Linux Notes
Installation section:
swap virtual memory is twice as large as memory, such as 4G (no setting if large)
Boot partition master boot 500M
/Root Full Allocation
You can also create a / data that can be used to mount things
--------------
Configuration section:
hostnamectl set-hostname name #Set Host Name exec bash #Refresh
Remote ssh login
ssh root@192.168.1.1
File viewing section:
Ls-R | wc-l where -R is a recursive view and WC is a statistic of how many rows there are
Ls-l View file properties rw-r--r and so on are owner, group, other permissions
File can see the file format
cd - Back to the last directory
vim!$A little confused (last character of last command)
Exclamation mark to call last command
If the previous one executed rm-rf*
Then!Rm=rm-rf *
Create a directory:
mkdir -p 1/2/3 #Recursive creation
mkdir test{1,2,3}perhaps mkdir test{1..99}Create 99
touch 123 #create a file
echo 123123 #Display 123123
echo 123123 >1.txt #Write 123123 in 1.txt
File lookup:
which: find command
locate: database-based lookup, fast lookup, need to update the database
find: traversal search, slow search, accurate (commonly used)
User and file rights management:
wrx:r=4,w=2,x=1
vim /etc/passwd #User Profile vim /etc/group #Group Profile vim /etc/shadow #User Password File vim /etc/gshadow #Group Password File vim /etc/sudoers #User Title File
User Add
useradd -u 3000 openstack #Create a user name OpenStack with uid 3000
User Rights
chown: Modify the file or directory to belong to the master/group
chown student ahdifu/ #Modify the ahdifu folder to belong to student
Modify file permissions
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| u | Represents the owner of the file |
| g | Group representing file |
| o | Other Users |
| a | Users Used |
| + | Add permissions |
| - | Delete permissions |
| = | Give privileges directly |
chomd u+w file #Subordinate to Groups to Increase w Permissions chomd o=wrx file #Give wrx (write, read, execute) permissions to other users chomd u-w file #Delete w permissions belonging to groups chomd 0765 file #Abbreviation
Supplement: ll-d filename=ls-ld filename
File Access Control List
setfacl: file access control list, set permissions for specific users
-m Set Permissions
-x Revoke permissions
Example:
setfacl -m u: student: rwx ahdifu/ #u means for the user
getfacl can see detailed groups and permissions
sticky permissions
...
SGID Permissions (Required)
chmod u+s filename chmod g+s filename chmod o+t filename
text processing
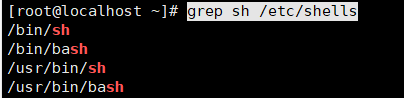
grep tool:
Used to filter information
grep sh /etc/shells
Filter effect as shown in the diagram
chattr +i test lsattr test.txt #Even root users cannot delete modifications after use
Network management:
ip addr #View local ip address information systemctl status network.service #Old Version systemctl status NetworkManager #8.3 Network Management Tools nmcli connection up ens160 #Use this refresh if the ip does not change after configuring the network ifconfig ens160 down ifconfig ens160 up
Network reboot is required to edit network card profile directly
nmcli conn up ens160 = nmcli connection up ens160 nmtui #Commands can be used to configure network cards
The above commands are based on the NetworkManager tool, and if the service is not turned on, the configuration of the network ip address cannot be modified.
systemctl status NetworkManager systemctl stop NetworkManager systemctl start NetworkManager systemctl enable NetworkManager #Start-Up Self-Starting systemctl disable NetworkManager nmcli connection show #View all network card connections _______________________________ nmcli connection reload nmcli connection up eth0 The above two are equivalent to those in version 7/etc/init.d/network restart
The following commands view port usage
netstat -tunalp netstat -tunlp | grep 8080 #View specified port usage ##netstat can be replaced with ss
Software management:
Installation of software:
rpm -ivh package_name #Multiple software packages can be installed at the same time, either locally or on the network
For example, we installed tree-1.7.0-15.e18.86_64rpm
Find/mnt-name tree This command finds a file named tree
This command checks to see if it is installed by default: rpm-qa tree*
(If so, delete the file using rpm-e package_name)
Next enter the installation command rpm-ivh t*, (t=tree)
Select tree-1.7.0-15.e18.86_64rpm to install
Decompression tool:
tar compression tool
| option | function |
|---|---|
| -c | Create archive file |
| -x | Extract Archive File |
| -c | Specify the extraction location, defaulting to the current directory |
| -f | Specify the archive file to operate on |
| -t | List which files are in the archive |
| -v | Show archiving process |
| -exclude | Exclude a file |
Common compression tools on Linux:
-z uses gzip compression
-j uses bzip2 compression
-J uses xz compression
General combination usage:
tar -czvf #Create an archive and gzip compression tar -xzvf #Extracting gzip compressed archive files tar -cjvf #Create an archive and use bzip2 compression tar -xjvf tar -cJvf #Create archives and use xz compression
Other compression tools (zip compression tools)
Use which zip to see if zip is installed or if not
zip /root/file.zip * #Compress all files in the current directory to / root / and name them file.zip uzip /root/file.zip /root/jieya #Unzip file.zip to jieya folder