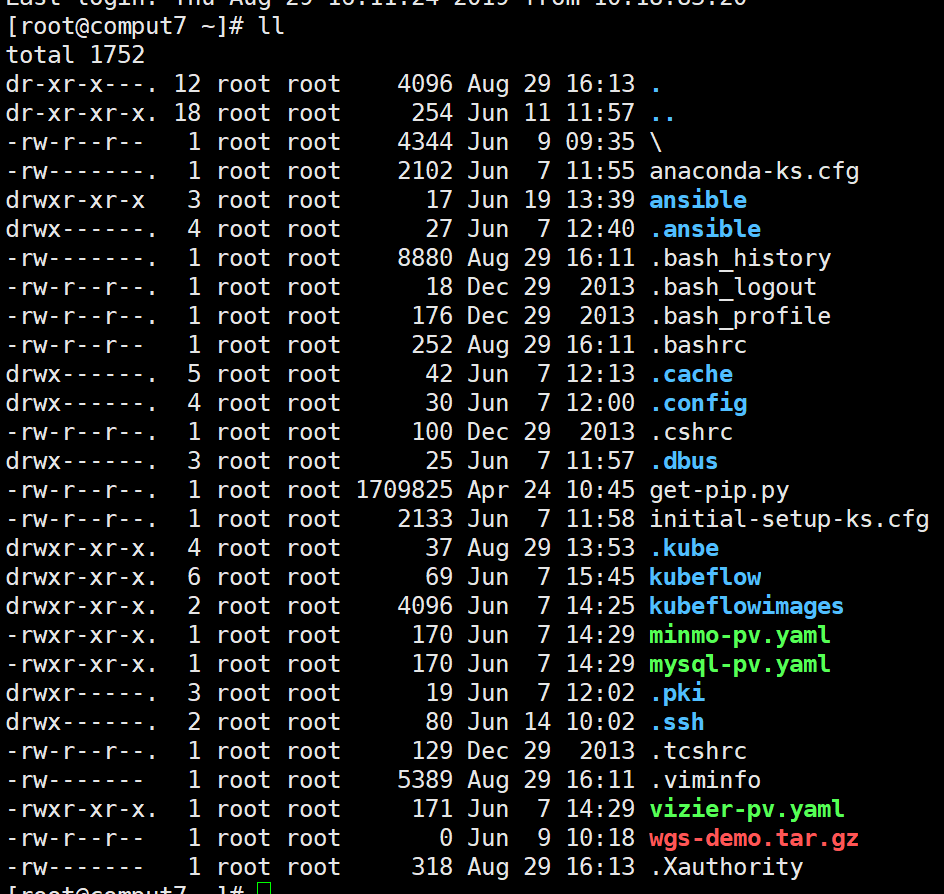
L l command is actua ll y ls-l, of course, if you want to show hidden information is ls-al.
Personally, I particularly like ll instead of ls -al, and I want to have the same color.
Today, how to reinstall the environment variables in the software installation is not correct. Command: unset PATH
Then add environment variables manually:
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin:/root/bin
But the ll command was gone.
Solution 1 (no color):
Add at the top of ~/. bashrc file
alias ll='ls -la'
Then run the command: source ~/.bashrc
At this point, ll will be there, and reopening the terminal will take effect, but there is no color, as shown below:
Solution 2:
Copy A / etc/profile file from another machine and you will find the color. Maybe my previous / etc/profile file is broken.
The centos7 file is as follows. It is not clear whether other systems are the same.
Link:
Link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1iqDphAxqxTuB-H75LRpGA Extraction Code: zzp2
# /etc/profile
# System wide environment and startup programs, for login setup
# Functions and aliases go in /etc/bashrc
# It's NOT a good idea to change this file unless you know what you
# are doing. It's much better to create a custom.sh shell script in
# /etc/profile.d/ to make custom changes to your environment, as this
# will prevent the need for merging in future updates.
pathmunge () {
case ":${PATH}:" in
*:"$1":*)
;;
*)
if [ "$2" = "after" ] ; then
PATH=$PATH:$1
else
PATH=$1:$PATH
fi
esac
}
if [ -x /usr/bin/id ]; then
if [ -z "$EUID" ]; then
# ksh workaround
EUID=`/usr/bin/id -u`
UID=`/usr/bin/id -ru`
fi
USER="`/usr/bin/id -un`"
LOGNAME=$USER
MAIL="/var/spool/mail/$USER"
fi
# Path manipulation
if [ "$EUID" = "0" ]; then
pathmunge /usr/sbin
pathmunge /usr/local/sbin
else
pathmunge /usr/local/sbin after
pathmunge /usr/sbin after
fi
HOSTNAME=`/usr/bin/hostname 2>/dev/null`
HISTSIZE=1000
if [ "$HISTCONTROL" = "ignorespace" ] ; then
export HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
else
export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups
fi
export PATH USER LOGNAME MAIL HOSTNAME HISTSIZE HISTCONTROL
# By default, we want umask to get set. This sets it for login shell
# Current threshold for system reserved uid/gids is 200
# You could check uidgid reservation validity in
# /usr/share/doc/setup-*/uidgid file
if [ $UID -gt 199 ] && [ "`/usr/bin/id -gn`" = "`/usr/bin/id -un`" ]; then
umask 002
else
umask 022
fi
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh /etc/profile.d/sh.local ; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "${-#*i}" != "$-" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null
fi
fi
done
unset i
unset -f pathmungeNever edit this document in the windows system. If linux and windows code differently, I will make a blank under windows and then make a mistake.
-bash: $'\r': command not found
Replace your / etc/profile with the above file
Execution command: source/etc/profile
All right, now all terminals can be opened using ll and are colored: