ipvsadm
The ipvsadm command is the management tool of lvs Cluster in the application layer. We can use this ipvsadm to manage the configuration of lvs. In fact, it implements the cluster service management: add, delete, change, RS management of cluster service: add, delete, change and view the cluster status.
Management cluster service: add, change, delete;
Add (A), change (E):
ipvsadm -A|E -t|u|f service-address [-s scheduler] [-p [timeout]]
Delete:
ipvsadm -D -t|u|f service-address
-t|u|f service-address:
-t: Port of TCP protocol, VIP: TCP port, such as - t 172.16.10.6:80
-u: Port of UDP protocol, VIP: UDP port
-f: firewall MARK, a number, can be defined by iptables
[- s scheduler]: Specifies the scheduling algorithm of the cluster. The default is wlc
RS on Management Cluster: add, change, delete;
Add (a), change (e):
ipvsadm -a|e -t|u|f service-address -r server-address [-g|i|m] [-w weight]
Delete:
ipvsadm -d -t|u|f service-address -r server-address
-R server address: rip[:port], indicating the IP address of RS
Type lvs:
-g: gateway, dr type
-i: ipip, tun type
-m: masquerade, nat type
-w weight: weight
To view the status information of a cluster:
ipvsadm -L|l [options]
options:
-c, --connection: Show current LVS Connect
--timeout: List timeouts
--daemon:
--stats: status information
--rate: transmission speed
--persistent-conn: Insist on linking up
--sor: Sort the list.
--nosort: Unsorted
-n, --numeric: output IP Digital form of address and port
Saving and overloading rules:
Save and reload:
ipvsadm -S = ipvsadm-save
ipvsadm -R = ipvsadm-restore
Clear all defined:
ipvsadm -C
Clear all data related counters:
ipvsadm -Z [-t|u|f service-address]
The implementation of LVS NAT cluster
Simple flow chart:
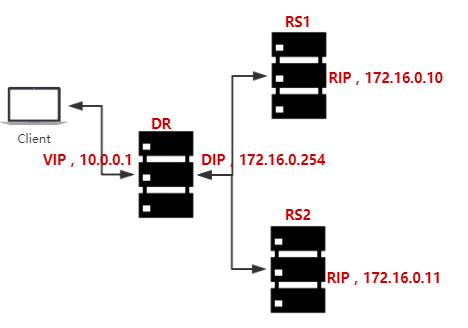
Configure RS1:
[root@RS1 ~]# yum -y install httpd #Install Apache
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service #Turn off firewall
[root@RS1 ~]# ifconfig eno16777736 172.16.0.10/24 up #Configure NIC
[root@RS1 ~]# route add default gw 172.16.0.254 #Configuration routing
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf #Set httpd
Listen 8080
ServerName localhost
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /var/www/html/index.html
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 <h1>
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl start httpd #Enable httpd
[root@RS1 ~]# ss -tan
LISTEN 0 128 :::8080 :::*
Refer to RS1 for configuration of RS2.
Configure DR:
[root@DR ~]# yum -y install ipvsadm #Install ipvsadm tool
[root@DR ~]# ifconfig eno16777736 10.0.0.1/24 up #Configure vip
[root@DR ~]# ifconfig eno16777736:0 172.16.0.254/24 up #Configure dip
[root@DR ~]# sysctl -a | grep ip_forward #Make sure the core forwarding function is turned on
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 10.0.0.1:80 -s rr #Configure lvs cluster rules
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 10.0.0.1:80 -r 172.16.0.10:8080 -m
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 10.0.0.1:80 -r 172.16.0.11:8080 -m
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 10.0.0.1:80 rr
-> 172.16.0.10:8080 Masq 1 0 0
-> 172.16.0.11:8080 Masq 1 0 0
Client test:
# The scheduling algorithm uses rr and polling mode, so the ratio when calling RS is 1:1
[root@client ~]# for i in {1..20}; do curl http://10.0.0.1; done
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
<h1> RS1 172.16.0.10 </h1>
<h1> RS2 172.16.0.11 </h1>
The implementation of LVS Dr cluster
Simple flow chart:
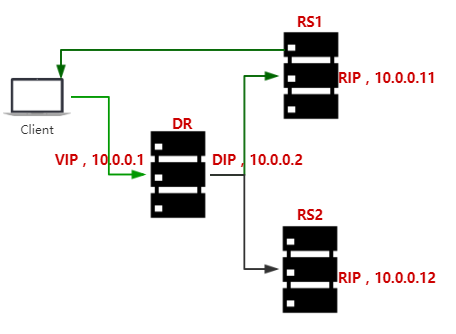
Configure RS1:
[root@RS1 ~]# ifconfig eno16777736 10.0.0.11/24 up #Configure NIC
[root@RS1 ~]# ifconfig lo:0 10.0.0.1 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 10.0.0.1 up
[root@RS1 ~]# route add -host 10.0.0.1 dev lo:0 #Configuration routing
[root@RS1 ~]# echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_ignore #Set arp response
[root@RS1 ~]# echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_ignore
[root@RS1 ~]# echo 2 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_announce
[root@RS1 ~]# echo 2 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_announce
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf #Set httpd
Listen 80
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /var/www/html/index.html
<h1> RS1 10.0.0.11<h1>
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl start httpd #Enable httpd
[root@RS1 ~]# ss -tan
LISTEN 0 128 :::8080 :::*
Refer to RS1 for configuration of RS2.
Configure DR:
[root@DR ~]# ifconfig eno16777736 10.0.0.2/24 up #Configure dip [root@DR ~]# ifconfig eno16777736:0 10.0.0.1 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 10.0.0.1 up #Configure vip [root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 10.0.0.1:80 -s wrr #Configure lvs cluster rules [root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 10.0.0.1:80 -r 10.0.0.11 -g -w 1 [root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 10.0.0.1:80 -r 10.0.0.12 -g -w 2 [root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -ln IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096) Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags -> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn TCP 10.0.0.1:80 wrr -> 10.0.0.11:80 Route 1 0 0 -> 10.0.0.12:80 Route 2 0 0
Client test:
# Scheduling algorithm use wrr,The specific gravity is 1.:2 [root@client ~]# for i in {1..20}; do curl http://10.0.0.1; done <h1> RS1 10.0.0.11 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS1 10.0.0.11 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.11 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS1 10.0.0.11 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.11 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS1 10.0.0.11 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.11 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1> <h1> RS2 10.0.0.12 </h1>
RS1 configuration script reference:
#!/bin/bash
#
vip=10.0.0.1
rip=10.0.0.11
mask1=255.255.255.255
mask2=255.255.255.0
case $1 in
start)
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_ignore
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_ignore
echo 2 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_announce
echo 2 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_announce
ifconfig eno16777736 $rip netmask $mask2 up
ifconfig lo:0 $vip netmask $mask1 broadcast $vip up
route add -host $vip dev lo:0
;;
stop)
ifconfig lo:0 down
echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_ignore
echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_ignore
echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_announce
echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_announce
;;
*)
echo "Usage $(basename $0) start|stop"
exit 1
;;
esac
DR configuration script reference:
#!/bin/bash
#
vip=10.0.0.1
mask1=255.255.255.255
dip=10.0.0.2
mask2=255.255.255.0
port=80
rs1=10.0.0.11
rs2=10.0.0.12
scheduler='wrr'
type='-g'
case $1 in
start)
ifconfig eno16777736 $dip netmask $mask2 up
ifconfig eno16777736:0 $vip netmask $mask1 broadcast $vip up
ipvsadm -A -t ${vip}:${port} -s $scheduler
ipvsadm -a -t ${vip}:${port} -r ${rs1} $type -w 1
ipvsadm -a -t ${vip}:${port} -r ${rs2} $type -w 2
;;
stop)
ipvsadm -C
ifconfig eno16777736:0 down
;;
*)
echo "Usage $(basename $0) start|stop"
exit 1
;;
esac