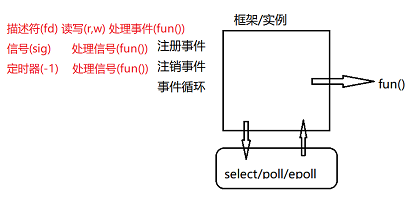
IO multiplexing: listen to multiple file descriptors at the same time
1.select
- Interview frequency
- What are the disadvantages of select and poll = > using epoll
- epoll ET mode and LT mode
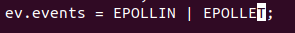
The focus is on the read event EPOLLIN, because the read event requires data in the buffer before it can be read, and if there is no data, it will be blocked. Therefore, it is necessary to judge whether there is data in the acceptance buffer first, and the write event (EPOLLOUT) can be written only if the buffer is empty
- select: listen to multiple file descriptors at the same time, up to 1024, read, write, exception and collection
Kernel: polling mode
Time complexity: O(n) - poll: supports more file descriptors and more event types than select
Kernel: polling mode
Time complexity: O(n)
Disadvantages of select and poll:
-Finding ready descriptors requires traversing all descriptors O(n)
-The kernel is polling
-Descriptors and events need to be passed to the kernel each time - epoll: solve the defects of select and poll
- select: the number of ready descriptors. I don't know who it is. If the number is small
Read, write and exception events, up to 1024
Check whether there is data within 5 seconds
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include<sys/select.h>
int main()
{
int fd = 0;//stdin 0 stdout 1 stderr 2 keyboard corresponding descriptor
fd_set fdset; //Collection descriptor detected by select
while(1)
{
struct timeval tv = {5,0}; //Timeout
FD_ZERO(&fdset); //Clear each bit in the collection
FD_SET(fd,&fdset); //fd adding multiple data to the collection requires a loop
int n = select(fd+1,&fdset,NULL, NULL,&tv); //Get the number of ready descriptors. It is impossible to know who found the data with descriptor 1 through the loop
//fd+1 detects only the previous bits that may have data
if(n == -1)
{
printf("err \n"); //fail
break;
}
if(n == 0)
{
printf("time out \n");//End of time
}
else
{ //n> 0 has data
if(FD_ISSET(fd,&fdset)) //success
{
char buff[128] = {0};
read(fd,buff,127}; //Read data output
printf("read:%s\n",buff);
}
}
}
}
2. poll
- poll: listen for multiple file descriptors at the same time
Support more file descriptors than select; Using arrays to implement
#include<poll.h>
POLLIN: shujukedu
Poll: Data writable
POLLRDHUP: the TCP connection is closed by the other party, or the other party has closed the write operation
Create socket:
136 int socket_init()
137 {
138 int sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);//Create socket
139 if(sockfd ==-1)
140 {
141 return -1;
142 }
143 //bind() can be bound, but generally not
144 struct sockaddr_in saddr;
145 memset(&saddr,0,sizeof(saddr));
146 saddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
147 saddr.sin_port = htons(6000);
148 saddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
149
150 int res = bind(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&saddr,sizeof(saddr));
151 if(res == -1)
152 {
153 return -1;
154 }
155
156 if(listen(sockfd,5) == -1)
157 {
158 return -1;
159 }
160
161 return sockfd;
162
163
164 }
3. epoll
- epoll: it is suitable when there are many file descriptors
Use a set of functions to implement
#include<sys/epoll.h>
- epoll_create(): create a kernel event table. It is stored in the kernel space. It does not need to pass descriptors and events every time. The event is only passed to the kernel once. The data structure used by the event is a red black tree
- epoll_ctl():
- epoll_wait(): get ready descriptor
4. ET LT mode
- ET, LT mode
ET epoll high efficiency mode edge trigger
LT select poll epoll horizontal trigger
4.1 LT mode
- LT mode
For example, when your mother calls for dinner, she calls once and continues to call until you eat
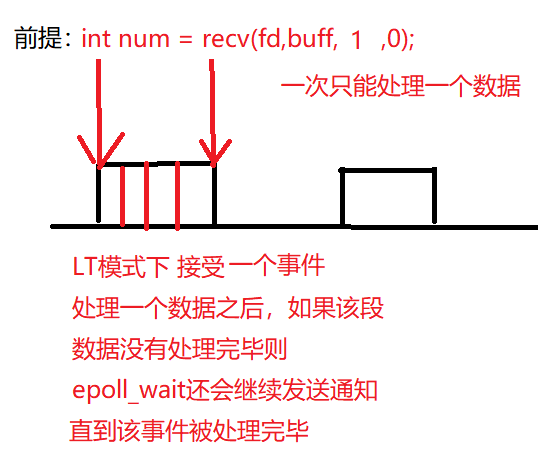
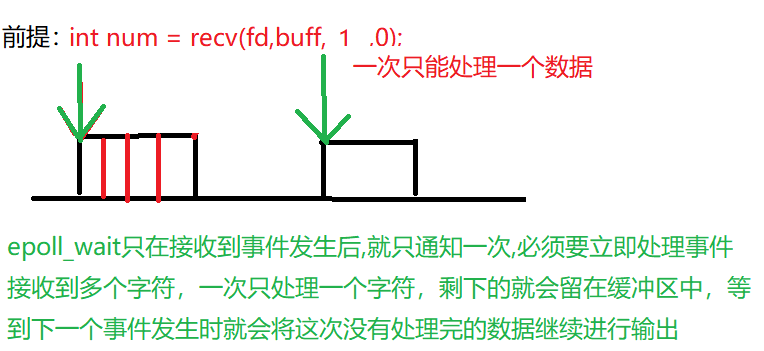
When the data entered by the client is hello, epoll_wait returns six times, one character at a time, and epoll when h is finished_ Wait will continue to send notifications until the entire data is read
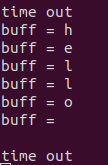
4.2 ET mode
- ET mode
- There is no data loss in TCP protocol
For example, only one character can be processed at a time. If the data sent by the client is hello, only h will be processed for the first time, and the rest will be stored in the buffer until the next epoll_ When there is another event notification in wait, c will be output, which will be l next time;
- In order to read all data in one event notification, the data needs to be read circularly
- If you do not cycle, you can only read one at a time. When you cycle to read data, if recv reads the last empty, blocking will occur
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
- int fcntl(int fd,int cmd...) / / add non blocking attribute
- After non blocking is set, the loop can be used to prevent blocking caused by empty data after reading
- Using cycle can make epoll in ET mode_ All data can be read in one wait notification,
15 void setnonblock(int fd) //Set non blocking property for fd
16 {
17 int oidfl = fcntl(fd,F_GETFL);
18 int newfl = oidfl | O_NONBLOCK;
19 if(fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,newfl) == -1)
20 {
21 printf("fcntl err\n");
22 }
23 }
epoll_create idea: create a kernel event table
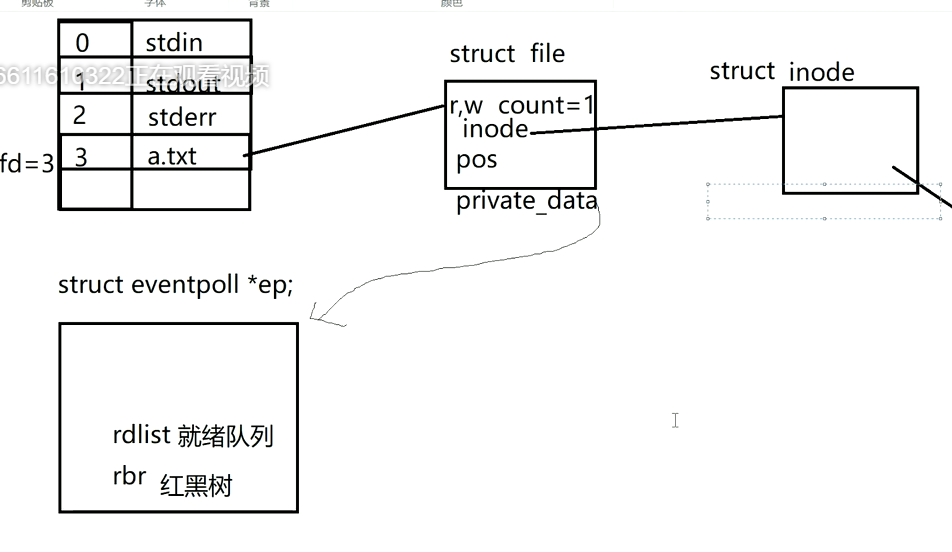
epoll_ctl(): adds a file descriptor to the kernel event table
5. libevent
libevent: commonly used in server-side programming, encapsulating poll and epoll
Define instance Base
Create event
Register (add) to libevent
The event loop starts to detect that the underlying call is select poll epoll_wait and other functions
Call the callback function fun() method with the ready event
win handle: file descriptor