template according to Diango's hierarchical thinking.
Therefore, we first create a directory of template s under the project and create an index.html file.The contents of the file will be supplemented later.
3) UI - Beautify the interface with bootstrap
Create a new static directory in the project and place it in the bootstrap directory.
Also add a reference to the static directory at settings.py:
STATIC_URL='/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS=(os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static"),)
4) Controller Layer-Business Logic, modify view.py
To provide data to the template layer, we define a function that receives user input from html and returns it to the user after view ing.
5) Routing System-urls.py
The url entered by the browser, forwarded to the business logic through this urls.py file
increase
import from ai import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', views.login),
path('login/', views.login),
]
4. Start the Web service
Execute Command
python manage.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8000
python manage.py runserver IP:8000
5. View the effect
Browser open url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/
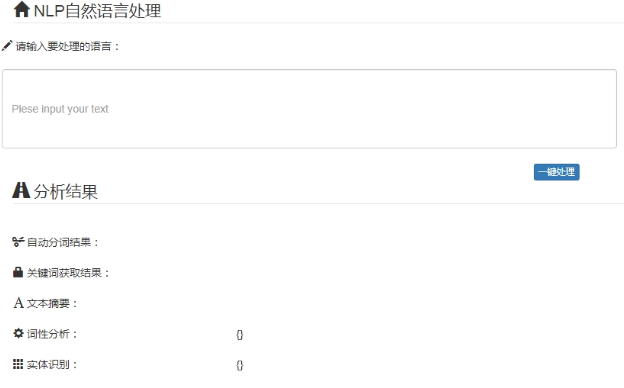
Primary Code:
views.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from django.shortcuts import render import jiagu # Create your views here. from django.shortcuts import render,redirect words="" keywords="" knowledge="" summarize="" def login(request): # request Contains all information submitted by the user words = "" keywords="" knowledge="" summarize="" text="" pos="" ner="" newPos={} newNer={} dict1 = {'B-PER':'Name','B-LOC':'place name','B-ORG':'Organization Name','I-PER':'Name','I-LOC':'place name','I-ORG':'Organization Name','O':'Not a noun phrase'} dict2 = {'n':'Common Noun','nt':'Time Noun','nd':'Location Noun','nl':'Location Noun','nh':'Name','nhf':'surname','nhs':'name', 'ns':'place name','nn':'Family Name','ni':'Organization Name','nz':'Other Specialty','v':'verb','a':'Adjective','m':'Numeral','d':'adverb','w':'Punctuation','ws':'Non-Chinese character string','i':'Idiom','j':'Abbreviation', 'r':'Pronoun','p':'Preposition','c':'Conjunction','u':'Auxiliary word','e':'Interjection','vd':'Trend Verbs','vl':'copulative verb','vu':'May Verb','x':'Non-morpheme words','m':'Numeral','q':'Classifier','mq':'undetermined','o':'An onomatopoeia','k':'Succeeding component'} if request.method == 'POST': inputText = request.POST.get('input',None) output = request.POST.get('output',None) text=inputText words = jiagu.seg(text) # Participle, can be used model Select the word breaking mode, or default if not filled in, mmseg Then use mmseg algorithm if (len(text)<=6): try: keywords = jiagu.keywords(text, 1) except ValueError: print("The keywords are not set properly, please contact the administrator!") elif (len(text)<=30): print(len(text)) keywords = jiagu.keywords(text, 3) else: try: keywords = jiagu.keywords(text, 5) except ValueError: print("The keywords are not set properly, please contact the administrator!") knowledge = jiagu.knowledge(text) # Knowledge Extraction summarize = jiagu.summarize(text, 1) # abstract pos = jiagu.pos(words) # Part of speech labeling ner = jiagu.ner(text) # Named Entity Recognition j=len(pos)-1 tmp=0 tmp2=0 while tmp<=j: k=pos[tmp] newPos[tmp]=(words[tmp],k,dict2[k]) tmp=tmp+1 i=len(ner)-1 while tmp2<=i: t=ner[tmp2] newNer[tmp2]=(text[tmp2],t,dict1[t]) tmp2=tmp2+1 print(words) print(keywords) print(newPos) print(knowledge) return render(request, 'login.html',{"text":text,"words":words,"keywords":keywords,"knowledge":knowledge,"summarize":summarize,"pos":newPos,"ner":newNer})
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>login</title> <style> label{ width: 80px; text-align: right; display: inline-block; } </style> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="/static/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css" > </head> <body> <div class="container"> <form action="/login/" method="post" class="form-horizontal"> <filedset> <legend><lable> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-home"></span> NLP natural language processing </lable></legend> <div class="row"> <!--Raster system, per row Rows 12 columns in 3 div,Every,3 individual div 3 columns, 2nd div 5 columns, or 3 columns+5 column+4 column=12 column--> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-pencil"></span> Please enter the language to be processed: <input type="text" name="input" placeholder="Please enter the text you want to process:for example:Guangzhou City" class="form-control" style="margin: 20px 0px 0px; height: 104px; width: 807px;" required value={{text}} > </div> <div class="row"> <br> <div class="col-sm-7 col-sm-offset-7"> <input type="submit" value="One-click processing" class="btn btn-xs btn-primary" > <!-- <button type="reset" value="Reset" class="btn btn-xs btn-warning"></button>--> </div> </div> <legend><lable> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-road"></span> Analysis results </lable></legend> <br> <div class="row"> <div class="col-sm-3"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-scissors"></span> Automatic word segmentation results: </div> <div class="col-sm-6"> {%for output in words%} {{output}} {% endfor %} </div> <div class="col-sm-3"></div> </div> <br> <div class="row"> <div class="col-sm-3" ><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-lock"></span> Keyword Acquisition Results: </div> <div class="col-sm-6"> {%for output in keywords%} {{output}} {% endfor %} </div> <div class="col-sm-3"></div> </div> <br> <div class="row"> <div class="col-sm-3" ><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-font"></span> Text summary: </div> <div class="col-sm-6"> {%for output in summarize%} {{output}} {% endfor %}</div> <div class="col-sm-3"></div> </div> <br> <div class="row"> <div class="col-sm-3" ><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-cog"></span> Word Analysis: </div> <div class="col-sm-6"> {{pos}} </div> <div class="col-sm-3"></div> </div> <br> <div class="row"> <div class="col-sm-3" ><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-th"></span> Entity recognition: </div> <div class="col-sm-6"> {{ner}} </div> <div class="col-sm-3"></div> </div> <br> <div class="row"> <div class="col-sm-3" ><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-tree-deciduous"></span> Map of Knowledge Relationships: </div> <div class="col-sm-6"> {{knowledge}} </div> <div class="col-sm-3"></div> </div> </filedset> </form> </div> </body> </html>
Appendix: Knowledge used:
1. Django gets data submitted by user interface forms
In view.py:
if request.method == 'POST':
# Get data submitted by users via post
inputText = request.POST.get('input',None)
In html:
<form action="/login/" method="post" class="form-horizontal">
<input type="text" name="input" value={{text}} >
2. Django returns user interface data and displays it in html
In view.js
return render(request, 'index.html',{"text":text,"words":words})
In html:
<div class="col-sm-6">
{%for output in words%}
{{output}}
{% endfor %}
</div>